MATHEMATICS
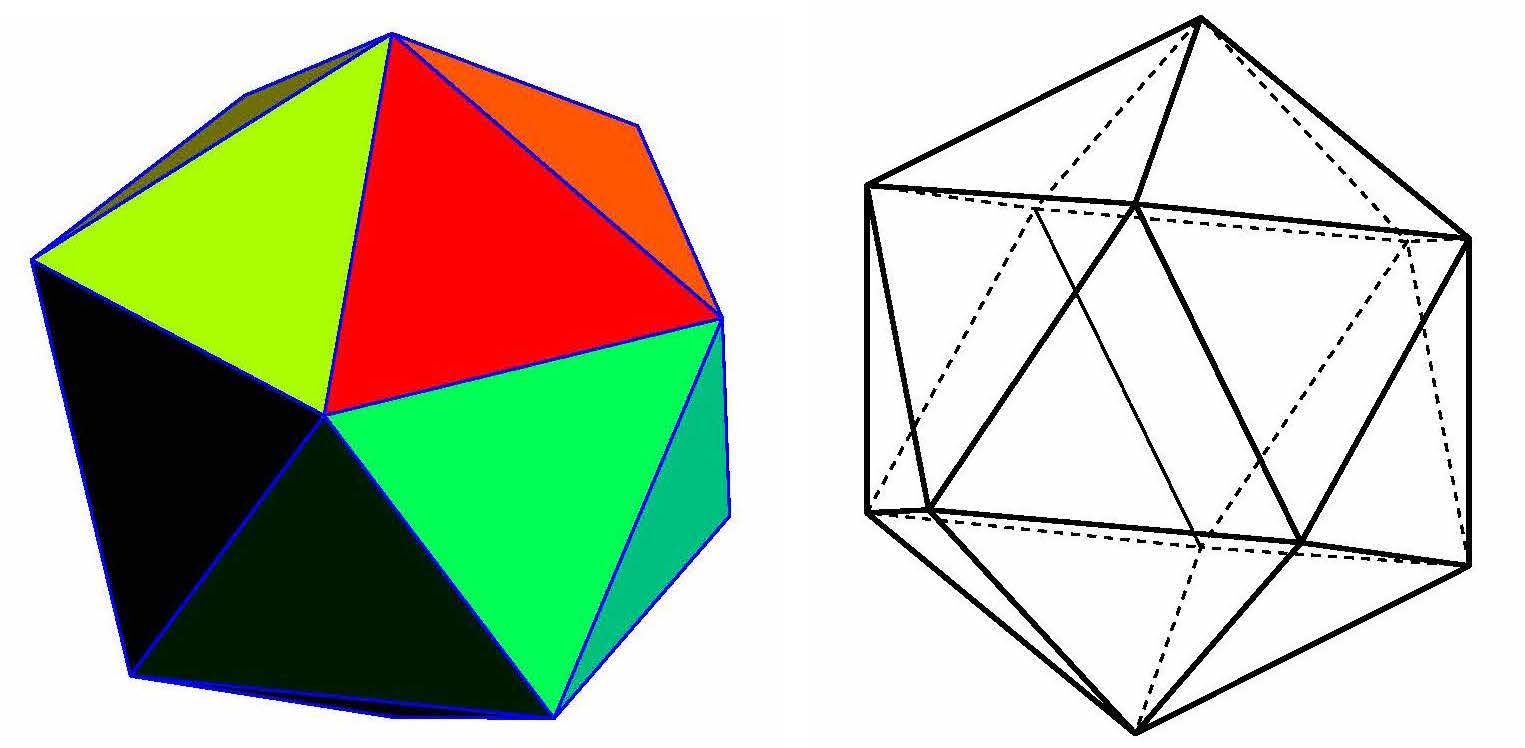
To study point groups, their irreducible characters are essential. The table of irreducible characters of the icosahedral group A5 is usually obtained by using its duality to the dodecahedral group. It seems that there is no literature which gives a routine computational way to complete it. In the works of Harter and Allen, a computational method is given and the character table up to the tetrahedral group A4 using the group algebra table and linear algebra. In this paper, we employ their method with the aid of computer programming to complete the table. The method is applicable to any other more complicated groups.
