MATHEMATICS
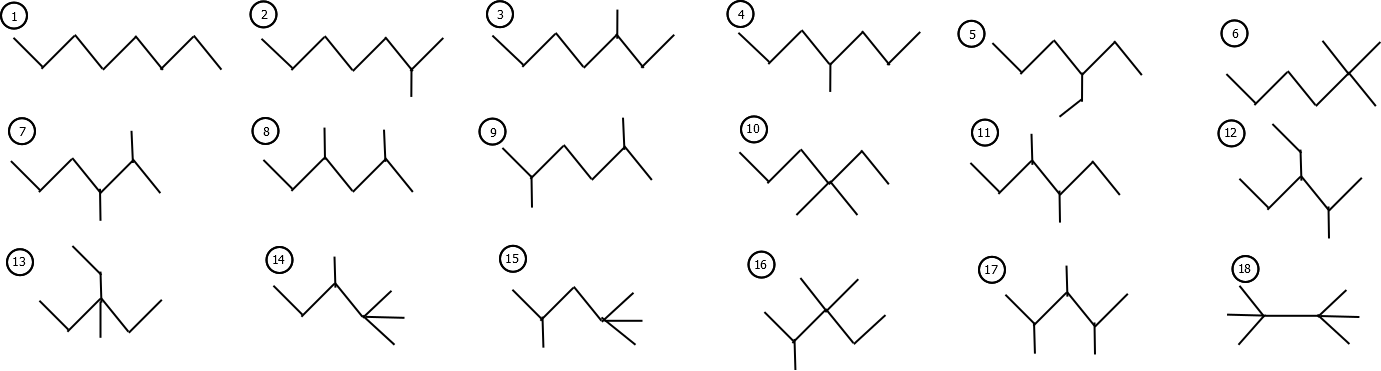
The Z-matrix of a simple graph Γ is a square symmetric matrix, whose rows and columns correspond to the vertices of the graph and the ijth entry is equal to the sum of the degrees of ith and jth vertex, if the corresponding vertices are adjacent in Γ, and zero otherwise. The Zagreb eigenvalues of Γ are the eigenvalues of its Z-matrix and the Zagreb energy of Γ is the sum of absolute values of its Zagreb eigenvalues. We study the change in Zagreb energy of a graph when the edges of the graph are deleted or rotated. Suppose Γ is a graph obtained by identifying u ∈ V(Γ1) and v ∈ V(Γ2) or adding an edge between u and v, then it is important to study the relation between Zagreb energies of Γ1, Γ2 and Γ. The highlight of the paper is that, the acentric factor of n-alkanes appear to have a strong positive correlation (where the correlation coefficient is 0.9989) with energy of the Z-matrix. Also, the novel correlation of the density and refractive index of n-alkanes with spectral radius of the Z-matrix has been observed.
PHYSICS
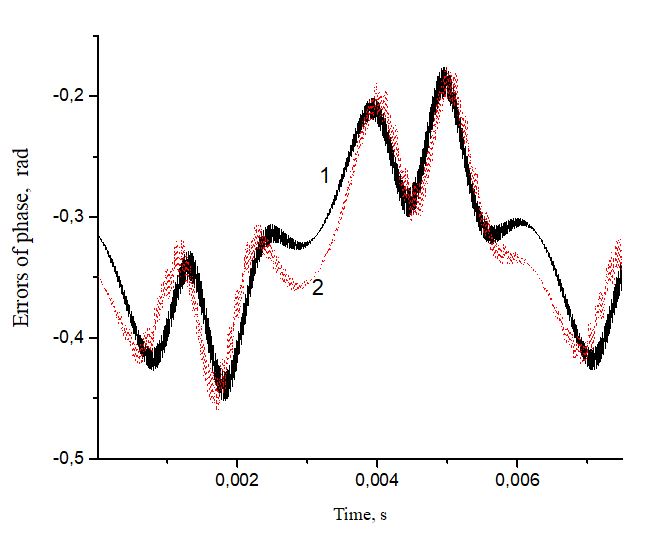
This article explores phase errors created by low-pass filter in interferometric signals which are processed by In-Phase and quadrature demodulation algorithm (IQ-demodulation). These errors were calculated using the analytical method and were compared with mathematical modeling, which uses pre-calculated parameters: phase, sampling period, infinitesimal parameters. In this paper, we show that phase errors calculated with analytical method clearly correlate with mathematical modeling errors. This work made it possible to calculate corrections to the demodulated phase, which, in turn, made it possible to refine the phase calculation step in IQ demodulation algorithm using the arctangent function. The resulting formulas describing the correction to the demodulated phase will increase the accuracy of the quadrature method, which is used to process signals from interferometric devices of various types, such as: reflectometers, geophysical seismic systems,
interferometric radiometry, etc.
