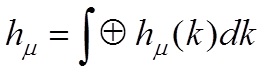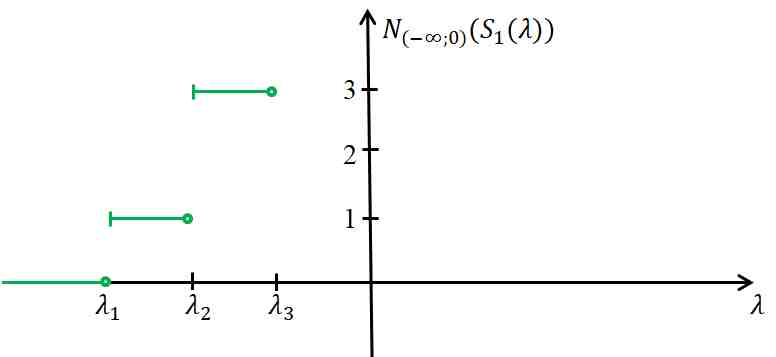MATHEMATICS
The two-particle Schrödinger operator h_(k); k 2 Td (where _ > 0, Td is a d-dimensional torus), associated to the Hamiltonian h of the system of two quantum particles moving on a d-dimensional lattice, is considered as a perturbation of free Hamiltonian h0(k) by the certain 3d rank potential operator _v. The existence conditions of eigenvalues and virtual levels of h_(k); are investigated in detail with respect to the particle interaction _ and total quasi-momentum k 2 Td.
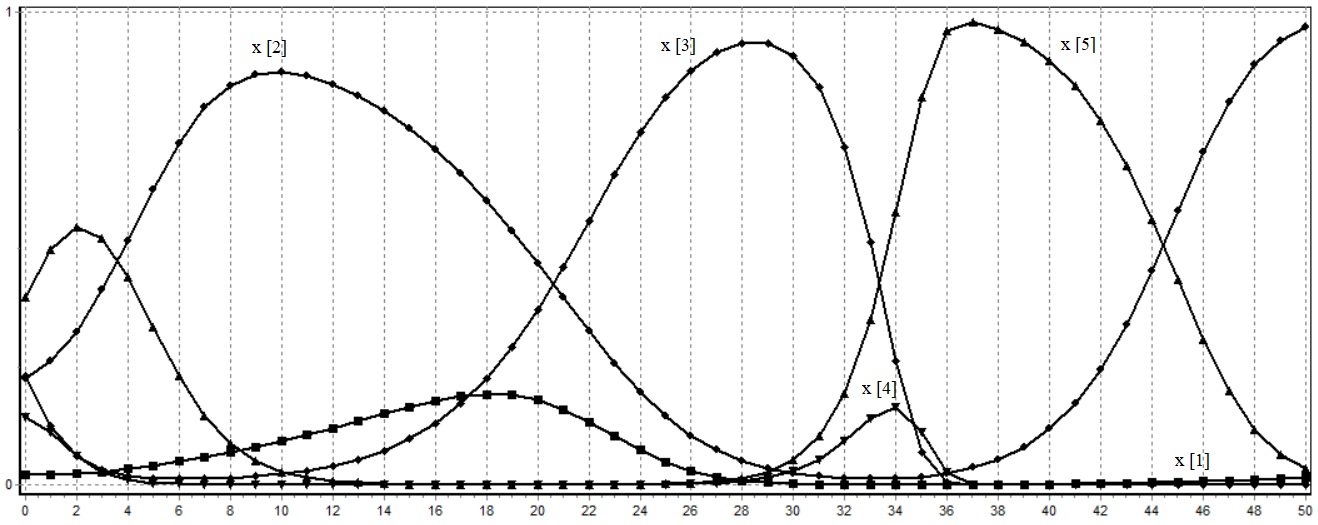
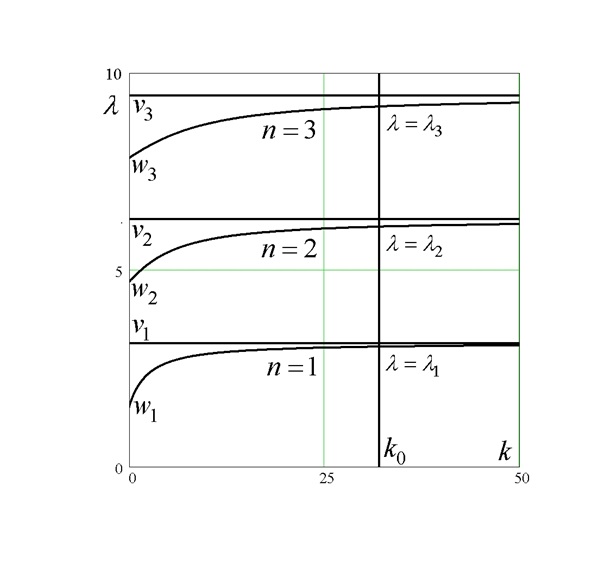
In the present paper, we consider a lattice spin-boson model A2 with a fixed atom and at most two photons. We construct the first Schur complement S1(_) with spectral parameter _ corresponding to A2. We prove the Birman–Schwinger principle for A2 with respect to S1(_). We investigate an important properties of S1(_) related to the number of eigenvalues of A2 for all dimensions d of the torus Td and for any coupling constant _ > 0.
