PHYSICS
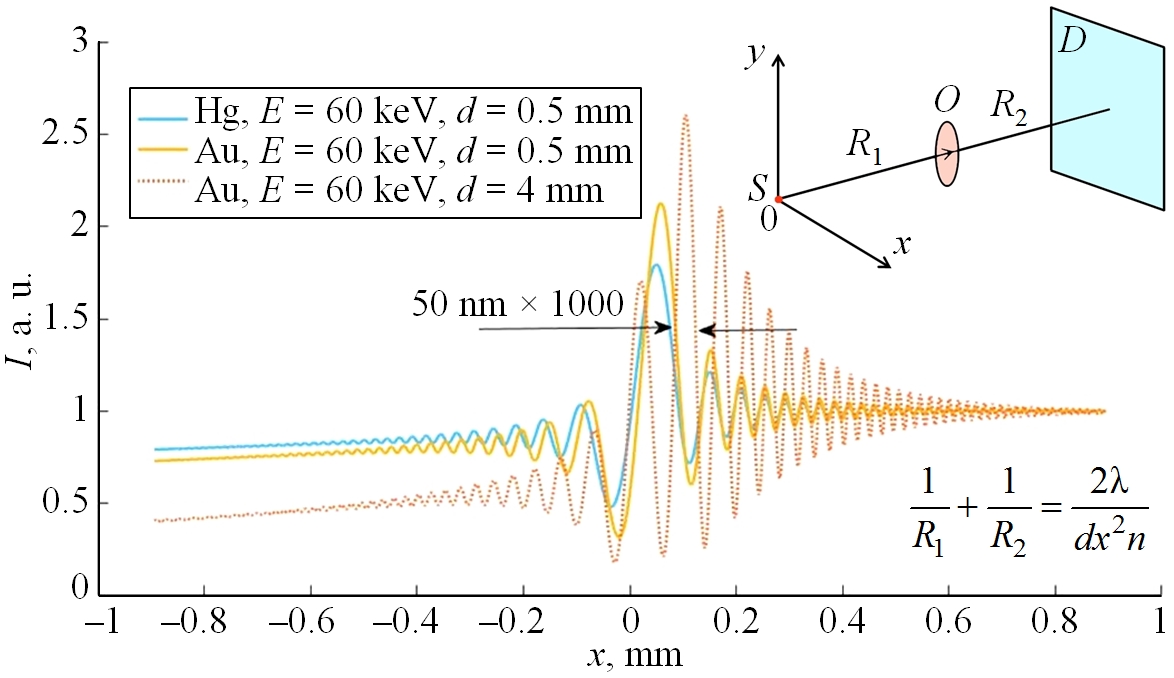
The work is devoted to the development of a method for testing the focal spot size of nanofocus and microfocus X-ray tubes based on phase contrast radiography of test objects. The method is based on the comparison of the interference X-ray image with the calculated values obtained by the exact numerical solution of the wave equation. The high sensitivity of the method to the size of the source is ensured by the fusion of interference fringes with contrast of different signs. The formation of X-ray phase contrast images of test objects is analyzed on the basis of the wave equation using numerical modeling of the intensity profile. An analytical expression has been obtained to estimate the size of the X-ray tube focus. The results of calculations of phase contrast profiles for a nylon fishing line and a reference nanofocus test are presented.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
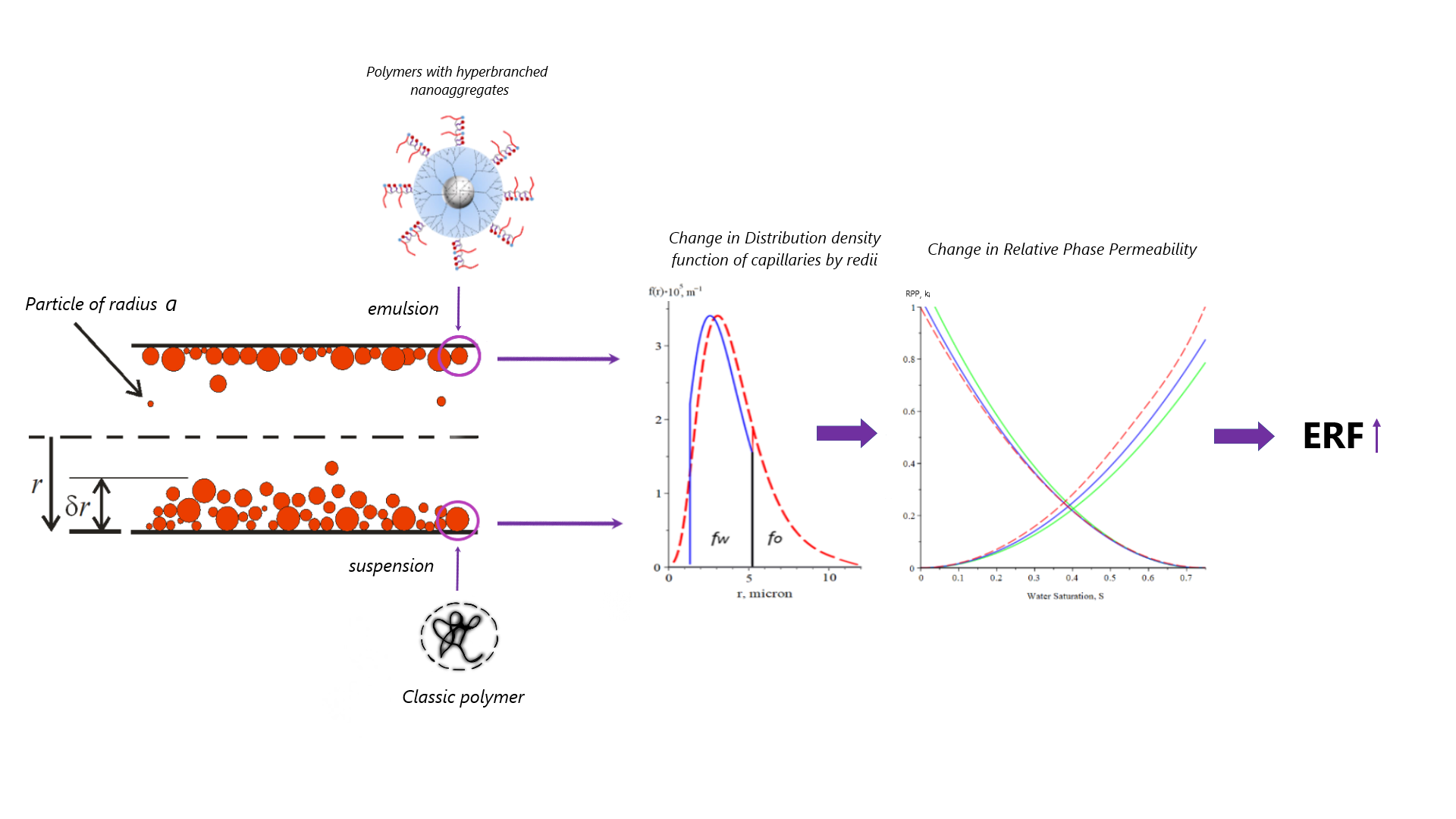
The study presents the results of comprehensive research on the efficiency of using polymer systems with nanoaggregates as oil displacement agents. Laboratory tests included experiments to determine the oil displacement coefficient on linear core models, as well as experiments to determine the oil recovery factor using parallel flow tubes of varying permeability, simulating the implementation of polymer flooding technology in stratified-heterogeneous oil-saturated reservoirs. The results of hydrodynamic studies using parallel flow tubes with polymer systems containing nanoaggregates demonstrated a significantly greater redistribution effect of filtration flows compared to traditional polymer solutions. The theoretical modeling of the polymer flooding process was conducted based on a percolation-hydrodynamic model, accounting for the specific flow characteristics of polymer systems with nanoaggregates in a porous medium. A comparison of the theoretical results with laboratory test outcomes showed good agreement.
