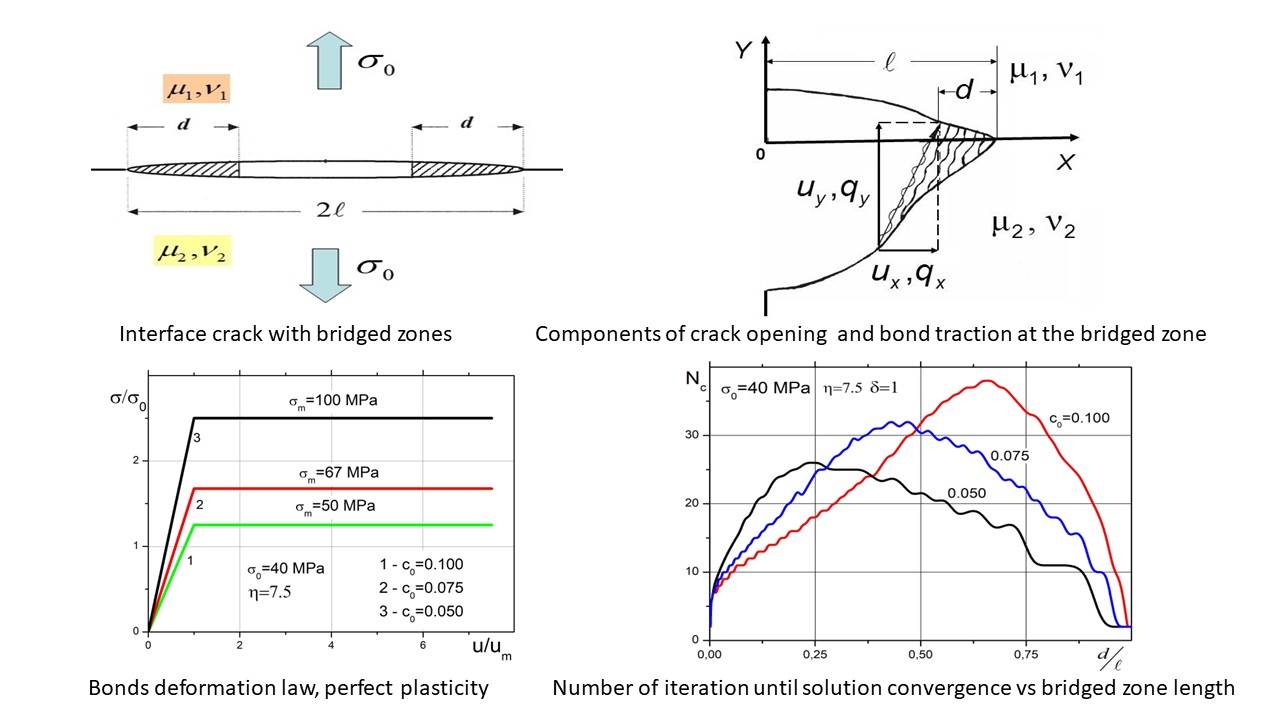
The model of different materials joint with bridged interface crack is considered. It is assumed that between the crack faces there are nanofibers constraining the crack opening. The size of the zone filled with nanofibers (the bridged zone) can be comparable to the whole crack length. The bond tractions depend on the crack opening at the bridged zone according to the prescribed nonlinear bond deformation law. The system of two singular integral-differential equations with Cauchy-type kernel is used for evaluation of bond tractions for the interface crack bridged by nanofibers. A phenomenological description of the bond deformation law in the crack bridged zone is used. Numerical experiments have been performed to analyze the influence of the bilinear bond deformation law parameters, the size of the crack bridged zone and also the magnitude of the external load on the convergence of the numerical iteration solution of the integral-differential equations system.
We consider a chemical process, the precipitate of which will be represented by a structure in the form of rings. The study and modeling of this process is relevant, since it becomes possible to form micro- and nanostructures based on this approach. We consider the version of the one-dimensional model of Keller and Rubinow which describes the formation of Liesegang rings due to the Ostwald supersaturation. The dependencies of the results obtained on the initial conditions and the model parameters were studied numerically.
In this paper, using the full security framework for continuous-variable quantum key distribution (CV-QKD), we provide a composable security proof for the CV-QKD system in a realistic implementation. We take into account equipment losses and contributions from various components of excess noise and evaluate performance against collective and coherent attacks assuming trusted hardware noise. The calculation showed that the system remains operable at channel losses up to 10.2 dB in the presence of collective attacks and up to 7.5 dB in the presence of coherent ones.
