The questions of solvability and construction of solutions of an inverse problem for second-order Fredholm integro-differential equation with degenerate kernel, final conditions at the end of the interval, two parameters, and two redefinition data are considered. The sets of regular parameter values are determined and the corresponding solutions are constructed. The specific features of the inverse problem are studied. Criteria for the unique solvability of the posed inverse problem are established.
We deal with a linear differential equation with piecewise constant argument. The considered equation with the initial condition has the unique solution. We obtain the sufficient conditions for existence of n -periodic solution for the considered problem and describe the positivity conditions for the solution.
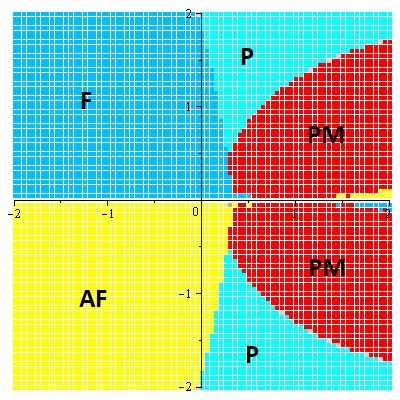
We investigate a problem of phase transition for all possible phases of "uncle-nephew" model on the semi-infinite Cayley tree of second order. It is proved that one can reach the phase transition for this model only in the class of ferromagnetic phase.
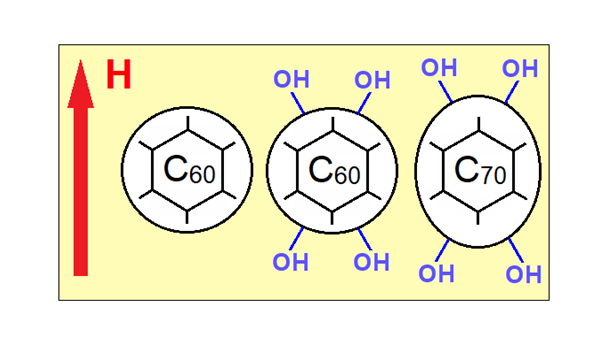
Using water-soluble hydrated fullerenes embedded in a polyvinyl alcohol matrix, samples were obtained that demonstrated the presence of optical anisotropy when they were formed in a magnetic field. Its existence was established in experiments on light scattering in films containing C60(OH)n and C70(OH)m molecules. The mechanism of the effect is presumably associated with the anisotropy of the shape of these molecules.
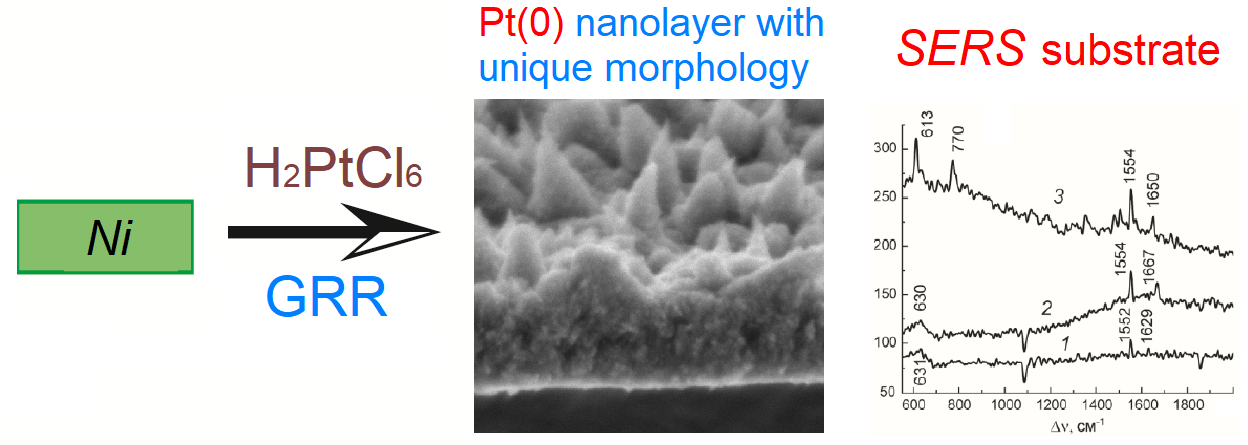