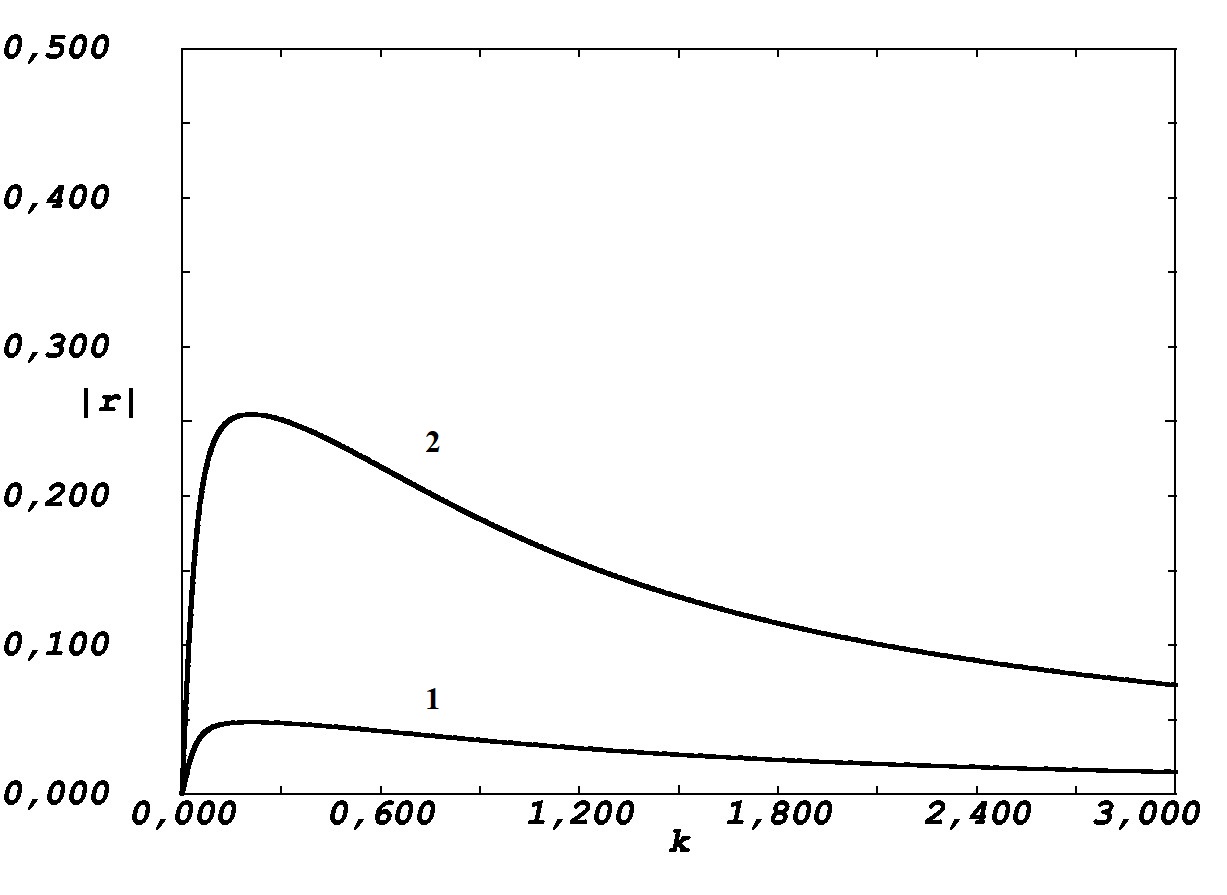
One-dimensional Rashba and Dresselhaus Hamiltonians with spin-orbit interaction are studied. It is assumed that there are point-like potentials on the line. The scattering problem is solved and the possibility of spin-flip is discussed.
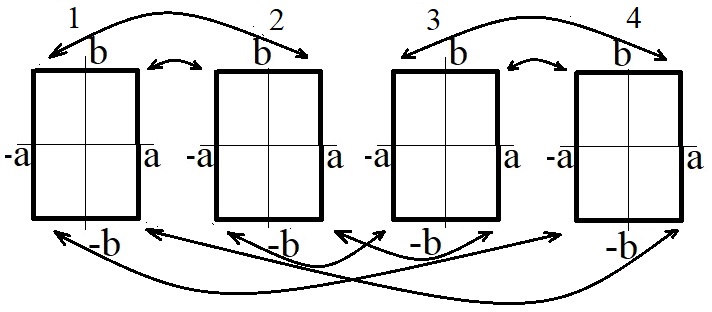
The spectral problem for the Schrodinger operator with a magnetic field on the flat M ¨ obius strip is ¨ considered. The model construction is described. It is compared with the case of the Laplace operator.