In the article, the problems of unique solvability and determination of the redefinition coefficient function in the initial inverse problem for a nonlinear Whitham type partial differential equation with impulse effects are studied. The modified method of characteristics allows partial differential equations of the first order to be represented as ordinary differential equations that describe the change of unknown function along the line of characteristics. The unique solvability of the initial inverse problem is proved by the method of successive approximations and contraction mappings. The determination of the unknown coefficient is reduced to solving the nonlinear integral equation.
Approximate analytical formulas are obtained for the eigenfrequencies of longitudinal oscillations of an elastic rod with different mechanical fixings of the ends. The eigenfrequencies are found by solving Sturm–Liouville problems with the third kind boundary conditions as roots of transcendental equations. Homogeneous boundary conditions contain one or more parameters whose values are calculated through the indices of mechanical system. Approximate expression for analytical dependencies of the eigenfrequencies on the single parameter are obtained for one-parametric problems, which are called reference ones. We propose a method for obtaining approximate analytical expression for dependencies of the eigenfrequencies on several parameters in boundary conditions by sequentially solving the reference problems. The two-parametric Sturm–Liouville problem is solved by the proposed method.
PHYSICS
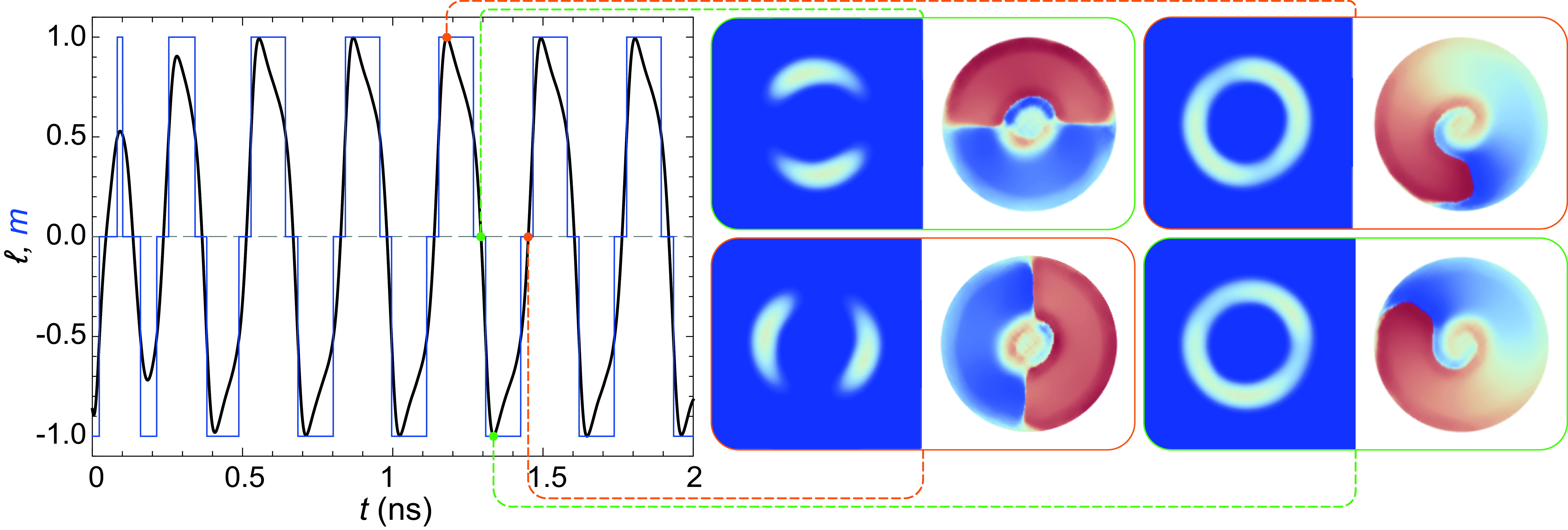
We study annular flows of exciton polaritons in exciton polariton condensates emerging in cylindrical optical micropillar cavities under the spatially localised non-resonant laser pumping. Annular flows indicate nonzero vorticity of the polariton condensate associated with the appearance of polariton vortices around the center of the micropillar. We report an experimental observation of single ring shaped condensates in the regime of vorticity oscillating in time. We reproduce the vorticity oscillations numerically and reveal possible control parameters for manipulating by the oscillation period.
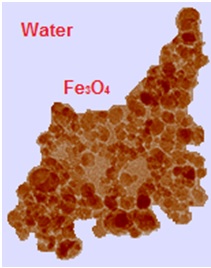
In this work, the aggregation of nanoparticles in an aqueous colloidal solution of magnetite, stabilized by creating a citrate shell on the particle surface is studied. Electron microscopy and