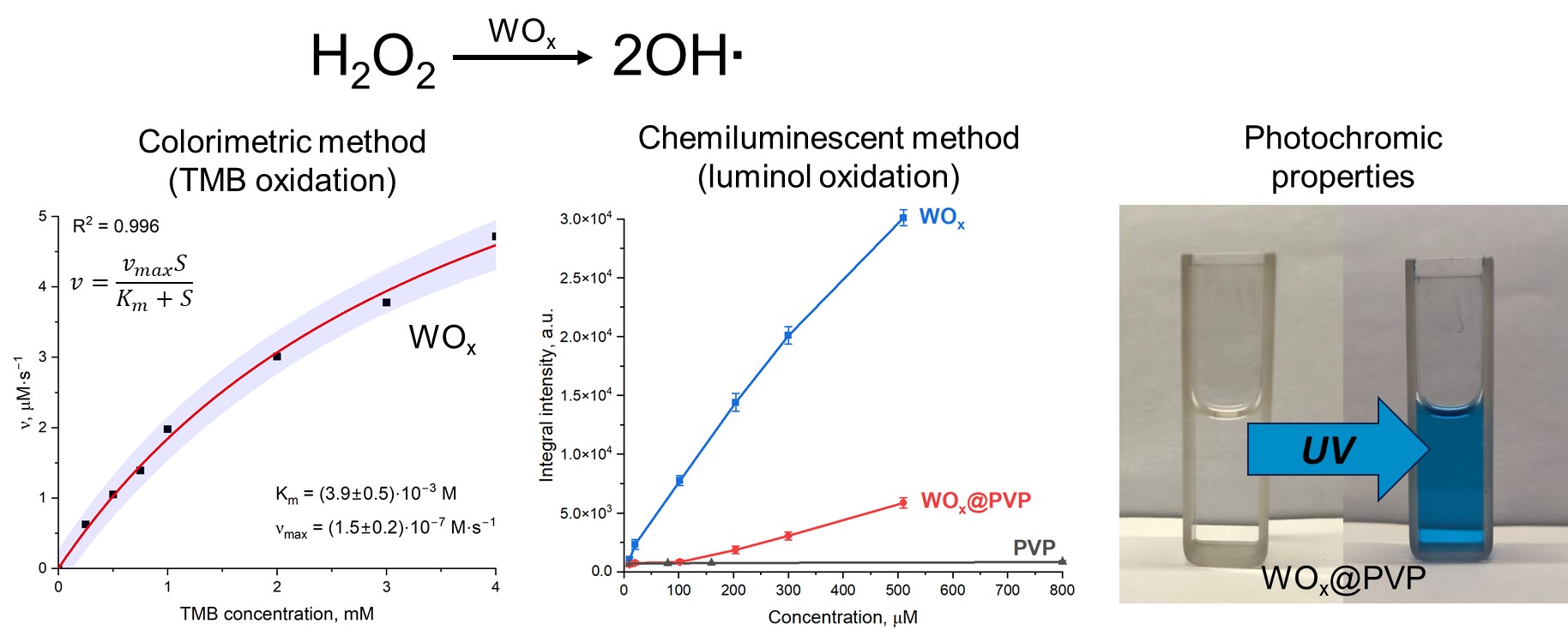
In this work, peroxidase-like activity of ultrasmall tungsten oxide nanoparticles including those stabilized with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was assessed using two independent approaches: the colorimetric method, which is based on the analysis of 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) oxidation, and the luminolenhanced chemiluminescence method. It was demonstrated that bare tungsten oxide nanoparticles effectively catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. In turn, the PVP-stabilized nanoparticles possess lower catalytic activity, which can be attributed to a decrease in the number of available active centres on the nanoparticle surface.
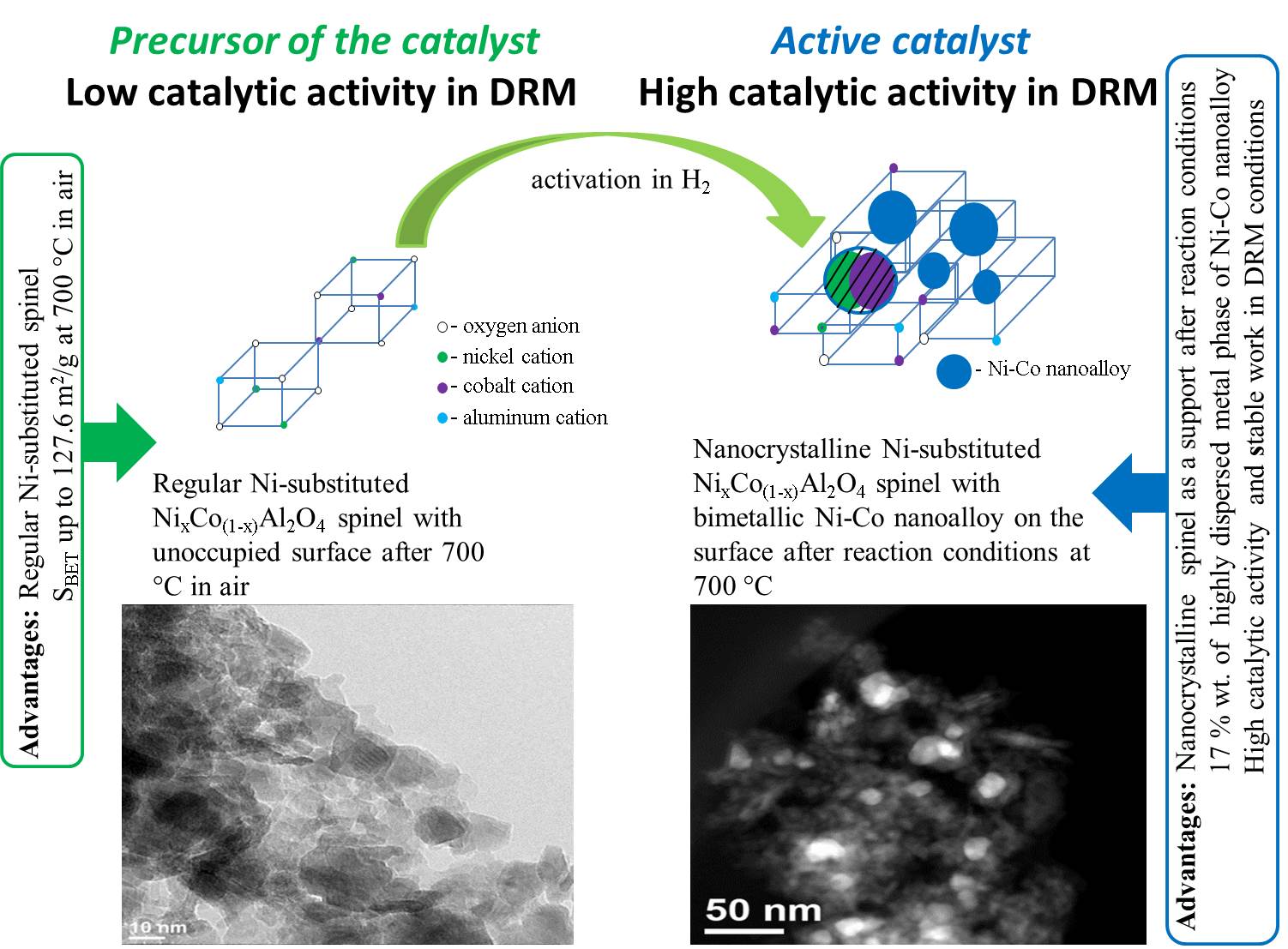
On the first step using co-precipitation method from Ni-, Co-, Al-containing solution a precipitates with a general composition of NixCo1-xAl2O4 (x = 0:1 – 0:5) were prepared. Calcination the obtained precipitates at 700 C in air makes the precursors of catalysts for DRM with a stable spinel-like framework in which nickel and cobalt species are homogeneously incorporated. Reduction of the precursors at 700 C in H2 and further work under reaction medium leads to formation of