At present, free-space QKD systems are being actively researched and developed. The main limitation of these systems remains the strong influence of atmospheric turbulence and weather conditions on the propagating Gaussian beam. In turn, a number of works have shown that vortex beams are more stable in a turbulent atmosphere. Thus, in this work, the use of vortex beams in the free-space QKD system with phase encoding under the condition of a turbulent atmosphere and their comparison with Gaussian beams are studied. The possibility of phase modulation preservation with additional modulation and demodulation of the vortex beam is also investigated.
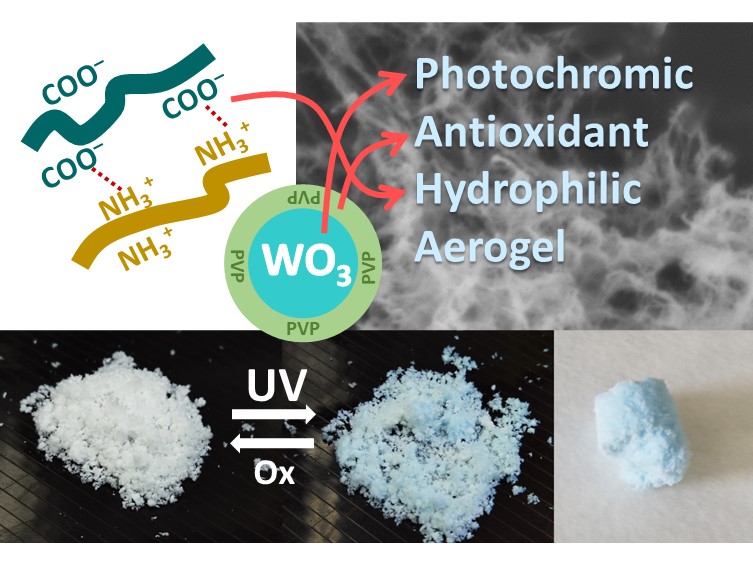
In this work, we report the first synthesis of photochromic aerogels and films based on TEMPO-oxidized cellulose and chitosan modified with tungsten trioxide nanoparticles. The blue coloring of aerogels based on WO3-modified biopolymers under UV light occurs due to the reduction of W+6 to W+5. The coloration of films of the same composition occurs due to the reduction of W+6 to W+5 and W+4. The photochromic properties of aerogels and films are reversible; oxidation by atmospheric oxygen leads to bleaching of materials. At that, films become colorless within a few days while aerogels with a high specific surface area (200 m2/g) become colorless within several minutes. The antioxidant properties of the WO3 sol and the WO3/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose/chitosan composite were studied by luminol-activated chemiluminescence method. The antioxidant capacity of WO3/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose/chitosan gel is 1.5 times higher than that of the commercially available antioxidant mexidol.
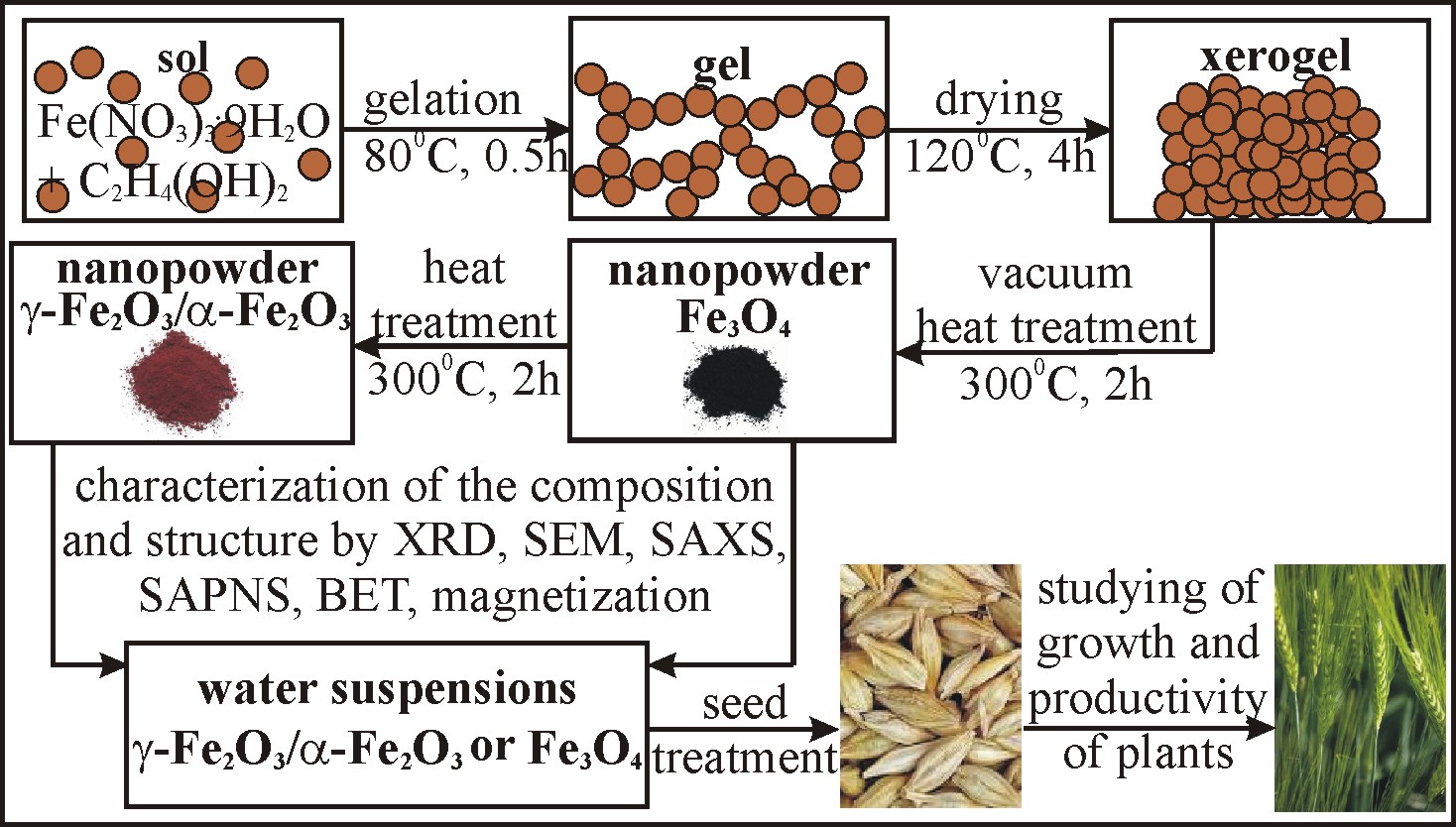