PHYSICS
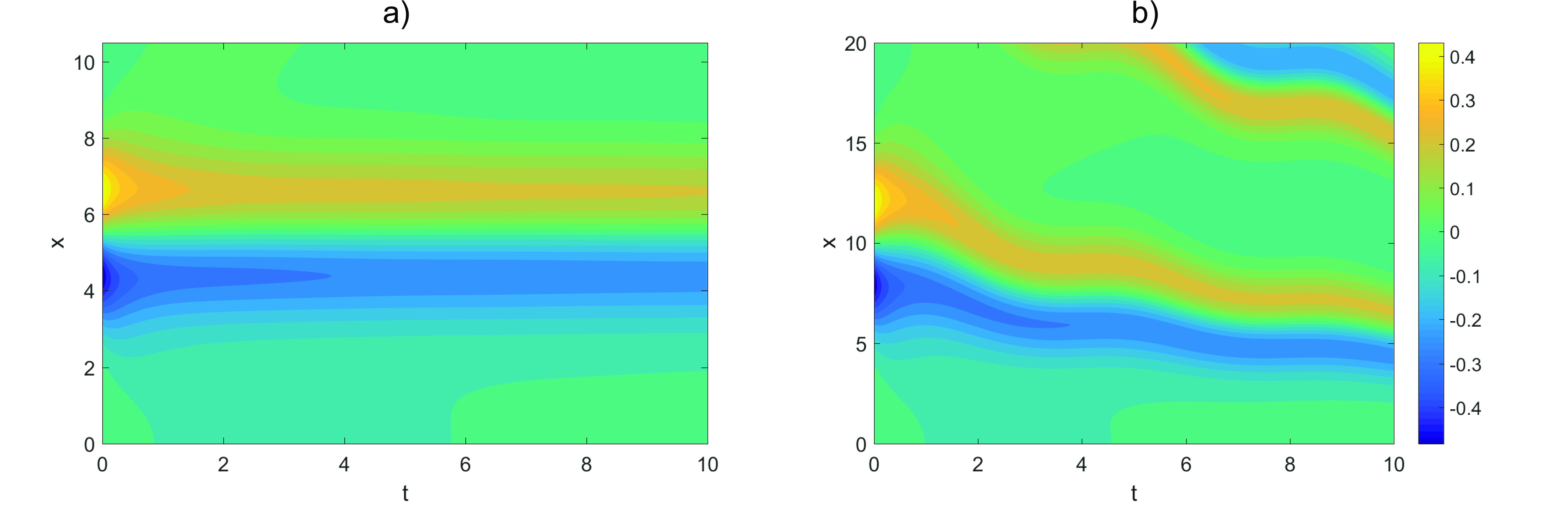
We consider the problem of fast forward evolution of the processes described in terms of the heat equation. The matter is considered on an adiabatically expanding time-dependent box. Attention is paid to acceleration of heat transfer processes. So called shortcuts to adiabaticity, implying fast forwarding of the adiabatic states are studied. Heat flux and temperature profiles are analyzed for standard and fast forwarded regimes.
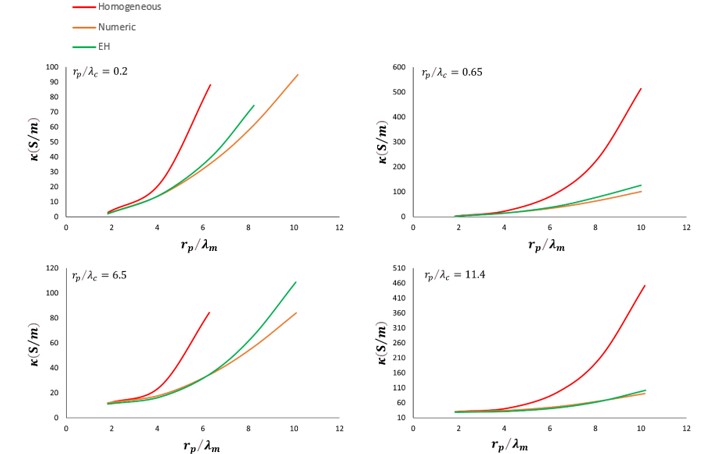
The validity of different analytical approximations solution is studied using the classical Poisson– Boltzmann (PB) equation based on a mean-field description of ions as ideal point charges in combination with the assumption of fully overlapped electrical double layers in the membrane pores. The electrical conductivity is calculated by numerical and approximate analytical methods in order to explain the process of ion transport. In this paper, a new analytical approximation named the extended homogeneous approximation (EH) is presented, which provides better results than the homogeneous approximation based on Donnan theory. Also, the results show that the electrical conductivity calculated by the EH, is coherent with the numerical method within specific limits.