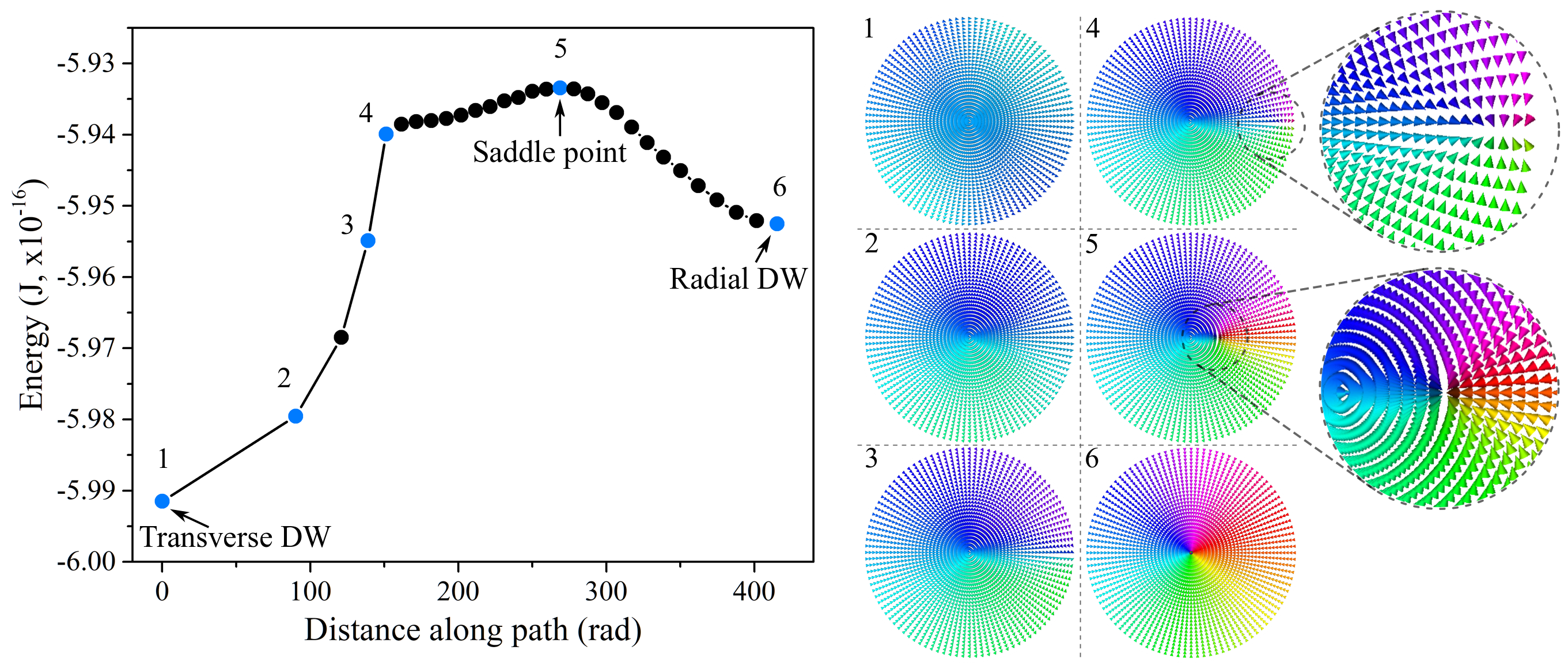
For magnetic wires and other systems with cylindrical symmetry, algorithms have been proposed for constructing a multidimensional energy surface, searching for minimal energy paths between locally stable states and the activation energies of transitions between such states. The mechanisms of nucleation and transformation of domain walls of various types in amorphous ferromagnetic nanowires with a nonuniform anisotropy distribution have been studied. The stability of the domain walls structure with respect to thermal fluctuations and random external perturbations has been assessed.
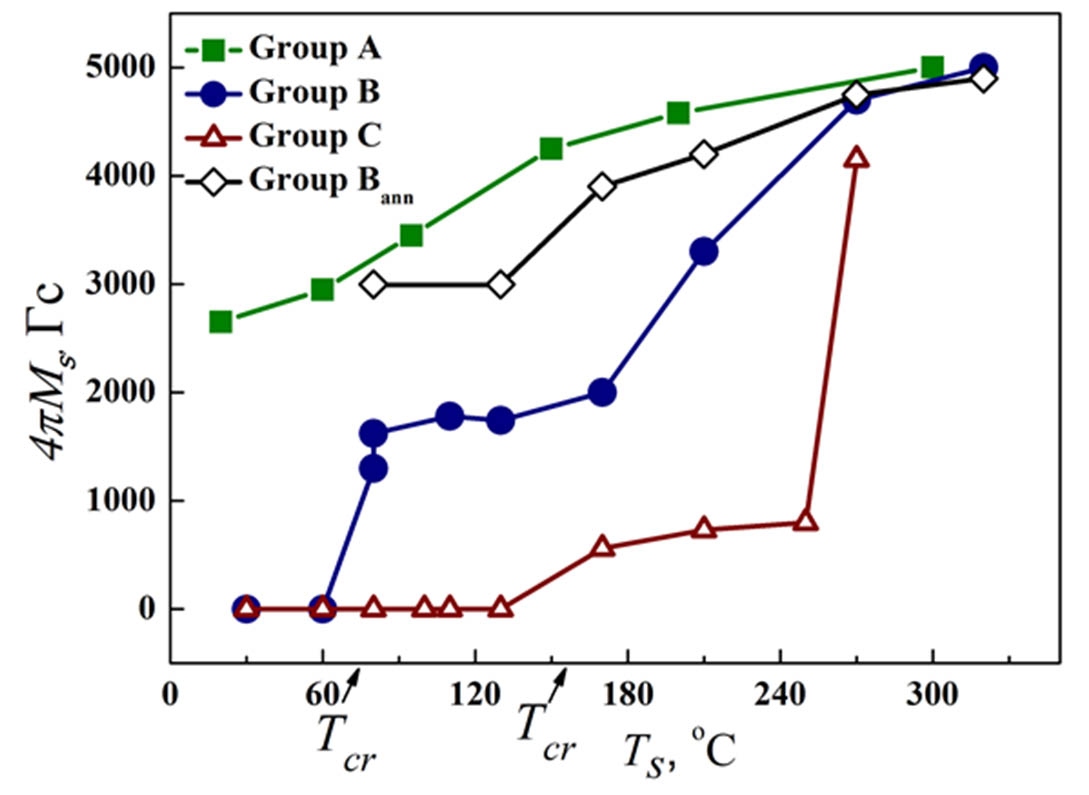
Three series of films were obtained by magnetron sputtering of the composite C-Ni target with different ratios C/Ni (vol. %) = 60/40; 40/60; 30/70. The effect of the substrate temperature on the structure and the size of film-forming nickel nanocrystallites with a carbon shell was studied with using X-ray diffraction analysis. The cluster nature of film deposition on the growth surface was established by using atomic force microscopy. The saturation magnetization of nickel nanoparticles 4πMS was measured by the inductive-frequency method and the substrate temperature dependence was studied. It has been shown that the films with a high carbon content exhibit magnetism only when deposited on hot substrates. The films with the minimum carbon concentration exhibit ferromagnetic behavior even when deposited on a relatively cold substrate.