The paper explores the morphology features of Pt(0) nanolayers obtained on the surface of chemically polished nickel as a result of the galvanic replacement reaction using H2PtCl6 solution. In a series of samples synthesized at a treatment time of 1-60 minutes, it is shown that the nanolayers consist of Pt(0) nanocrystals 5-10 nm in size, which form a continuous porous layer with a thickness depending on the treatment time in solution. For example, it is about 80 nm and 120 nm for samples obtained after 3 minutes and 20 minutes, respectively. Moreover, on the outer side of the nanolayer with respect to the substrate, these nanocrystals form arrays of pointed agglomerates directed along the normal to the surface. After drying in air, the Pt(0) nanolayer cracks and partially folded microscrolls form on the nickel surface, the number of which is the largest for the samples obtained with a longer treatment time. The features of the practical application of these samples as SERS substrates are studied using the Raman spectra of Rodamin 6G as an example. It is shown that the amplification factor is about 105-106 using 532 nm laser excitation.
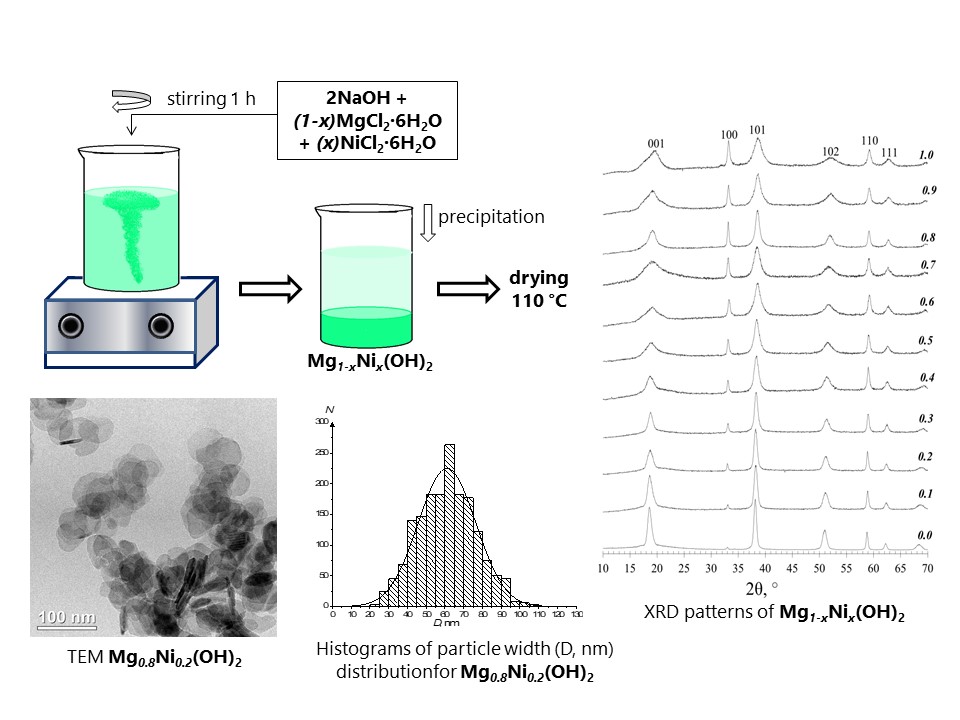
The effect of nickel content in Mg1-xNix(OH)2 nanoparticles produced by reverse co-precipitation on their structural characteristics, morphology and size parameters of crystallites and particles has been studied. The plate-shaped nanoparticles were shown to be predominantly single crystals. It has been determined that when the nickel content x in the hydroxide solid solution is not less than 0.4, the particle size sharply decreases and the number of stacking faults increases. The dependence of the dehydration temperature of Mg1-xNix(OH)2 nanoparticles on the nickel content has been revealed.