the active phase which represents by the ensembles of Ni–Co alloy nanoparticles located on the surface of nanostructured spinel. The effect of the catalysts composition on catalytic properties in DRM was investigated. The high and stable catalytic activity of representative samples in DRM conditions with extremely short contact time ( = 30 ms) due to the formation of 17 – 18 wt. % active phase which represents highly dispersed (3 – 4 nm) Ni–Co alloy nanoparticles stabilized on the spinel with nanocristalline structure.
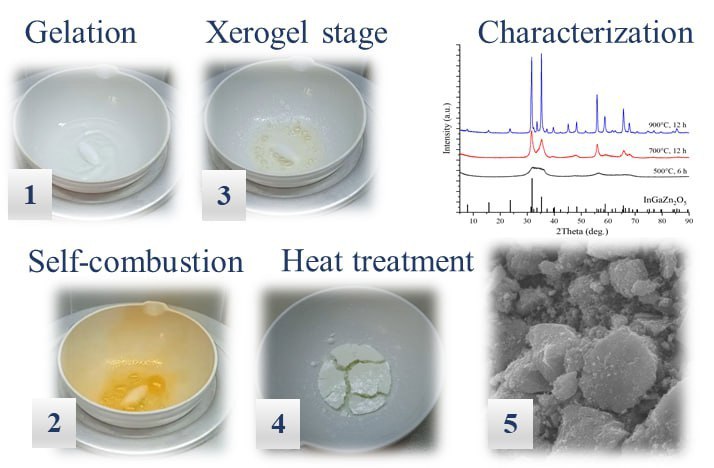
The study for the first time presents a method for producing indium-gallium-zinc oxide InGaZn2O5 using the nitrate-tartrate complex decomposition method. The material is characterized by X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy, IR- and UV-spectroscopy. It has been established that the use of tartaric acid as a precursor already at a temperature of 500 C leads to the formation of a single-phase homogeneous material consisting of nanocrystalline particles in the form of micrometer agglomerates. The proposed method for producing nanoparticles can be used in the future to produce semiconductor inks based on IGZO. KEYWORDS indium-gallium-zinc oxide, InGaZn2O5, IGZO, nanoparticles.