laser correlation spectroscopy were used as experimental methods. Optical measurements were carried out both at zero external magnetic field and in the fields differently oriented relative to the probing laser beam. It is shown that the samples tend to form large aggregates even without the application of the field, and in the case of its presence the behavior of these structures has features that distinguish them from other magnetic fluids.
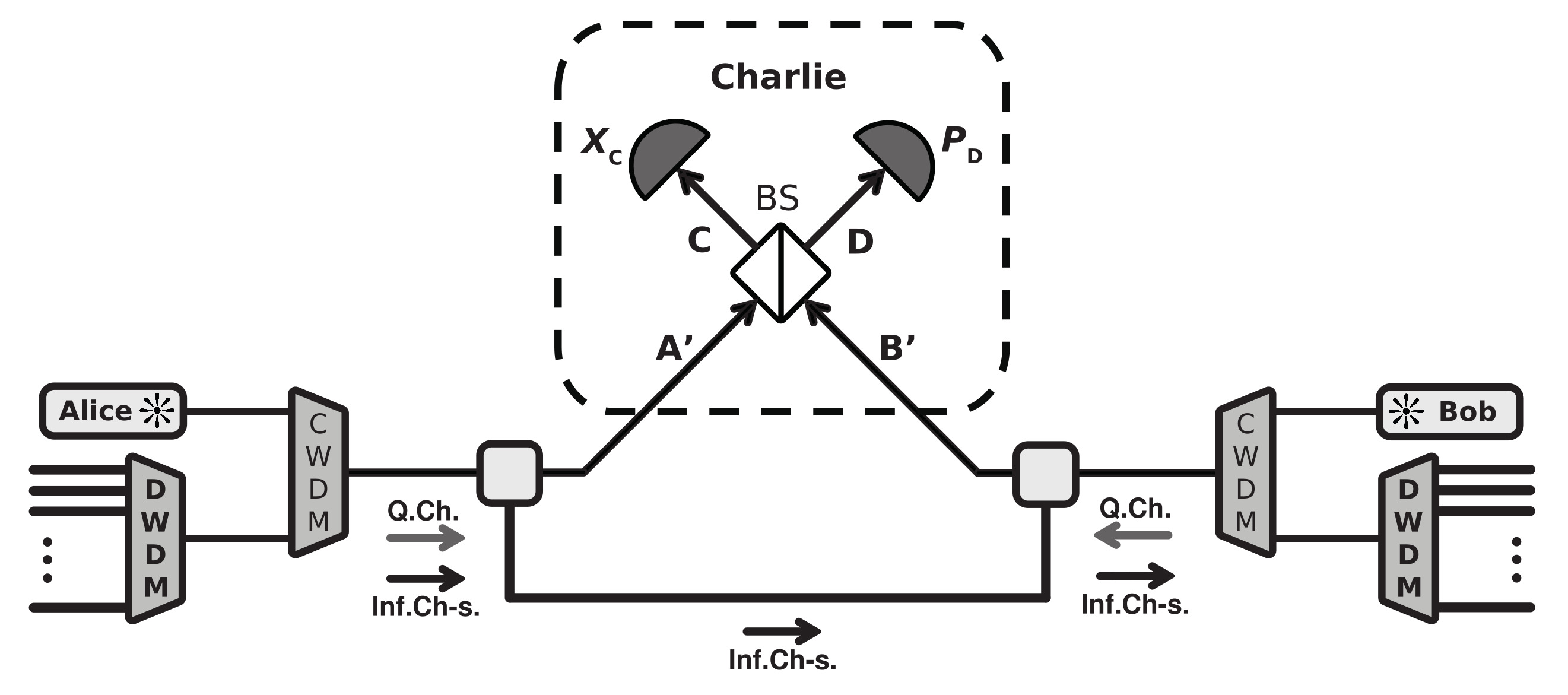
Numerically, a theoretical analysis of the noise impact caused by spontaneous Raman scattering, four-wave mixing, and linear channel crosstalk on the measurement-device-independent continuous variable quantum key distribution systems is conducted. The analysis considers symmetry and asymmetry of system paths, as well as possible channel allocation schemes, for a quantum channel located in C- and O-bans. Mathematical models for MDI CV-QKD system and the contributing noises’ description are provided. The secure key generation rate is estimated to state features of protocol operation when integrated with existing DWDM systems in the context of its implementation into telecommunication networks.