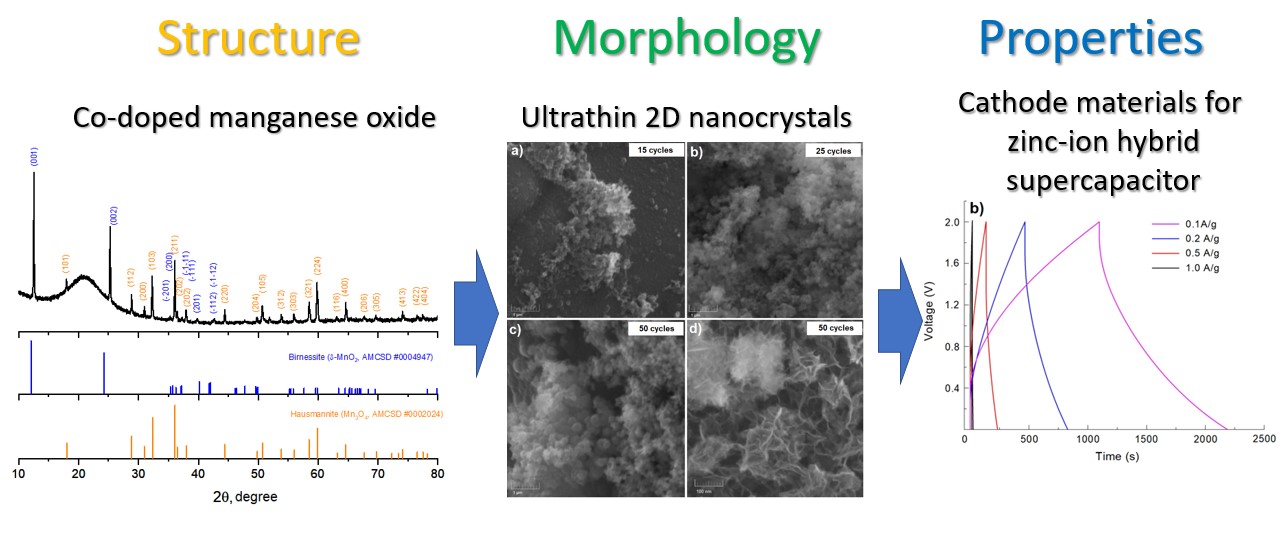
In the present work, we propose a novel promising route for synthesis of Co-doped manganese oxide nanostructure via successive ionic layer deposition method as cathode material of zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitor. The synthesized nanolayers were analyzed by SEM, EDX and XRD. It was shown that the synthesized nanolayers were formed from ultrathin (6-8 nm) two-dimensional nanocrystals containing birnessite MnO2 and hausmannite Mn3O4 crystal phases and having the morphology of “nanosheets”. Electrode based on nickel foam and Co-doped manganese oxide nanolayers exhibited a high specific capacity (514.5 F/g at 0.1 A/g) and excellent cycling stability (99 % capacity retention after 1000 charge-discharge cycles). Obtained results demonstrate that the 2D Co-doped manganese oxide is a promising material for effective zinc-ion hybrid supercapacitor.