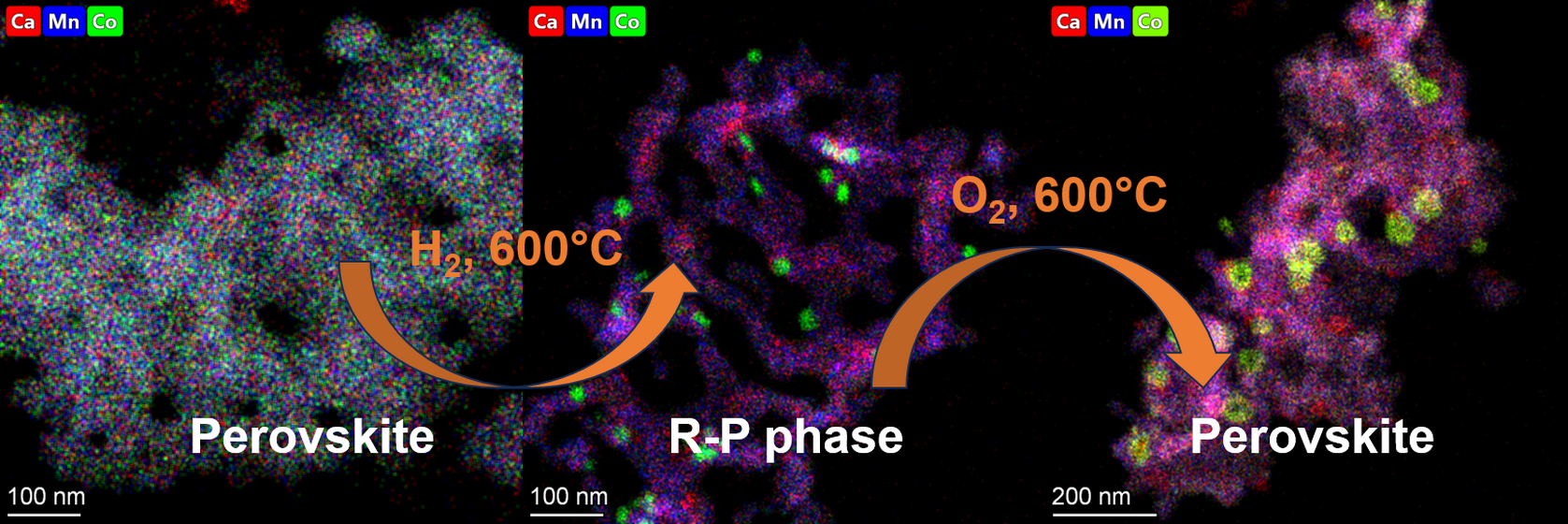
The structural and phase transformations of La0:6Ca0:4Mn1-yCoyO3±δ (y = 0:2 – 0:6) solid solutions in a reducing atmosphere were studied using in situ XRD and HRTEM methods. Experiments have shown that heat treatment in a reducing atmosphere of H2 leads to the partial decomposition of solid solutions, the nature of which differs from decomposition in an inert atmosphere. In the case of a system with a hydrogen-containing atmosphere, the heterogeneous reduction of the structure leads to the formation of an orthorhombic phase of LaMnO3-based perovskite with disordered vacancies, an additional phase of ordered Rudlesden–Poppertype perovskite based on La2CoO4 and Co and Ca2MnO4 nanoparticles on the surface of perovskite. In an environment with excessive partial oxygen pressure for the reduced sample, the reverse phase transition of the Rudlesden–Popper phase into the perovskite phase occurs.