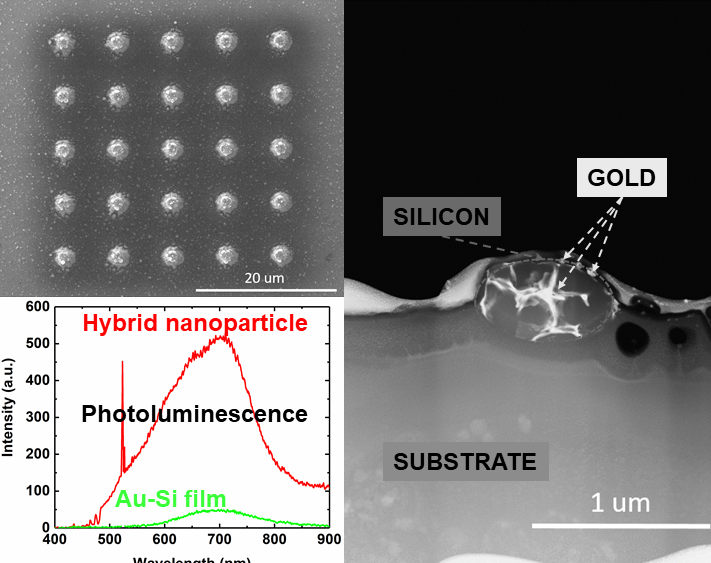
In this paper, we present a one-stage method for fabricating hybrid metal-dielectric nanostructures without the use of complex and expensive lithographic processes. The formation of arrays of nanoparticles occurs in the process of irradiation of a two-layer gold-silicon film with simultaneous mixing of materials. In this work, the internal structure of the obtained nanoparticles was studied using the methods of transmission scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and their broadband photoluminescence in the range of 450 – 900 nm was also demonstrated. These structures are promising as a source of radiation for optical measurements in lab-on-a-chip devices, which was shown by measuring the transmission spectrum of the Rhodamine B dye as an example.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
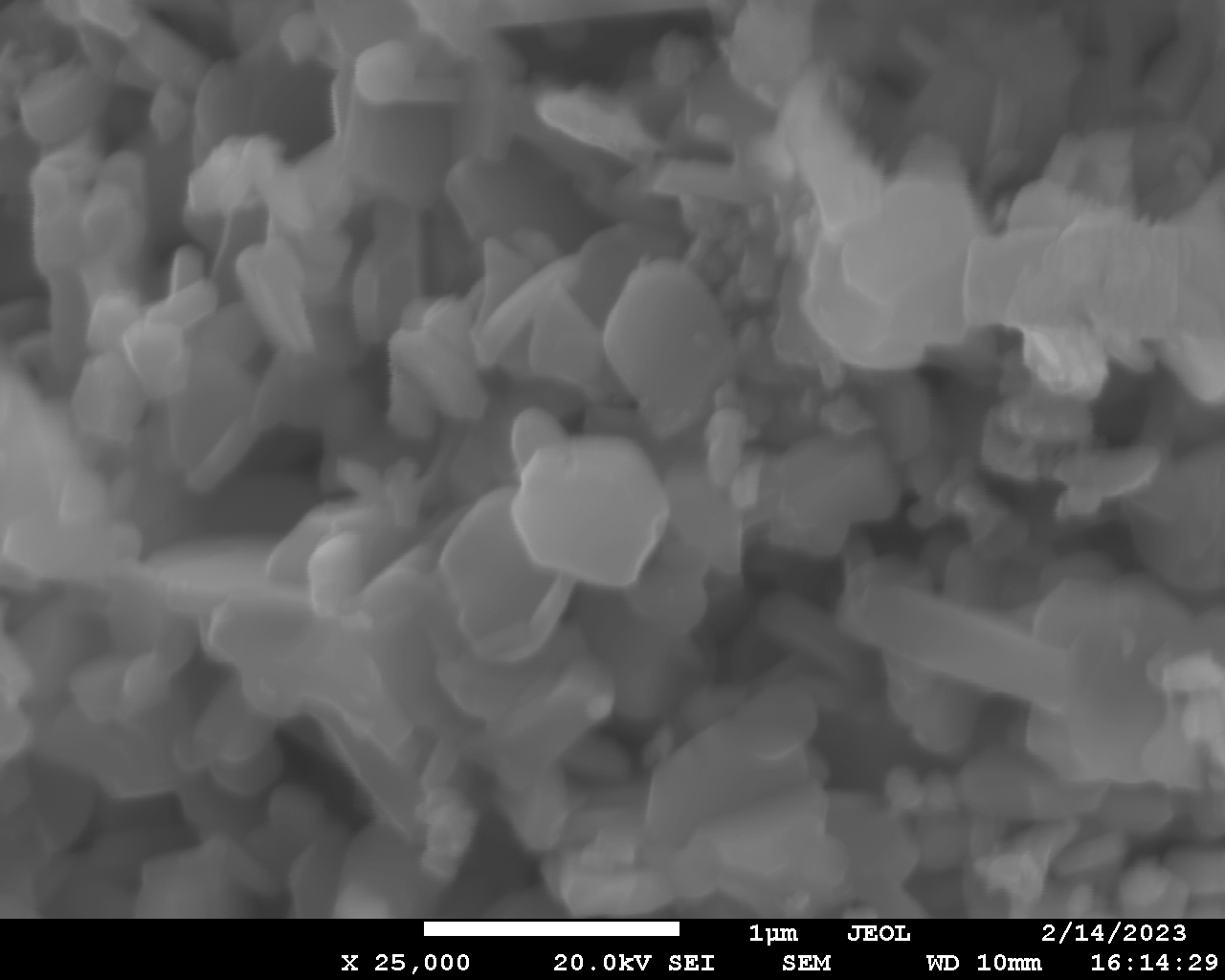
The purpose of this study is to obtain high-entropy oxides with the magnetoplumbite structure, in which the Pb cation is used as a divalent metal cation. The synthesis conditions were optimized, and a technique was developed to avoid