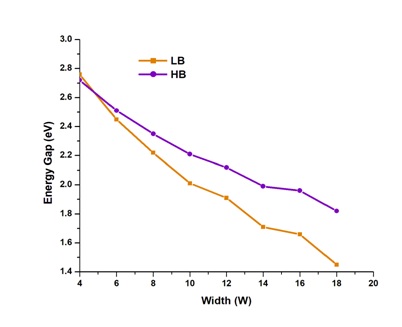
In this study, we have investigated the transport properties of low bucked (LB) and high buckled (HB) silicene based two probe devices such as I–V characteristics, conductance, transmission spectrum and projected device density of states. Firstly, we have opened a bandgap in both LB and HB zigzag silicene nanoribbon (ZSiNR) by hydrogen passivation and simulated for their transport properties. Further, we have doped the LB and HB ZSiNR structures by gallium (Ga) and arsenide (As) atoms in order to determine their changes in the transport properties. The results show that 4 atom width silicene nanoribbon shows a maximum band gap of 2.76 and 2.72 A for LB-ZSiNR and HB-ZSiNR, respectively. The 2 atom doped ZSiNR shows good ˚ transport characteristics in the voltage range of 0.5 to 1.5 V in comparison with 4 and 6 atom doped models. The obtained results were validated by calculating the transmission spectrum and projected device density of states. It is believed that the modelled devices will find number of futuristic applications in the electronic industry.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
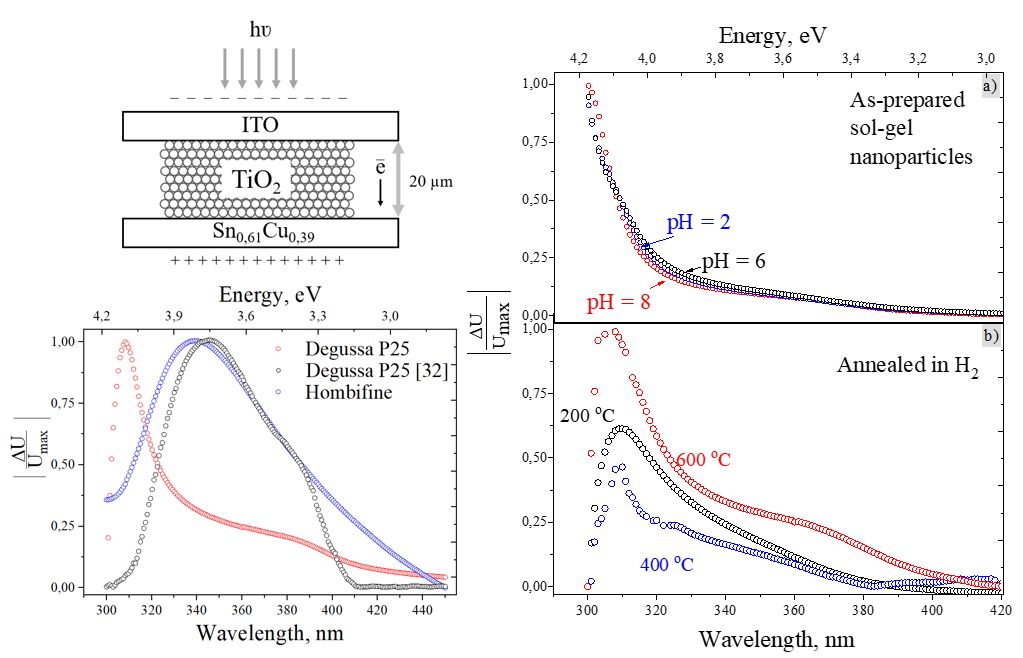
TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by the sol-gel method and modified by annealing in air and hydrogen atmospheres were studied by surface photovoltage spectroscopy (SPS). SPS measurements showed that the modified in air TiO2 nanoparticles have a more intense signal than those treated in hydrogen. A linear correlation was found between the SPS and the diffuse reflectance spectra of the samples.