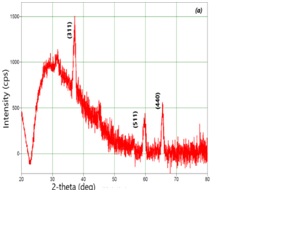
In this study, spinel type cobalt oxide (Co3O4) thick films are deposited on glass substrate by screen printing technique. All characterization was carried out for unannealed, annealed at 250 - 400 ◦C. The X-ray Diffraction (XRD) analysis indicates that prepared films have polycrystalline nature with cubic structure having preferential orientation through (311) plane. Crystallite size is found to be 18.52 nm. The lattice parameter found to be 8.036 - 8.138 A˚ approaches to standard value (a = 8 . 08 A˚). Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis of prepared films shows agglomeration of nanoparticles, occurrence of spherical-shaped grain aggregations. Spherical grain size increases from 47.66 to 77.33 nm with increase in annealing temperatures. A relation between structural and morphological properties is noted. The Energy Dispersive Analysis by X-Ray (EDAX) shows that all compositions have desired stoichiometric ratios. Besides electrical measurements, film D.C. resistance, resistivity was measured. It allows us to conclude that assured material has semiconducting nature. Specific surface area, Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR), activation energy decreases with increase in annealing temperature were calculated. It was shown that structural, morphological and electrical properties of Co3O4 films were improved by increasing annealing temperature.
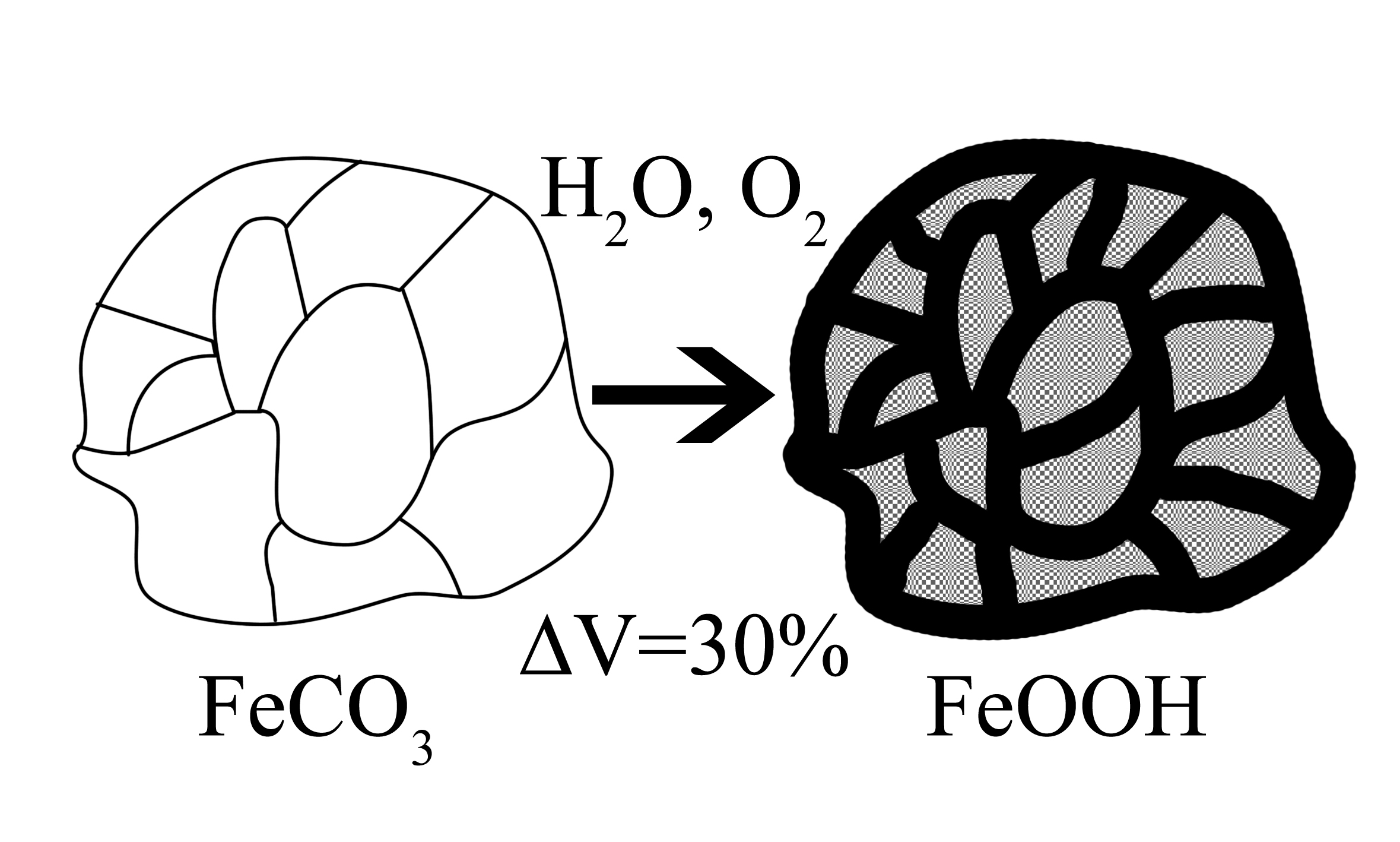