the evaporation of lead oxide. For the first time, single-phase samples of high-entropy oxides with the magnetoplumbite structure were obtained, its chemical composition is reflected by the formula PbFe2.4X2.4Y2.4Ga2.4In2.4O19. The particle size of the high-entropy phase is about 100 nm, which makes it promising for a number of applications. The effect of preliminary grinding of the initial components on the results of synthesis was studied. A synthesis mechanism is proposed. The results pave the way to synthesis and study of the properties of a new large subgroup of high-entropy oxides with the magnetoplumbite structure, which expands the possibilities of controlling the properties of ceramic magnetic materials.
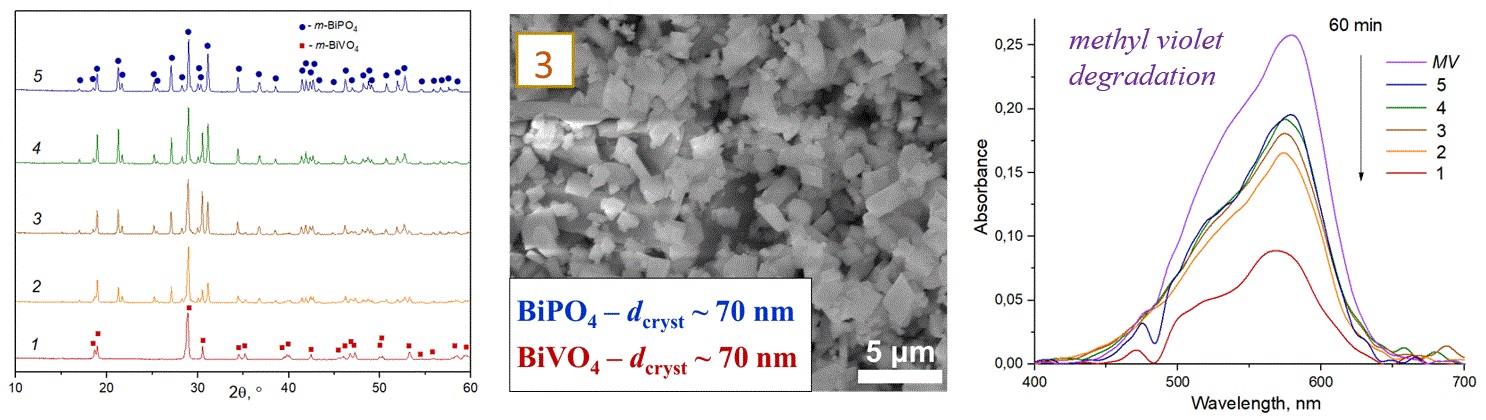
BiPO4/BiVO4 nanocrystalline composites were synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. The influence of the initial composition of the system on the phase state, the size of crystallites, and the morphology of the formed particles was determined. The photocatalytic activity of the nanocomposite was studied using the decomposition of methyl violet as an example.