Magnetite (Fe3O4) and maghemite with an admixture of hematite (γ-Fe2O3/ α-Fe2O3) powders are synthesized via sol-gel process and characterized using XRD, SEM, low temperature nitrogen adsorption, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and small-angle polarized neutron scattering (SAPNS). The synthesized γ-Fe2O3/ α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 samples are found to be porous systems featuring with a three-level hierarchically organized structure with different intrinsic scales and aggregation types for each of the structural levels. For both materials, the intrinsic size of the highest level exceeds 70 nm, and magnetic structure involves super-paramagnetic particles with a characteristic radius of magnetic-nuclear cross-correlations R_MN ≈ 3 nm. The biological activity of γ-Fe2O3/ α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 aqueous suspensions in certain concentrations in respect to seed treatment, growth and productivity of plants was studied using the example of spring barley variety Leningradsky under adjustable favorable conditions and physical modeling of stress effects (irradiation with high-intensity UV-B radiation, soil moisture deficiency).
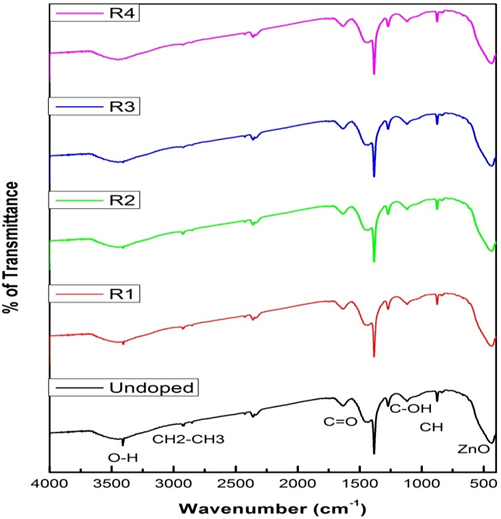
Hibiscus leaf extract mediated ZnO nanoparticles have been prepared through a hydrothermal method and the effects of extract doping on the structural, optical and electronic properties of ZnO NPs were studied. The photocatalytic oxidation of methylene blue dye under visible light irradiation was used to determine the photocatalytic performance of the prepared nanoparticles. The extracted ZnO nanoparticles (R3) exhibited the lowest band gap and the highest photocatalytic activity for the methylene blue dye. The photocatalytic performance of the (R3) prepared ZnO nanoparticles was stable after the nanoparticles were reused five times for the oxidation of methylene blue dye.