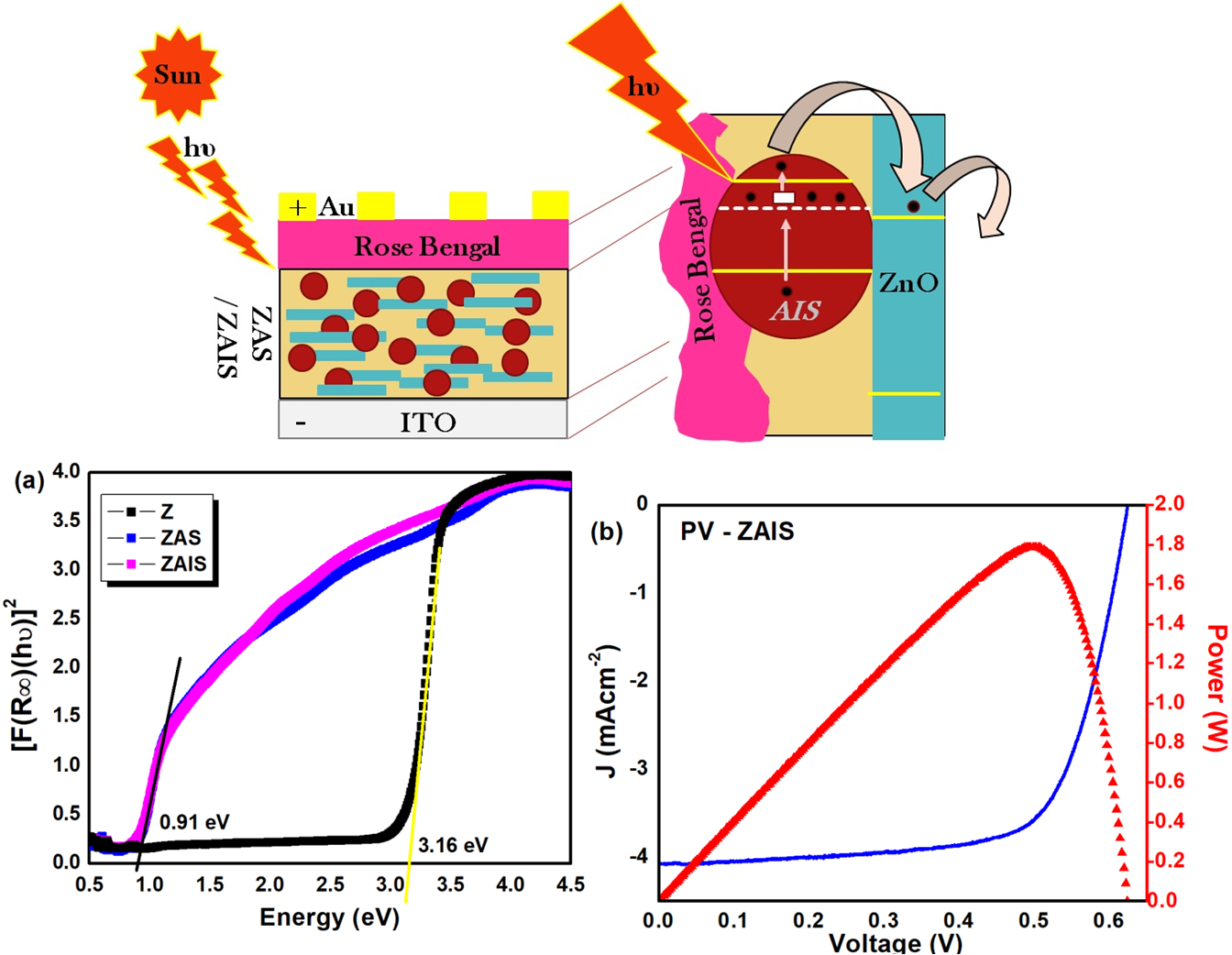
Nano-sized indium incorporated silver sulphide (Ag–In–S) nanocomposites were synthesized by simple wet chemical method as an electron transport layer in zinc oxide (ZnO) for high efficient photovoltaic (PV) cell. The inclusion of high conductivity indium ions in Ag2S will improve the facile electron transfer and the assembled hetero-structure features the solar light harvesting in PV cell. The powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies confirmed the formation of indium incorporated Ag2S (AIS) nanocomposites and ZnO/AIS (ZAIS) compound nanocomposites crystallizing in pure monoclinic phase and mixed wurtzite hexagonal, monoclinic and tertiary phases respectively. The wide particle size distributions in ZAIS clearly revealed the adherence of AIS nanocomposites in ZnO lattice thus, promoting the light adsorption property. In addition, the tuning of the optical bandgap covering the entire solar spectrum (UV, visible, and infra-red regions), multiple-band electron transitions and hence, promoting the fast electron transportation are effectively achieved in ZAIS compound nanocomposites. With this simple positive approach, the PV cell efficiency is pushed forward with the In3+ metal ion incorporation however; enhanced, enriched solar cell efficiency can be later tuned up with the detailed optimization studies