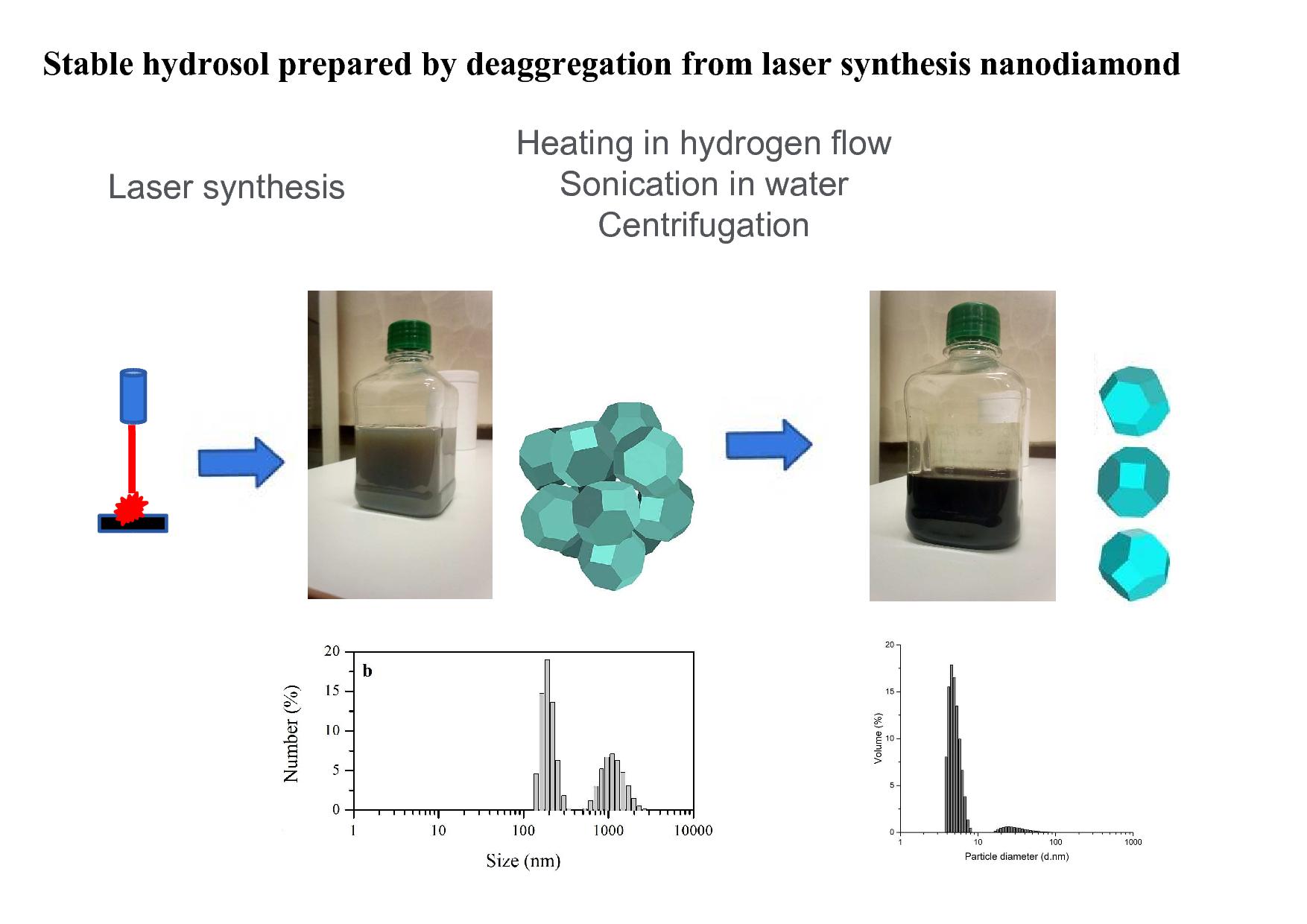
The new applications of nanodiamond in biology and nuclear physics require the use of products with a low content of impurities. One of the possible methods for obtaining a high-purity nanodiamond is the recently developed laser synthesis method. The aim of this work was to study the state of aggregation of laser synthesis nanodiamond particles in aqueous suspensions and to test the possibility of deaggregation of laser nanodiamond. The process of deaggregation of a laser synthesis nanodiamond is investigated. It was shown that the previously described process of deaggregation by milling with baking soda and the usual process of deaggregation give almost the same results. A solid phase from a colloidal solution of a laser synthesis nanodiamond has been isolated and investigated. The low content of impurities in the studied product was confirmed (less than 0.1% at.), the Raman, IR, and EPR spectra were studied.