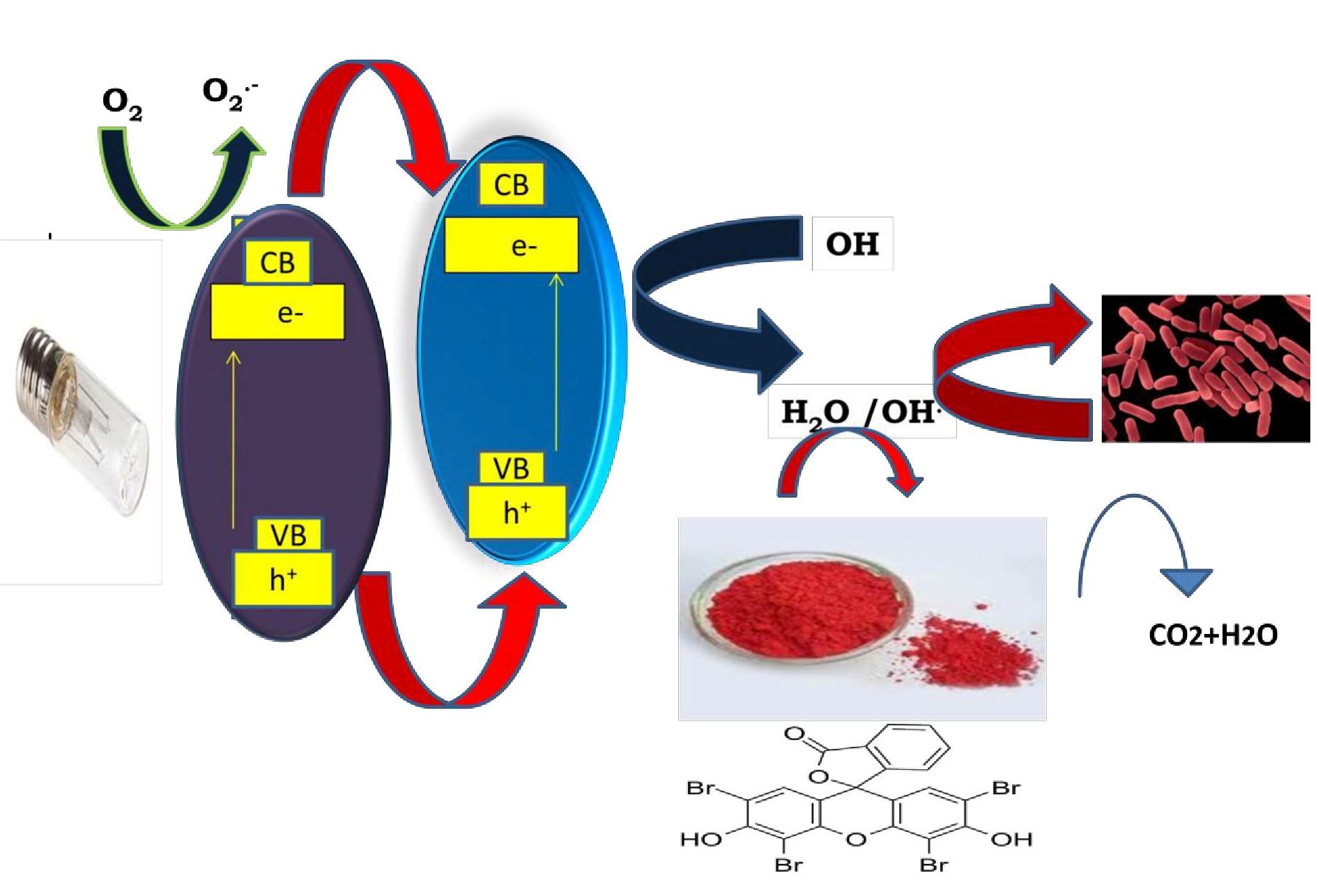
This paper aims to explore the photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of Mn and S co-doped TiO2 nanomaterial synthesized by the sol-gel method. Various instrumental techniques, XRD, BET, UV-Vis-DRS, TEM, XPS, SEM, FT-IR, were used to classify the catalyst samples. The characterization results show that the surface area is large, the particle size is small, band gap energy is low, the crystallite size is small, and the surface morphology is smooth. The efficiency of photocatalytic and antibacterial activity was evaluated by the degradation of Eosin yellow (EOY) and Bacillus subtilis (MTCC-441), respectively. The complete degradation of EOY was achieved in 70 min.