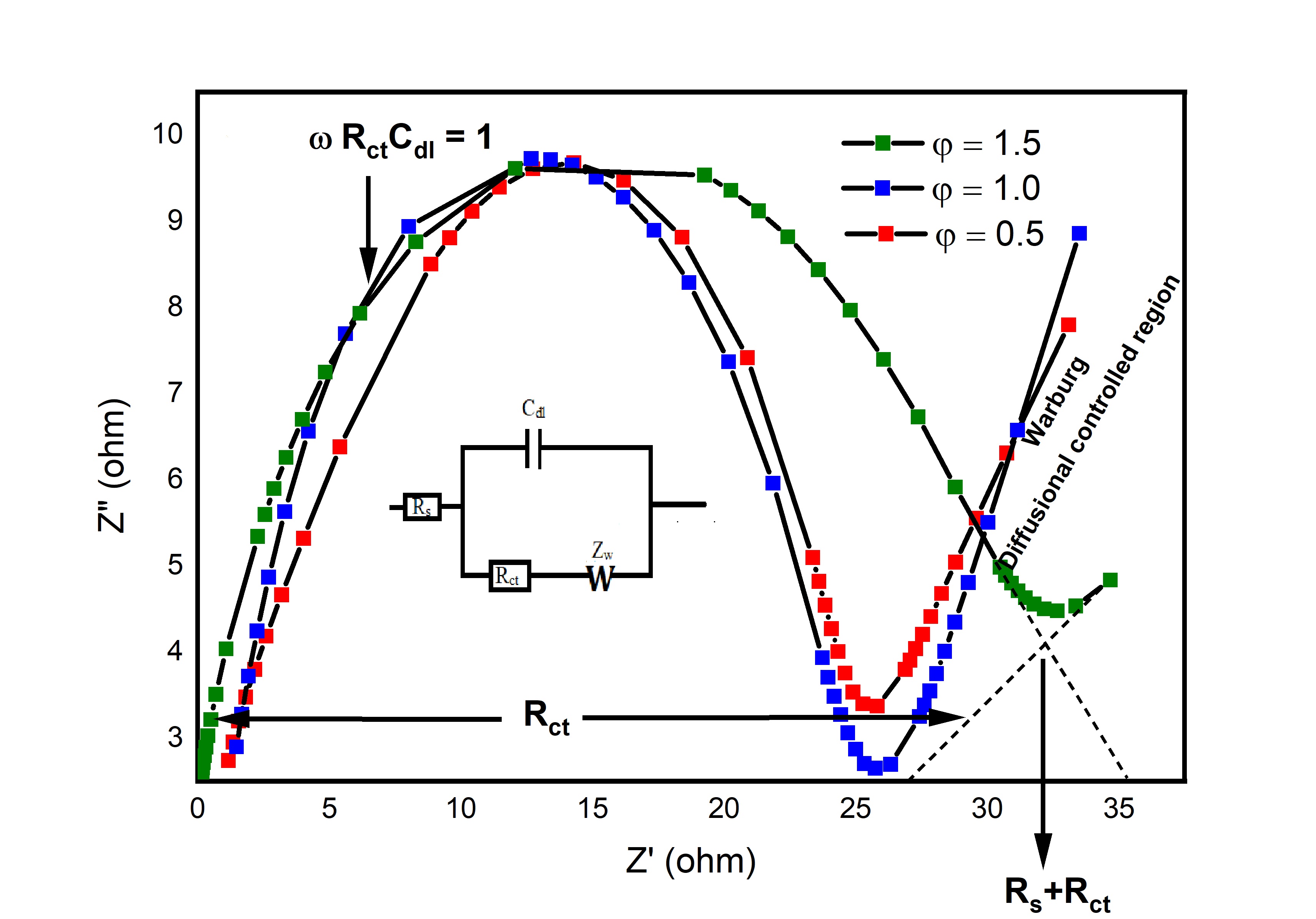
The BaZrO3 ceramics were prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion technique with three Fuel to Oxidant (F/O) ratios (ϕ = 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5) and annealed at 1200 ◦C for 2 hours. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Rietveld refinement data confirmed the cubic perovskite phase with the Pm3m (221) space group. These three samples are well indexed in JCPDS no: 06-0399. The ratio F/O = 1.0 gives one a small crystallite size and very high surface area. The ratio F/O = 1.5 provides a very high crystallite size and very low dislocation density. The oxygen vacancies in the samples were analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. The optical band gap energy value increases from 2.02 to 3.09 eV with increasing F/O ratio. Using of impedance spectroscopy for BaZrO3 at room temperature allows us to reveal decreasing Ionic conductivity with an increasing F/O ratio. The Nyquist plot for all samples exhibits a circular arc in the high-frequency zone and nearly a straight line in the low-frequency region. Due to the presence of low grain boundary with high ionic conductivity the BaZrO3 electrolyte material is used for energy storage in devices.