The processes in a system of nanoparticles of a concentrated colloidal solution of magnetite induced by laser light with a wavelength of 650 µm have been studied. It was found that radiation focused on a drying drop of this substance, under certain conditions, leads to the formation of large accumulations of particles, in some cases strongly protruding above the surface of the sediment or, on the contrary, to their displacement from the illuminated area. A qualitative discussion of possible mechanisms of the observed phenomena is carried out.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
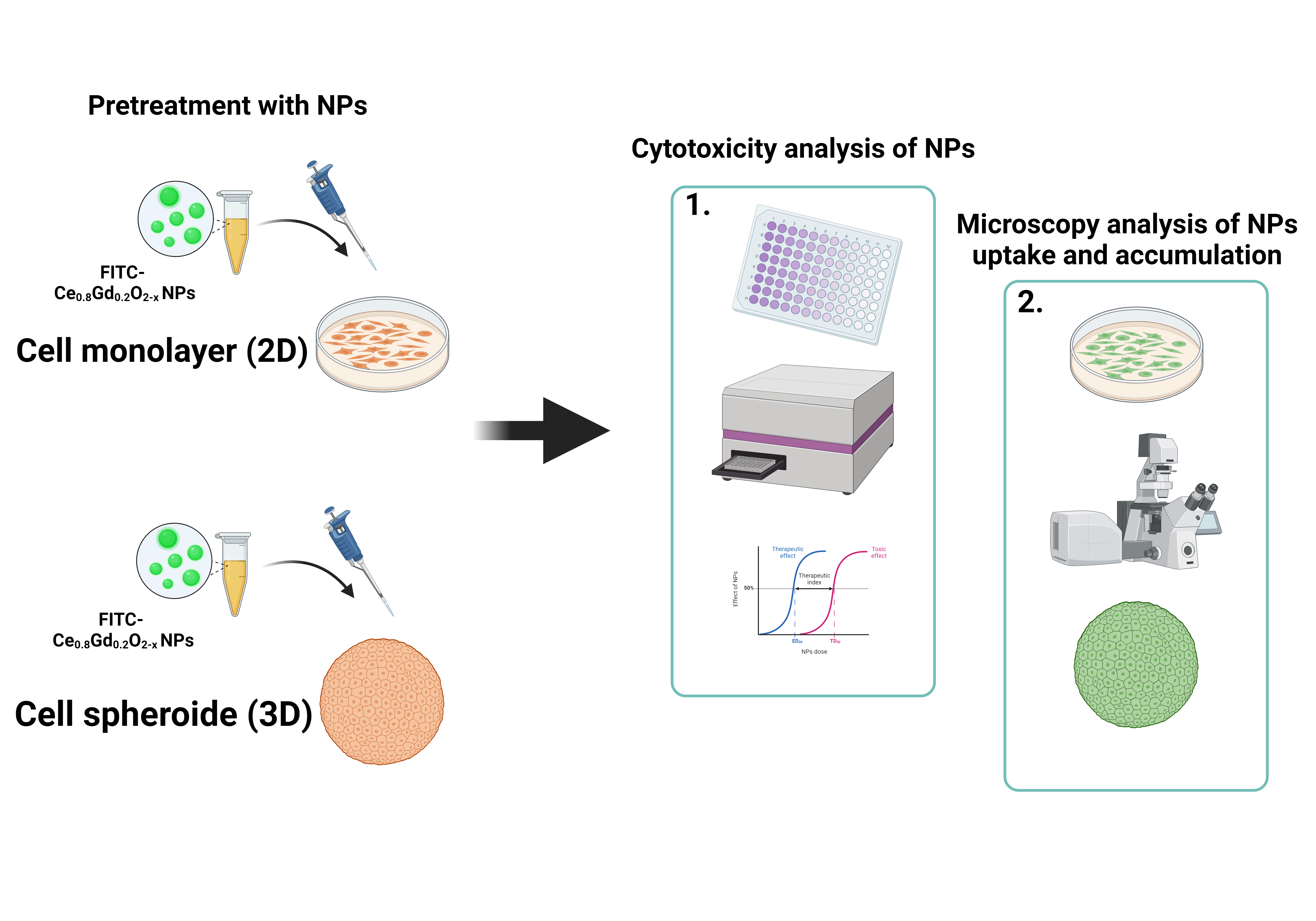
Cerium-containing nanoparticles have recently been identified as promising nanozymes for advanced biomedical applications. Additional modification of the core or the surface of CeO2 nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs) provides them with new functionalities, making them a unique theranostic agent. In this study, dextran-stabilized CeO2 NPs doped with Gd (Ce0.8Gd0.2O2−x) were synthesized and further functionalized with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC). The synthesized nanoparticles have a high degree of biocompatibility at concentrations up to 5 mg/mL and are readily internalized by human mesenchymal stem cells cultured both in monolayers (2D system) and cellular spheroids (3D system). The functionalization of CeO2 NPs with Gd and FITC dye allows for monitoring their accumulation within organs and tissues using both magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluorescence spectroscopy techniques.