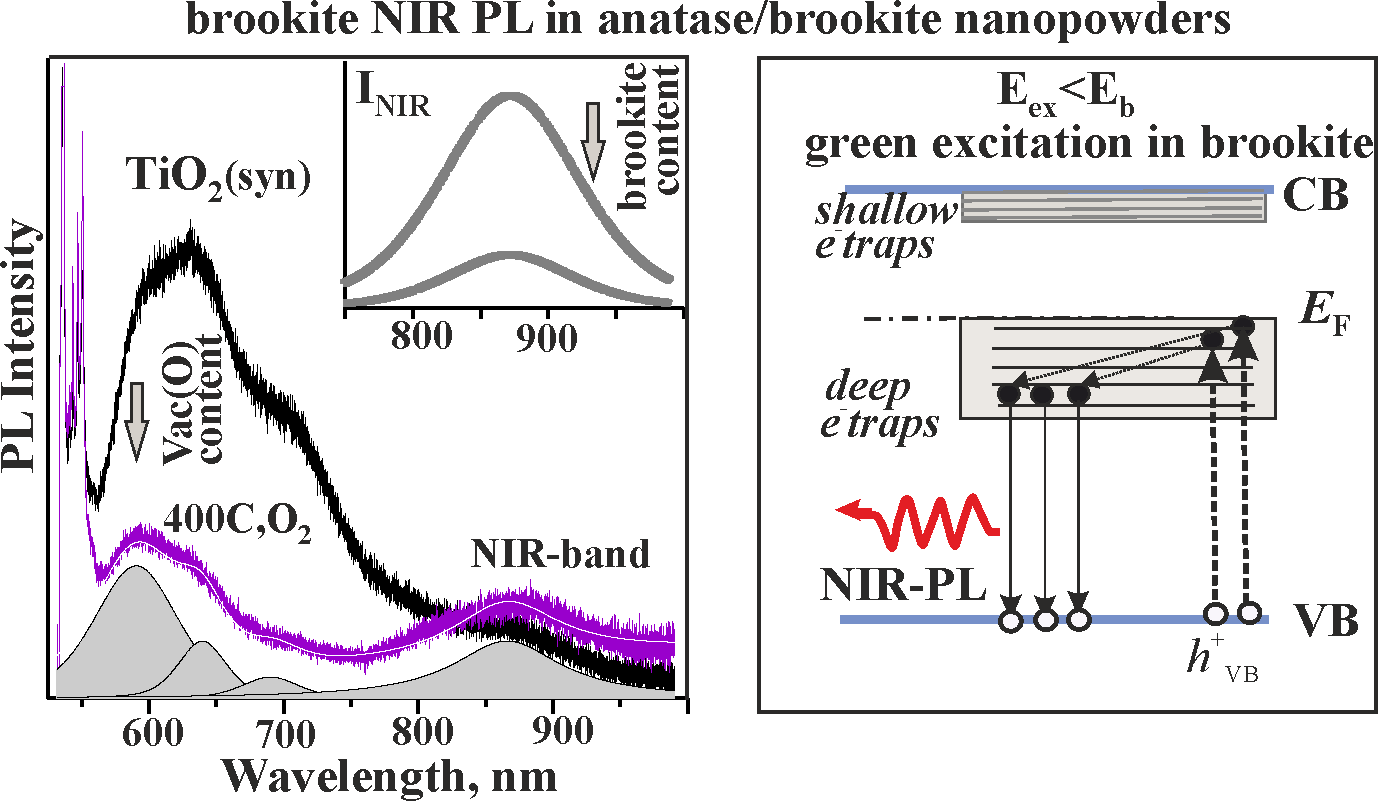
The properties are studied for near-IR photoluminescence (PL) observed at 865 - 870 nm for precipitated TiO2 powders having nanocrystalline anatase/brookite structure: the dependence of NIR PL on annealing in oxygen, on content and crystallinity quality of brookite, and on excitation energy (Eex). NIR PL in bi-phase powders was found to demonstrate a behavior characteristic of NIR PL in brookite. NIR emission intensity grows with increasing brookite content and at annealing in oxygen, when oxygen vacancies content decreases and crystallinity quality of brookite improves. The results indicate that in the bi-phase powders, brookite contains deep-level defect traps which are regarded responsible for NIR-PL in brookite and are favorable for photocatalytic reactions. NIR emission is observed for the band (Eex ~ Eb) and below band-gap green (Eex < Eb) excitation. A mechanism underlying NIR-PL in brookite with green excitation is suggested to be similar to that for the red PL known for anatase at below band-gap excitation.