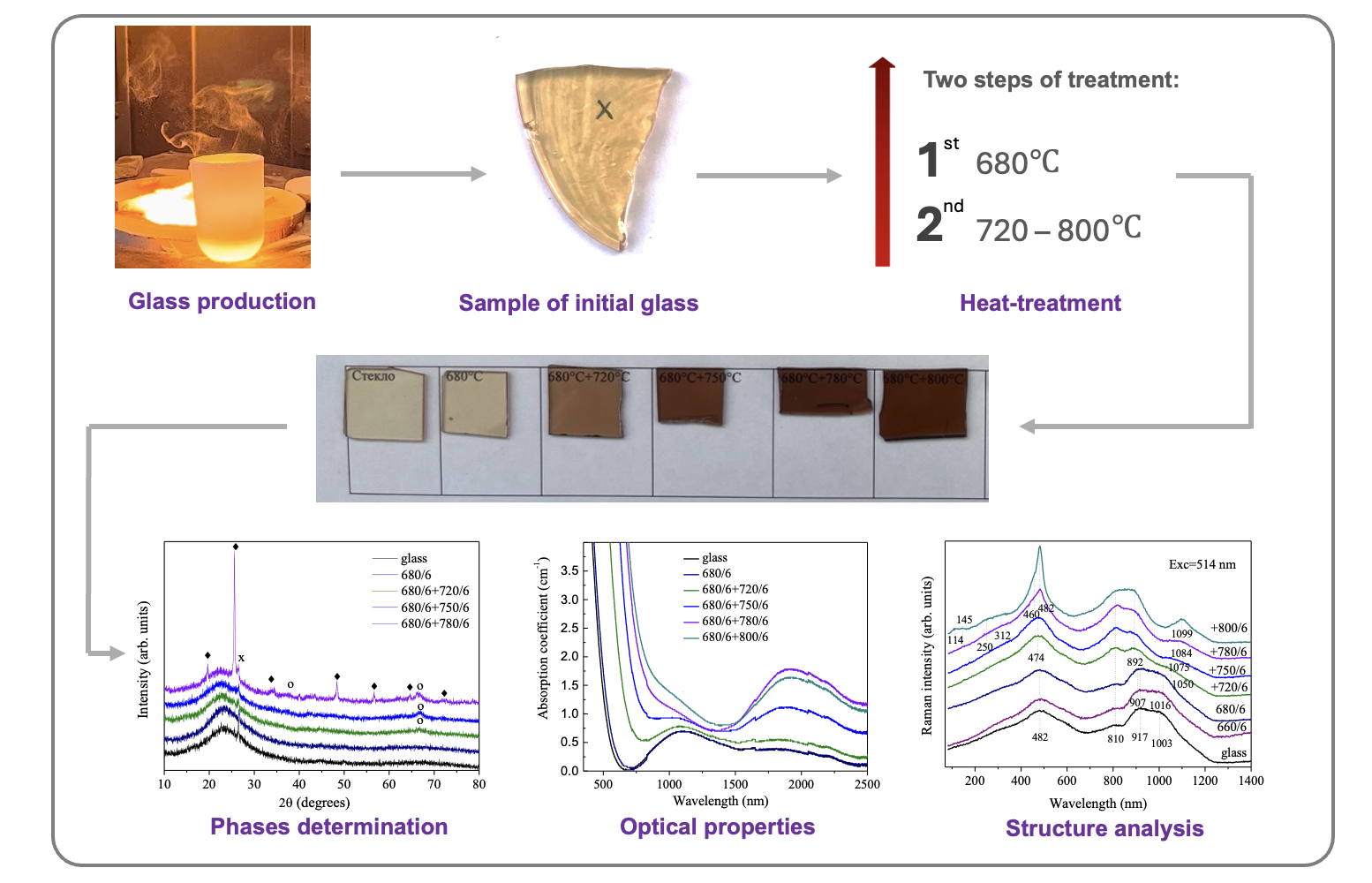
This study explores optical tuning of nanostructured transparent lithium aluminosilicate glassceramics nucleated by titania and doped with Fe2+ ions. The glass was melted at 1620 C and heat-treated between 660 C and 800 C, yielding nanocrystals of -Al2O3 (2 – 23 nm) and -quartz solid solutions (8 – 40 nm). Fe2+ ions in octahedral coordination in the initial glass are responsible for absorption in the 1000 – 1400 nm range. Tetrahedrally coordinated Fe2+ ions in -Al2O3 are responsible for absorption at 1550 – 2300 nm. Crystallization of -quartz solid solutions leads to decreasing the -Al2O3 fraction and corresponding decrease of absorption at 1550 – 2300 nm. Differential scanning calorimetry, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman and optical spectroscopy reveal the relationship between heat-treatment regimes, crystalline phase development, and optical performance, highlighting the potential of Fe2+-doped LAS glass-ceramics for advanced photonic applications. The glass-ceramics exhibit customizable optical properties, promising for saturable absorbers in passive Q-switching lasers.