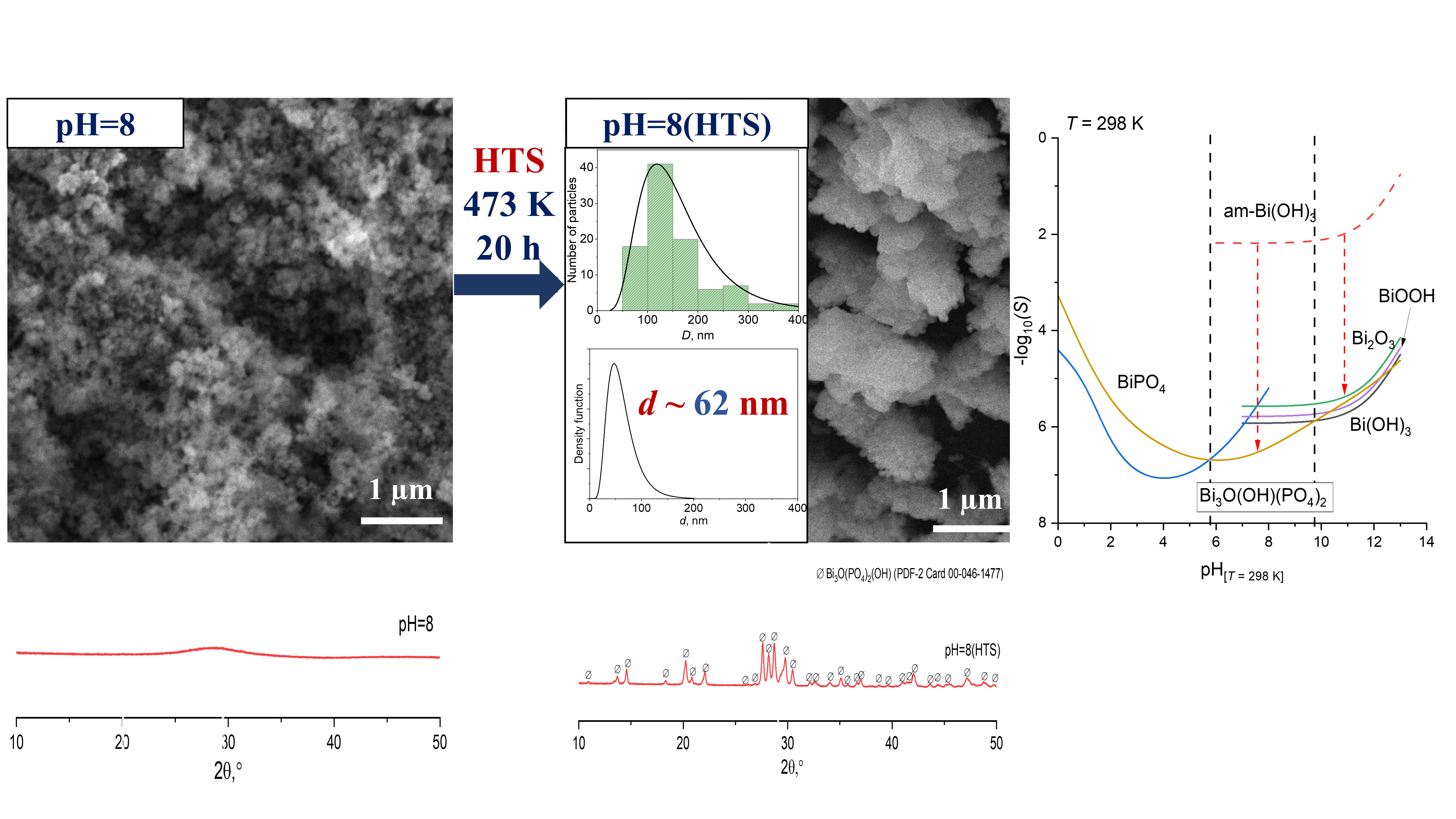
The work is devoted to studying the influence of pH values in an aqueous-salt medium on the formation of compounds in the Bi2O3–P2O5–H2O(OH−, H+) oxide system. It has been shown that in an acidic environment (pH = 2) at a temperature of 298 K, hexagonal BiPO4 forms, while at pH values of 8 and 12, X-ray amorphous substances are produced. After hydrothermal treatment at 473 K in an aqueous-salt environment, a monoclinic modification of bismuth phosphate forms from hexagonal bismuth phosphate in an acidic environment, and nanometer-sized particles of crystalline compounds Bi3O(OH)(PO4)2 (with a crystallite size of about 62 nm) and Bi2O3 (with a crystallite size of about 70 nm) form in weakly alkaline and alkaline media. Using the method of thermodynamic calculation, the dependences of the equilibrium molar solubility of these crystalline compounds on the pH value of the aqueous-salt suspension were obtained. Thermodynamic calculations showed that the BiPO4 compound is stable in the pH range from 0 to 5.8 at temperatures of 298 and 473 K. The pH range from 5.8 to 9.8 is characterized by the formation of the Bi3O(OH)(PO4)2 compound at 298 K, and a further increase in the pH value leads to the precipitation of Bi2O3, BiOOH or Bi(OH)3, which are similar in solubility, at 298 and 473 K. The data obtained from thermodynamic calculations are consistent with experimental data on the stability boundaries of BiPO4, Bi3O(OH)(PO4)2, and Bi2O3 compounds.