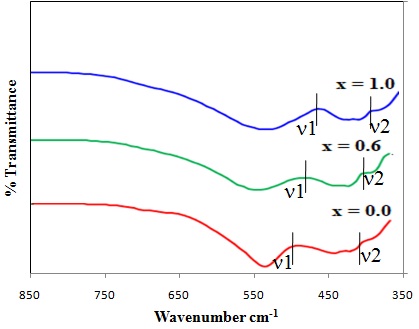
Magnesium-Zinc Ferrite nanoparticles of different compositions are synthesized by using the sol-gel auto-combustion method with citric acid as a fuel. Structural characteristics were studied using X-ray diffraction technique and it confirms the formation of cubic spinel structure. The ferrite nanoparticle size of synthesized powder ranges from 22 - 24 nm. The effect of change in Mg2+ content results in a change of the lattice parameter of ferrite nanoparticles. In the present paper, the structural parameters such as cation-cation and cation-anion distances, tetrahedral, octahedral bond lengths and bond angles, hopping lengths, shared, unshared tetrahedral, and octahedral edge are reported. FTIR spectra show two prominent peaks around 524 - 532 cm-1 (tetrahedral site) and 409 - 432 cm-1 (octahedral site) and the force constants of the octahedral and tetrahedral site of Mg-Zn ferrite were calculated. The elastic moduli and other factors such as longitudinal, transverse and mean velocity, Poisson ratio, and Debye temperature were determined.
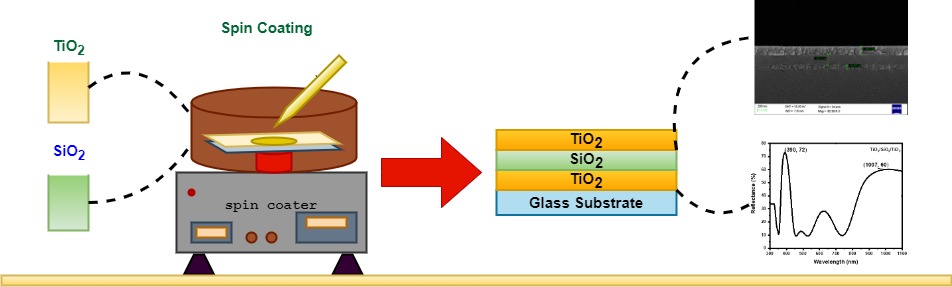
There are seasonal changes in the environment temperature which leads to additional usage of various devices like air-conditioners in the summer season and space heaters in the winter season. The usage of this equipment incurs increased consumption of electricity that can result in increased usage costs. High usage of air conditioners also releases large amounts of fluorocarbons that can contribute to global warming. Hence, to minimize the usage of air-conditioners and to protect from the seasonal temperature changes it is necessary to mold the light, which can be done by dielectric optical coatings. These coatings are derived from the thin films of varying refractive index that can be fabricated by many bottom-up techniques available in nanotechnology. Herein, we report one of the bottom-up technique i.e., sol-gel spin coating technique for the fabrication of a dielectric reflector that can serve as a window for the seasonal temperature changes by filtering the ultraviolet and near-infrared spectra. The fabricated reflector was investigated with FE-SEM for thickness and layer identification and UV-VIS-NIR spectroscopy analysis for the reflectance analysis.