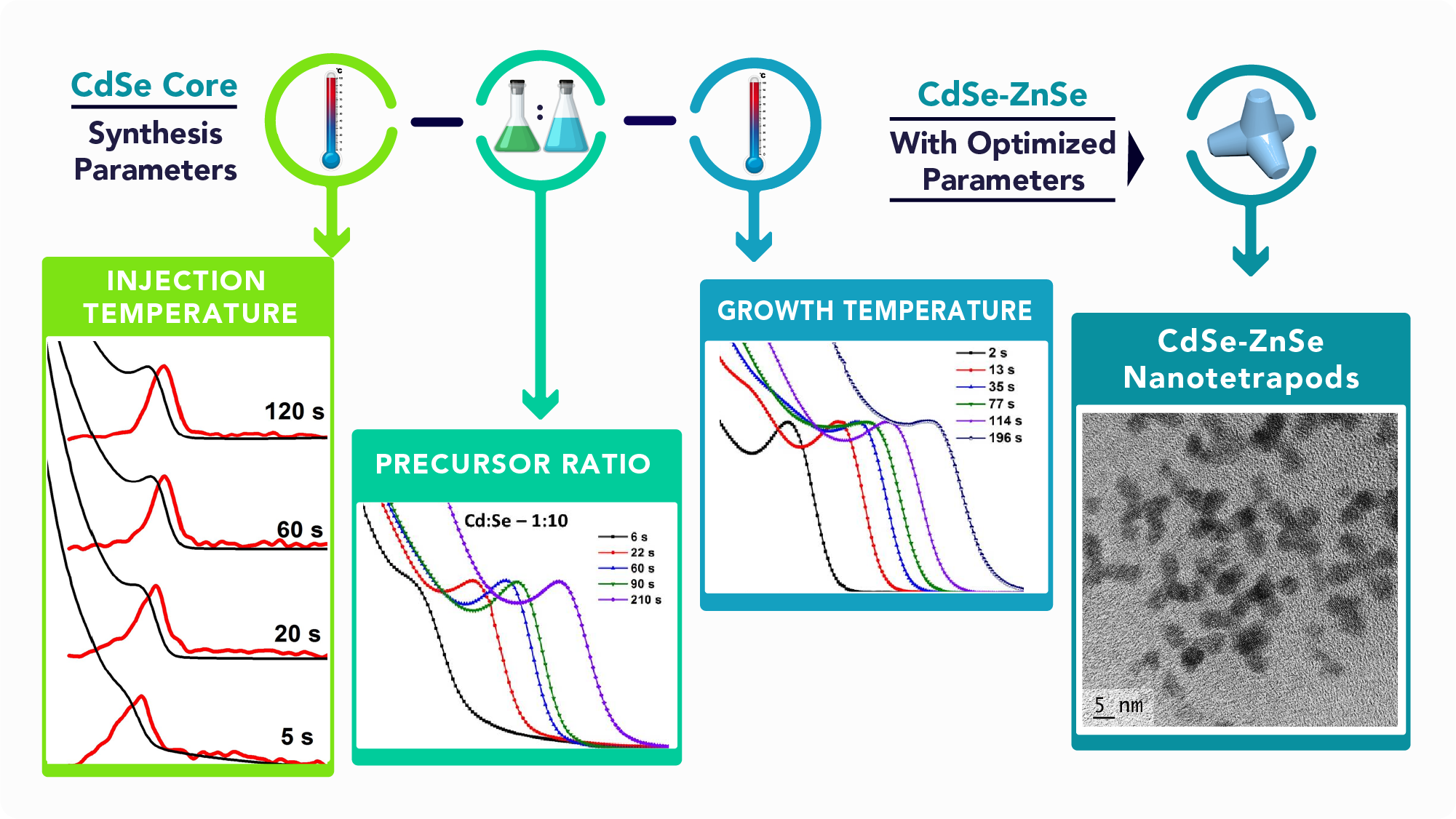
This paper reports a modified version of hot injection method for the synthesis of CdSe quantum dots and CdSe–ZnSe nano–tetrapod structures. In the present method, certain synthesis parameters such as injection temperature, growth temperature and precursor ratio were tuned to influence the growth kinetics and thereby the optical properties of the prepared CdSe QDs were enhanced. The influences of these parameters were studied and suitable conditions were optimized. Using the optimized parameters, CdSe–ZnSe nanostructures were synthesized with tetrapod morphology and their structural and optical properties were studied. The adopted modified version of synthesis is a facile method without stringent conditions such as inert atmosphere and therefore adaptable for the large-scale synthesis in industry.