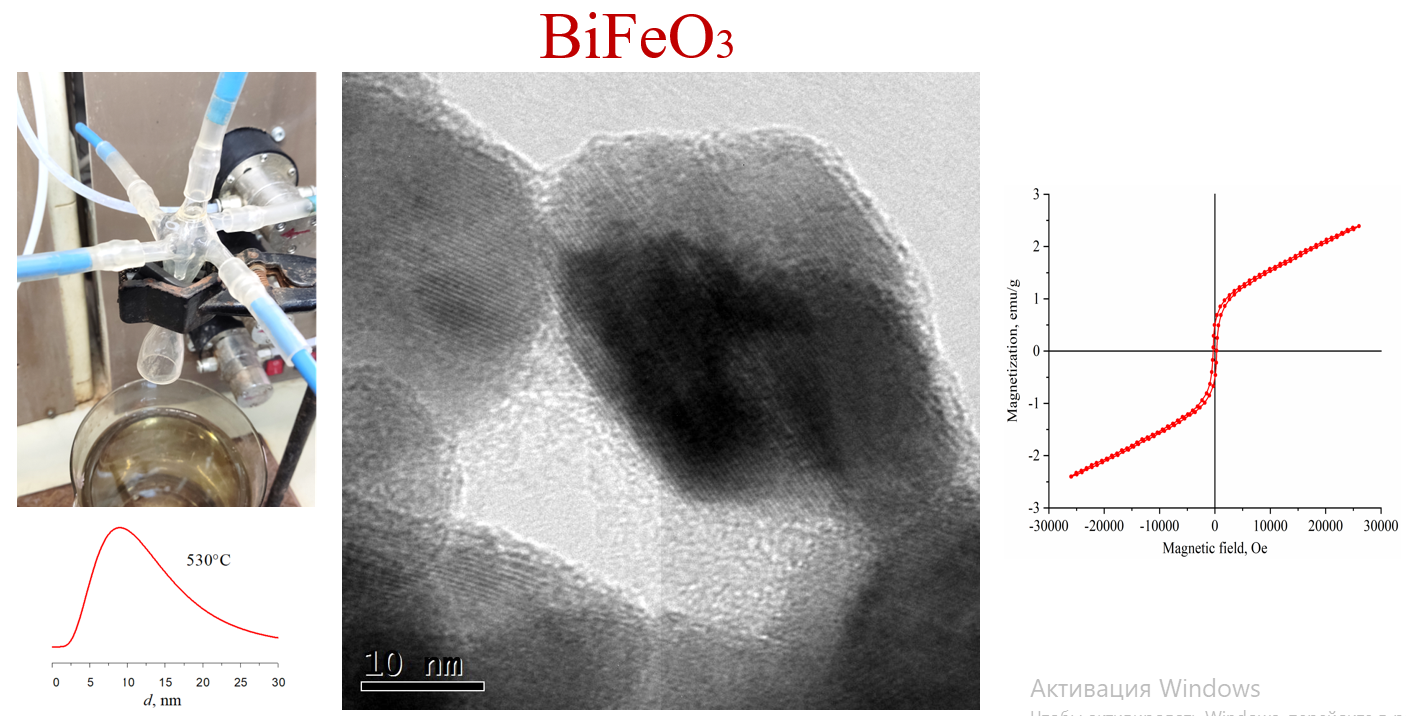
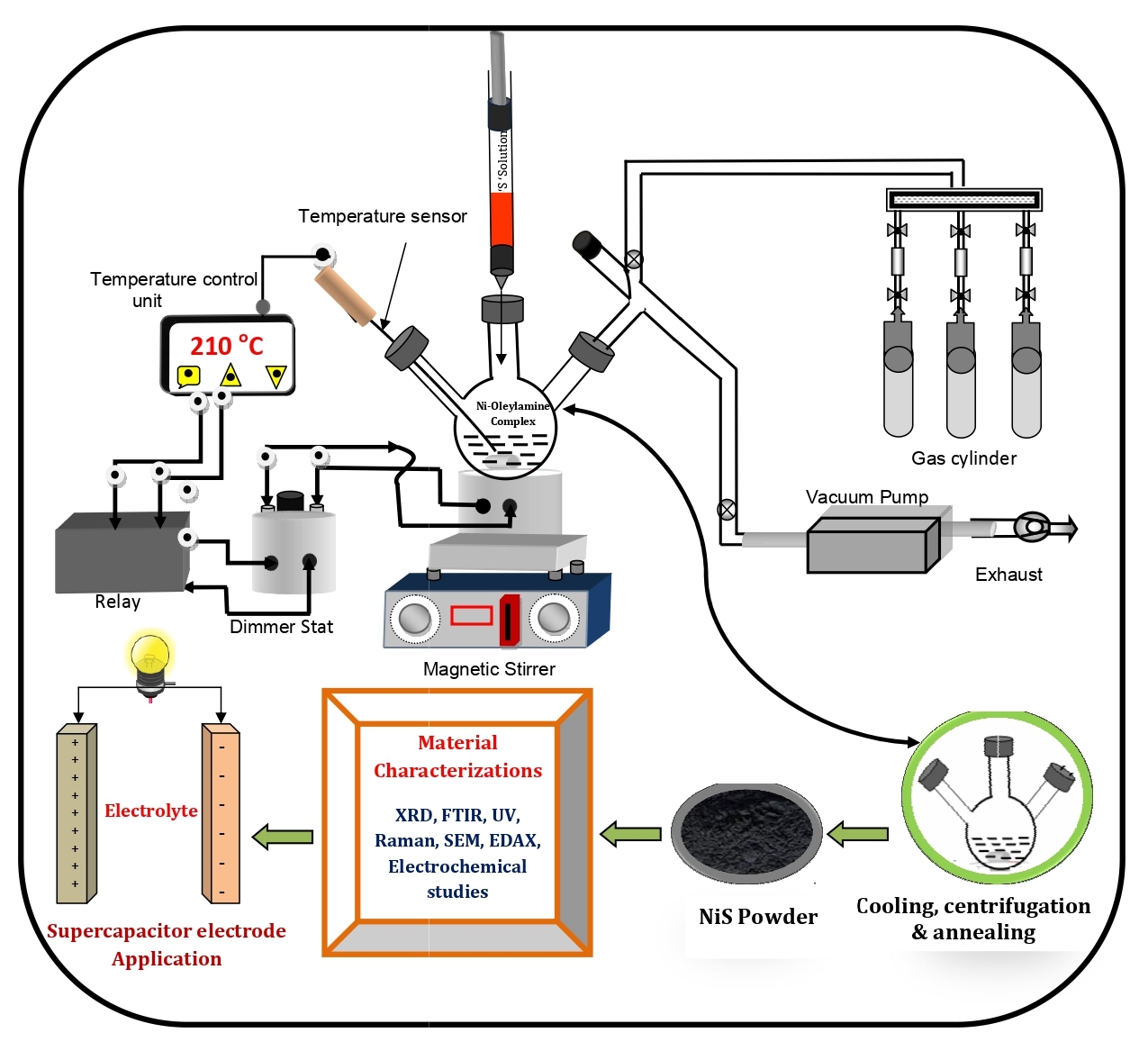
In this work, hydroxide deposition in a microreactor with intensively swirling flows was used to obtain BiFeO3, followed by heat treatment of co-precipitated bismuth and iron hydroxides. The study of the formation of nanocrystalline bismuth orthoferrite was carried out using a set of methods: EDXMA, TEM, XRD, 57Fe M¨ossbauer spectroscopy, DRS, etc. The photocatalytic activity and magnetic characteristics of the material were determined. It is shown that during heat treatment of hydroxide precipitation for 1 minute at a temperature of 530 ◦C, BiFeO3 nanocrystals with an average crystallite size of 14 ± 7 nm are formed. It was found that the resulting BiFeO3 nanopowder is represented by agglomerates of individual nanoparticles. The saturation magnetization and residual magnetization values of these bismuth orthoferrite nanoparticles are 2.31 and 0.48 