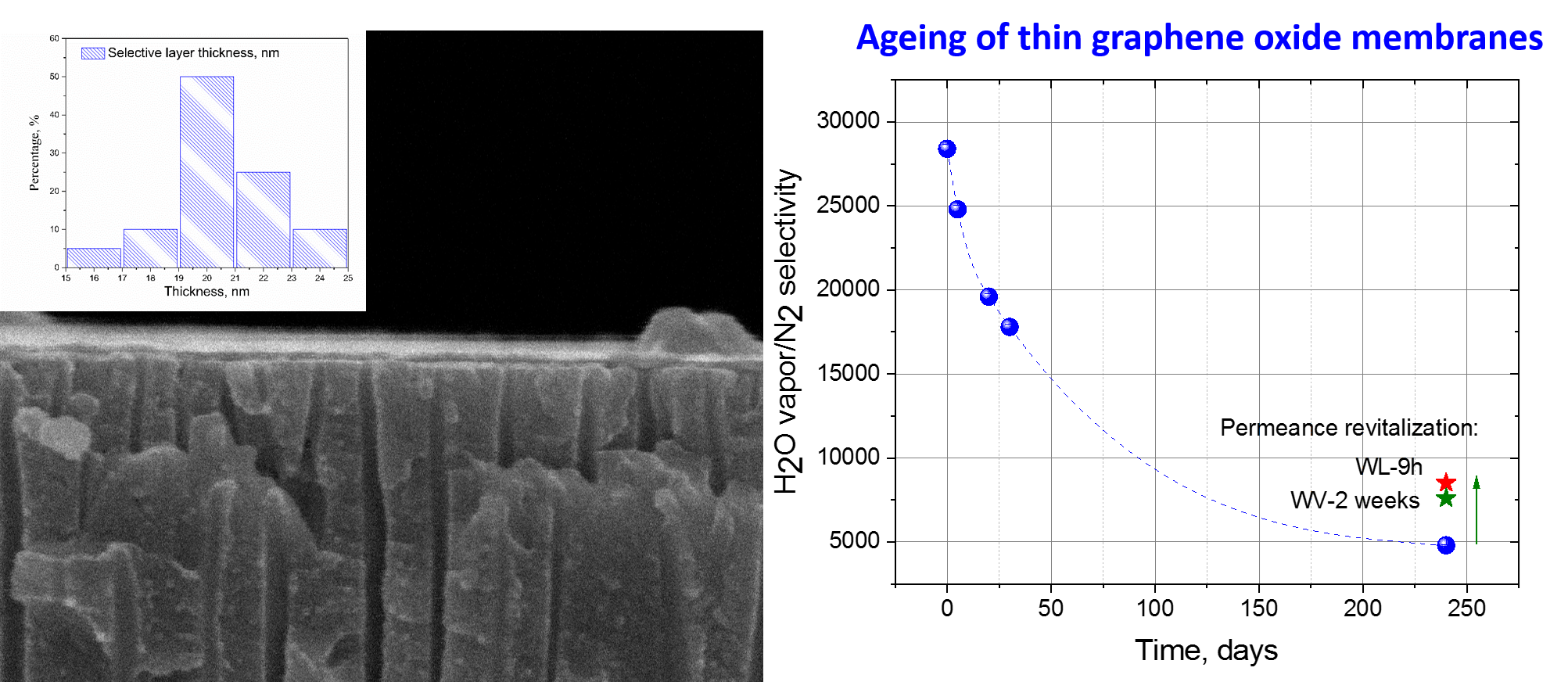
Composite membranes are formed based on ultrathin 20 nm-thick selective layers of graphene oxide nanoflakes deposited on porous anodic alumina substrates. The long-term dynamics of permanent gases transport and water vapor permeability across the composite membranes is measured during 240 days (8 months). It is revealed that the permeability towards permanent gases remains nearly constant during a prolonged period of time. Contrary, water vapor flux decreases rapidly within the first 30 days from the membrane preparation moment and reaches about 80% of permeability loss during 8 months. The rapid decrease of membrane permeability during the first month could be attributed to a gradual packing of graphene oxide nanoflakes, particularly, locating in the surface sublayers, into more tight microstructure due to the evaporation of remaining solvent (membrane drying) under ambient conditions. Further decrease in permeability during more prolonged time could be caused additionally by deoxygenation of surface GO nanoflakes preventing water vapors diffusion into the GO film. This phenomenon, the so called “ageing” accompanies graphene oxide thin films similarly to some types of highly-permeable polymers. Holding the aged membrane under saturated water vapors, and even liquid water, didn’t allow one to revitalize completely its permeability. The obtained results should be taken into account when designing membranes and other devices based on graphene oxide and its derivatives.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)