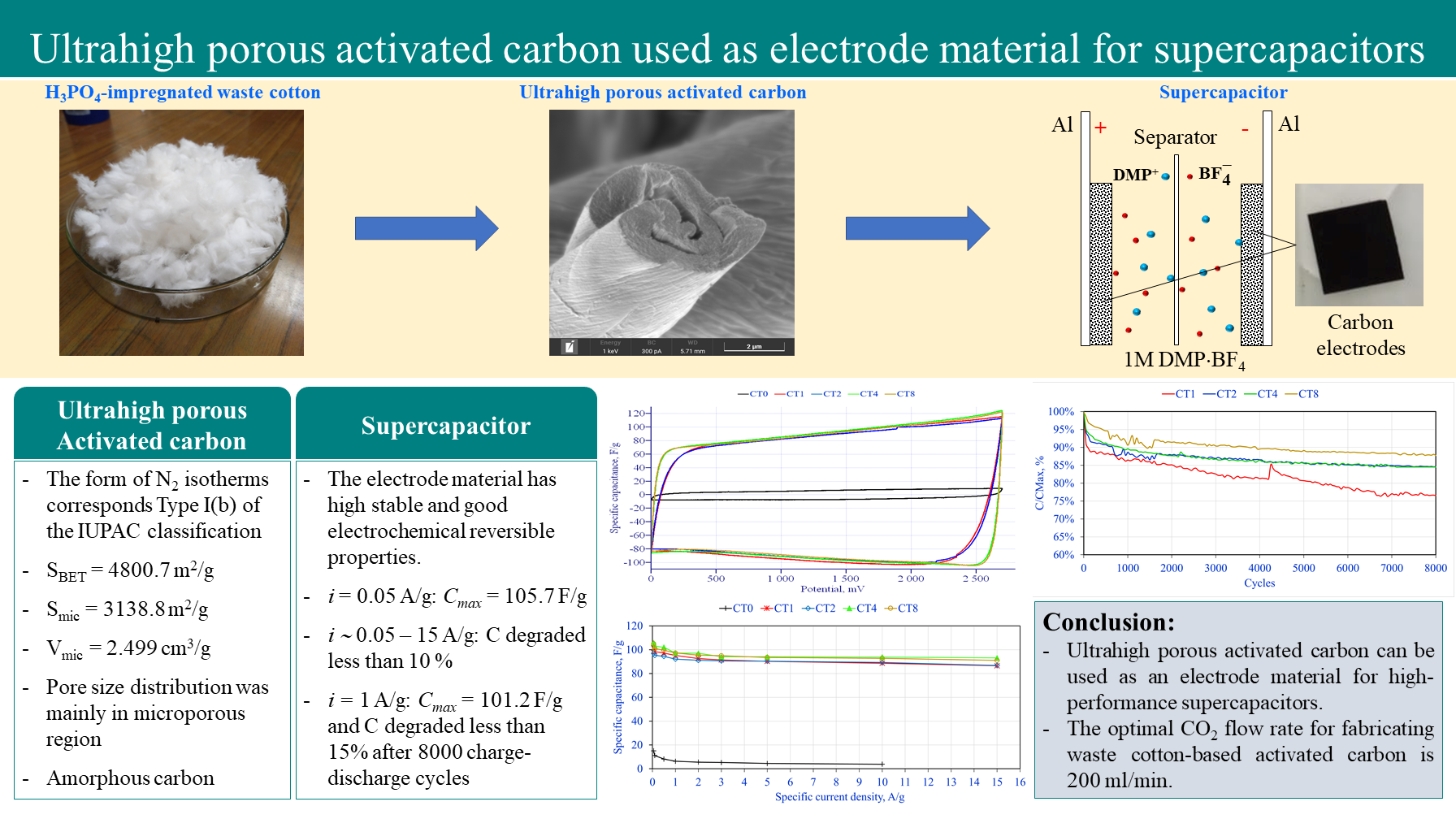
Ultrahigh porosity activated carbon (AC) was made from H3PO4-impregnated waste cotton precursor by carbonization in Ar and physical activation in variable CO2 flow rate with ultrahigh heating rate. The presence of CO2 in the activation plays an important role in the formation of the porous structure of AC. The obtained AC had outstanding physical and electrochemical properties. The specific surface area and micropore volume of AC reached 4800.7 m2 /g and 2.499 cm3 /g, respectively. The pore size distribution was mainly in the microporous region. The electrochemical double-layer capacitors (EDLCs) with AC-based active electrode and an electrolyte solution of 1 M 1,1-dimethylpyrrolidinium tetrafluoroborate in acetonitrile were fabricated. The specific capacitance of electrode material degraded less than 10 % with the highest value of 105.7 F/g at 0.05 A/g as the specific current varied from 0.05 A/g – 15 A/g. After 8000 charge-discharge cycles at 1 A/g, the specific capacitance of the AC-base electrode material fabricated at CO2 flow rate greater than 200 ml/min degraded less than 15 % with the highest value of 101.2 F/g. The optimal CO2 flow rate for fabricating waste cotton-based AC is 200 ml/min.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)