emu/g, respectively. According to the DRS results, band gap energy for the samples calculated at 530, 515, and 500 ◦C were 1.82, 1.86, and 1.91 eV, respectively, which ensures strong absorption of visible light by the samples. The sample showed higher photocatalytic activity in the X-ray amorphous state compared with nanocrystalline BiFeO3 in the process of Fenton-like discoloration of methyl violet under the action of visible light with reaction rate constants of the pseudo-first order 0.0256 and 0.0072 min−1, respectively.
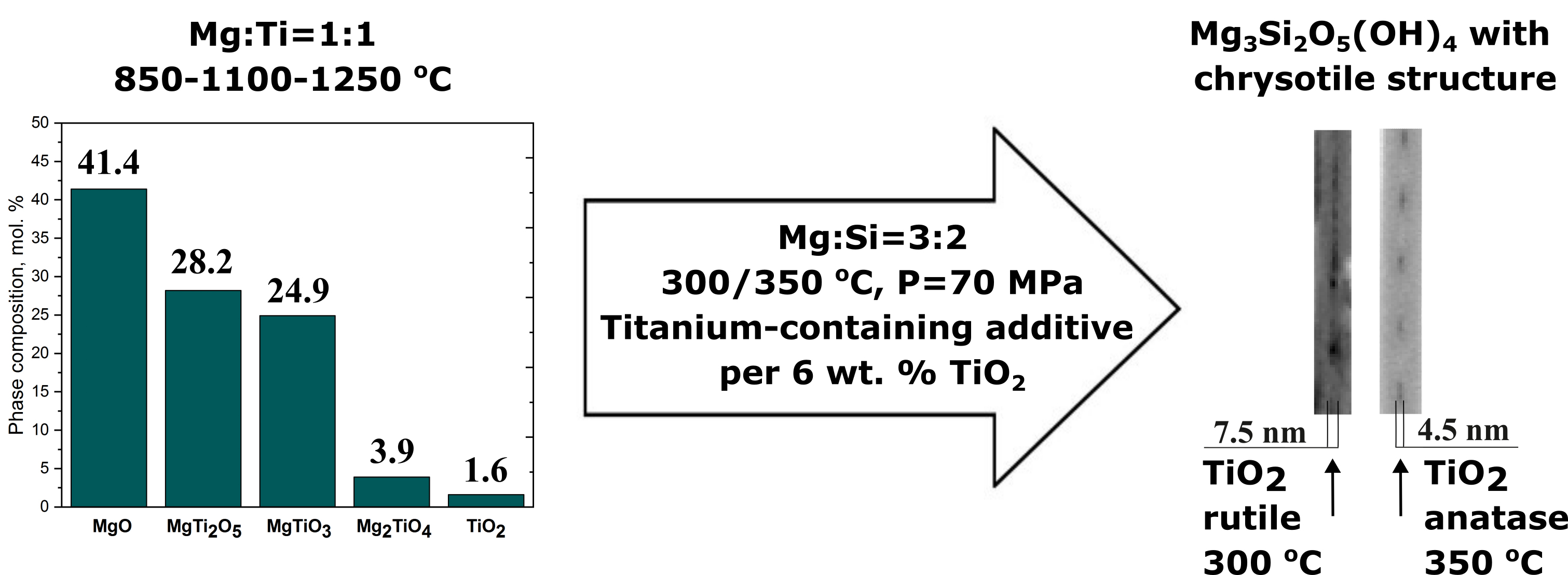
The paper studies the influence of titanium-containing compounds on the formation of hydrosilicate nanotubes under hydrothermal conditions. The possibility of titanium ions to enter the crystal structure, and of titania the nanotube channel, has been analyzed. The influence of temperature on the ratio of compounds forming under hydrothermal conditions was determined.