The structure of siderite aggregates and its weathering products from the Ruza deposit, Moscow Region, has been studied by X-ray phase analysis and electron microscopy. The initial siderite is a dense FeCO3 aggregate of micron-sized grains. The nodules are covered with an ocher weathered crust, the color intensity of which varies from light yellow to brown-black. A successive replacement of siderite by FeOOH goethite and lepidocrocite was revealed. It is accompanied by a sharp decrease in volume ( ∼ 30 %) and the formation of a microporous structure.
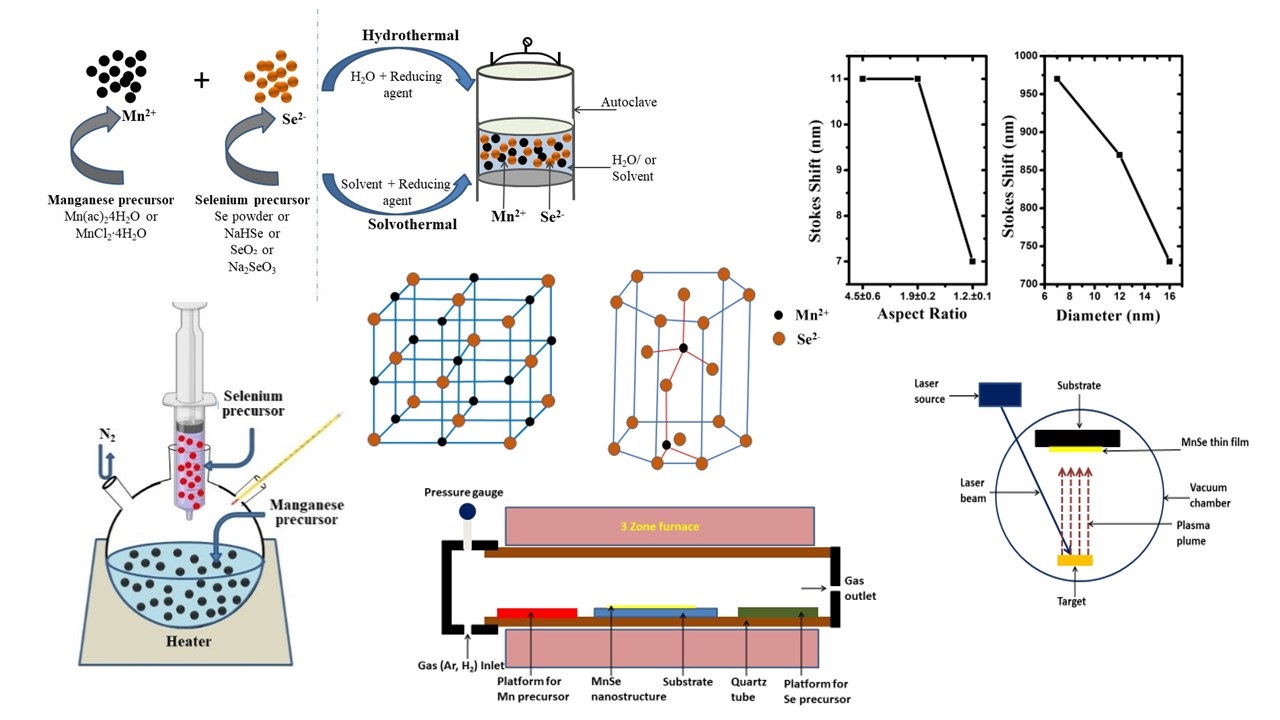
Manganese selenide is an important diluted magnetic semiconductor (DMS) material having both optical and magnetic properties especially in the nanometer scale. Because of the phenomena of polymorphism exhibited by MnSe, it can be an interesting material for controlled polymorphism synthesis by using different synthesis procedures. In this review article, we discuss various synthesis procedures (wet chemical and deposition methods) of different MnSe nanostructures and their optical properties. The dependence of various optical properties (UV-Vis spectroscopy, photoluminescence spectroscopy and time resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy) of the MnSe nanostructures on the methods of synthesis is discussed in this article. We are specially focused on the reaction parameters of synthesis process that influence on the optical properties of the MnSe nanostructures. Moreover, the Stokes shift is calculated for the MnSe nanostructures synthesized by different procedures. Large Stokes shifts observed for MnSe nanostructures create a promising potentials in various applications including multiplex assay, bio-imaging, bio-sensing etc.