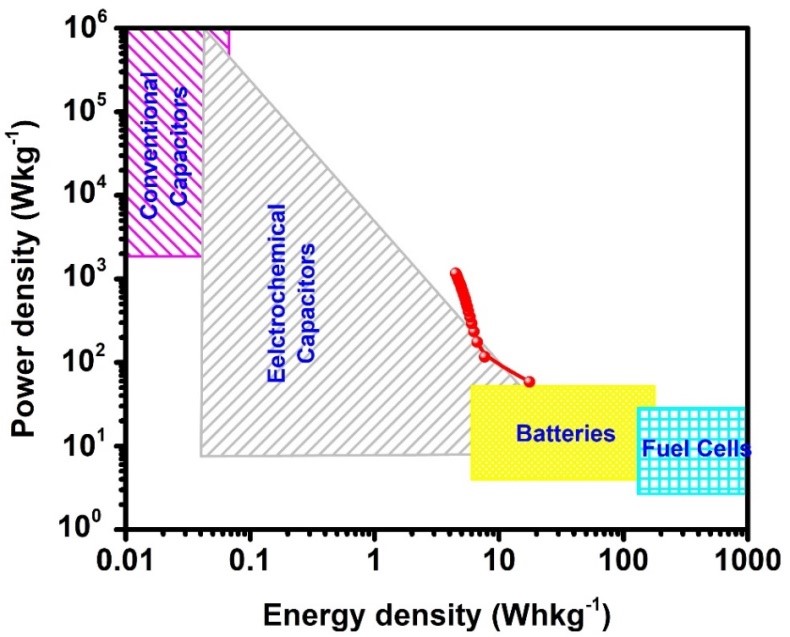
Graphene can be used to store energy as well as a supercapacitor material because of its unique physical and chemical properties, including high specific surface area, high chemical stability, high mechanical strength, and oxidation resistance. In this report, a facile, green, and cost-effective approach has been adopted to synthesize graphene sheets through an electrochemical exfoliation technique for supercapacitor applications. Graphene sheets were synthesized using aqueous electrolyte (Ag/AgCl, 0.1 M H2SO4) with four different exfoliation potentials such as 3, 5, 7 and 9 V. The prepared graphene sheets were subjected to characterization techniques such as Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The Raman results revealed that the defect density and thickness of the graphene layers increased with increased in the exfoliation potential and then eventually decreased. Among all potentials, the maximum crystalline size of graphene was observed for the potential of 5 V, an intermediate crystalline size of 9 V, and minimum for 7 V, showing that the exfoliated graphene layer was sensitive to the exfoliation potential. XPS study shows the structural oxidation (relative percentage of carbon and oxygen) of the exfoliated graphene at different potentials. The results indicate that electrochemically exfoliated graphene (5 V) has been successfully produced. The behaviour of 5 V graphene has been examined using a charge-discharge (CD) curve and cyclic voltammetry (CV) for supercapacitor applications. The maximum value of specific capacitance obtained is 198 F g-1 at a current density of 0.14 A g-1 in 6 M KOH. The highest value obtained for energy density and power density is 17 W h kg-1 and 1176 W kg-1.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)