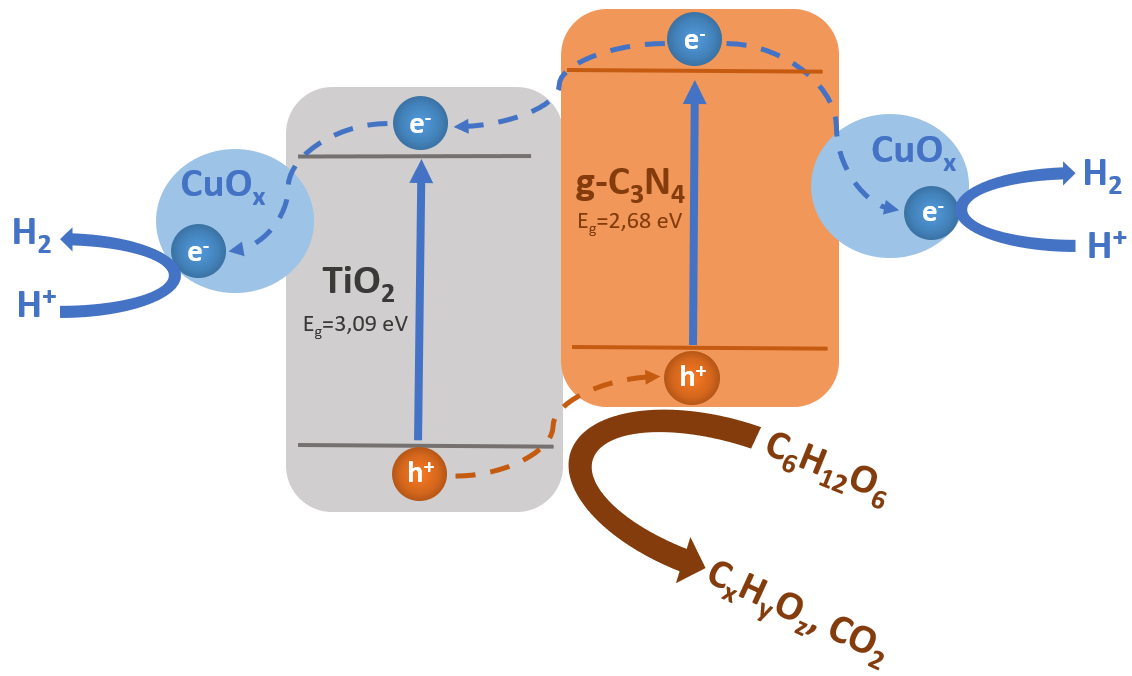
Two strategies for synthesis of copper-modified composite photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride and titanium dioxide for hydrogen evolution reaction are presented. The first one is based on the mechanical dispersion of separately prepared g-C3N4 and commercial TiO2 (Evonik P25), modified with copper. Another approach is co-calcination of melamine and commercial TiO2 with subsequent modification by copper. The samples were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM). The synthesized photocatalysts were tested in hydrogen evolution from glucose aqueous solution under visible light irradiation (440 nm). The largest photocatalytic activities met 235 and 259 µmol·g−1·h−1, corresponding to the first and the second photocatalyst series, respectively. The most active photocatalyst from the first series 1 wt. % g-C3N4/1 wt. % CuOn/TiO2 maintained its hydrogen production rate during a 6-hour cyclic stability test.