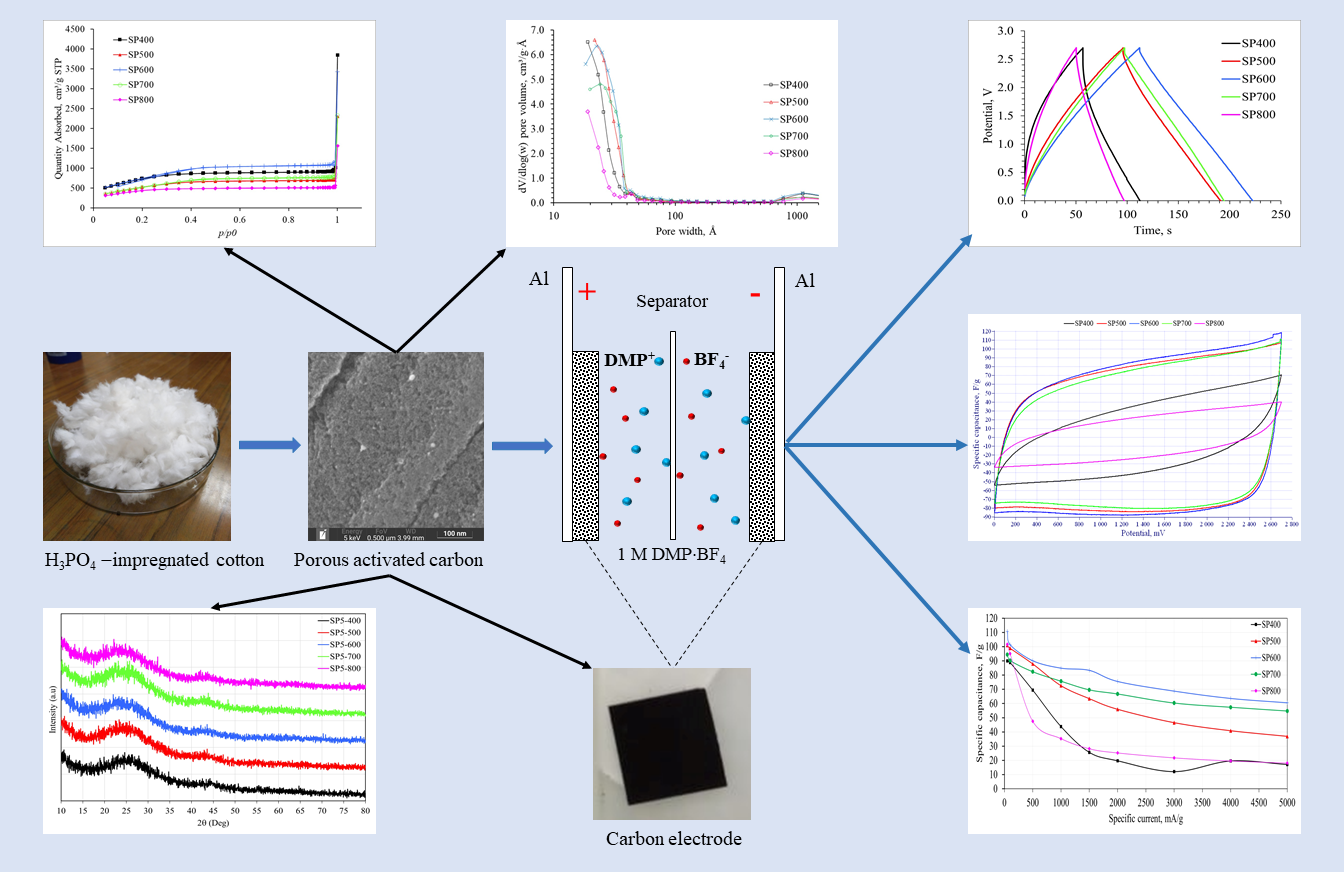
H3PO4-impregnated waste cotton was used as precursor to fabricate high porous activated carbon (AC) by the carbonization and activation processes with ultrahigh heating rate. The obtained activated carbon has unique physicochemical properties such as the structure mainly amorphous and ultrahigh specific surface area of 2769.7 m2/g for samples fabricated at carbonization temperature of 600 ◦C. The double-layer supercapacitors with activated carbon electrodes and electrolyte based on 1,1-dimethylpyrrolidinium tetraflu-oroborate solution in acetonitrile of 1 M concentration were fabricated. The specific capacitance of electrode material fabricated from AC obtained at carbonization temperature of 600 ◦C reached 110.8 F/g at the current density of 50 mA/g and 85.1 F/g at 1000 mA/g. At 1000 mA/g, the degradation was less than 25% after 5000 charge/discharge cycles. The carbonization temperature of 600 ◦C is considered as optimum for fabricating activated carbon and the obtained activated carbon can be used for supercapacitor electrode materials.
Growth of Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were obtained by Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) technique. Castor oil was vapourised above its boiling point and pyrolysis of oil was carried out by passing vapours over finely dispersed nickel metal at 650 ◦C. After characterization study of carbon material, scanning electron microscope (SEM) image revels that there is a growth of densely packed nanotubes with average diameter 30 - 40 nm. The XRD study of purified carbon nanotubes shows graphitic nature of carbon. Electrochemical application of CNTs obtained was studied in Supercapacitor. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) was used to study the capacitive behaviour of carbon nanotubes in KOH electrolyte. A capacitance of 9.89 F/g (based on the weight of the carbon material) was obtained.
This work is devoted to experimental study of boron doped delta layers in CVD diamond. Delta layers with a thickness of 0.8 - 2 nm were grown with a concentration of boron atoms of (1 - 1.7)·1021 cm-3, and localized inside undoped defect-free diamond. The layers thickness and boron concentration were measured by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). The surface density and the Hall mobility of holes, the layer resistance at room temperature, and temperature dependences of these parameters are presented. Performed electrical measurements showed that, despite the perfect (from the point of view of the possibility of quantum effects) profile of delta layers, no significant increase was observed in the hole mobility compared to uniform doping with the same concentration of boron atoms. An explanation is proposed for the results of electrical measurements based on calculations of the delta layer profile and the concentration of delocalized holes depending on the layer thickness. It is discussed which parameters of the boron doped delta layers are needed in order to obtain a significant increase of the hole mobility in heavily doped diamond.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)