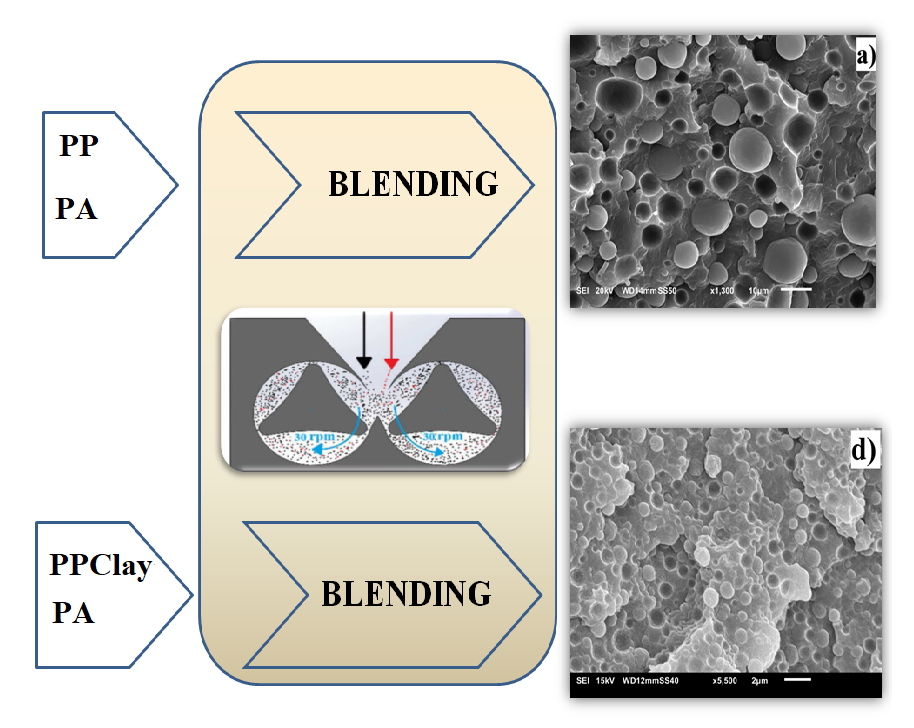
We study rheological, morphological and mechanical properties of polyamide-6 (PA) and polypropylene (PP) blends in the presence of layered silicates (two types of organically modified montmorillonite - Cloisite30B for PA and Cloisite20A for PP). For comparison, we used maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene (PP-g-MA) as a compatibilizer and in all compositions weight ratio of PA and PP was constant 80/20, respectively. Introduction of layered silicates always led to more viscous melt and increased storage modulus. It is also identified that layered silicates cause more finer-dispersed morphology than PP-g-MA. Elastic modulus and yield strength were increased when the layered silicates were introduced in either composites or blends.
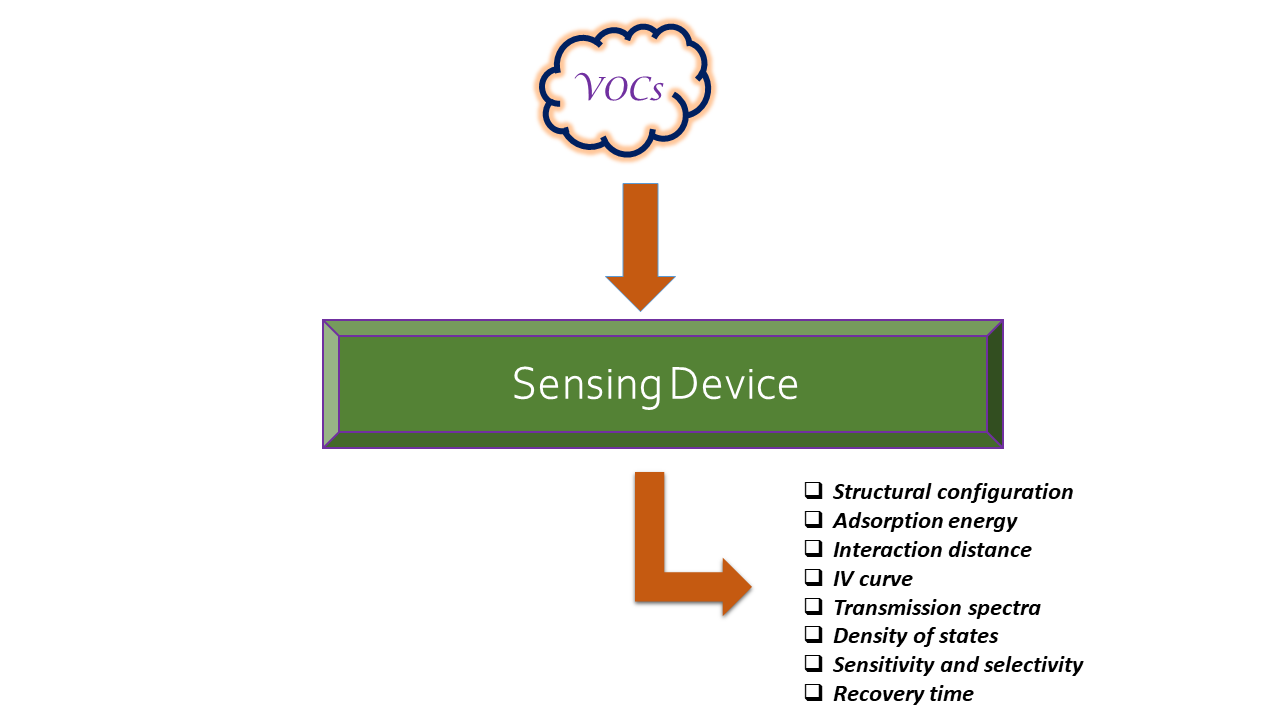
In this work, we perform an intricate computational analysis to investigate the adsorption mechanism of human breath exhaled VOCs, namely, methanol and ethanol, along with interfering water vapour on the surface of armchair silicene nanoribbon (ASiNR) by employing density functional theory to analyse the structural, electronic, and transport properties. The findings indicate that the most favorable adsorption configuration for methanol and ethanol involves the hydroxyl group (-OH) oriented towards the silicene surface, after optimisation. Moreover, we have calculated the adsorption energies which shows that ethanol is strongly physisorbed than methanol and water molecules on the ASiNR surface. Apart from that, the results of IV characteristics, transmission spectra and density of states corroborate these observations. In addition, we have computed the sensitivity (%), the results of which revealed that methanol demonstrates a high sensitivity of 42 % compared to other molecules towards the surface of ASiNR. Furthermore, the recovery time of the sensor was found to be extremely long, which indicates that ASiNR based device has great potential for use as disposable sensors and scavengers for toxic gas molecules.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)