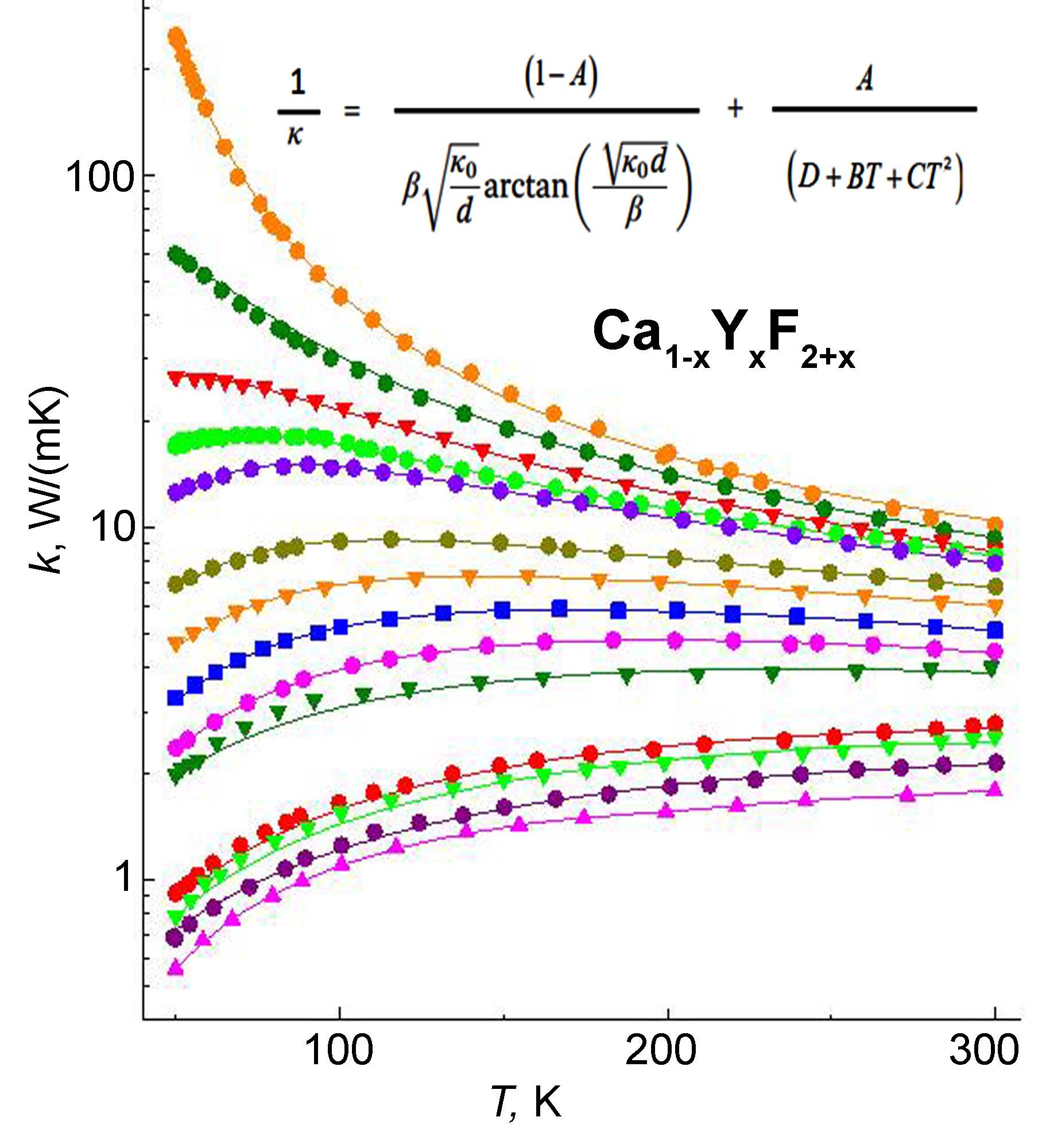
A series of Ca1-xYxF2+x solid solution x = 0:0005, 0:003, 0:007, 0:013, 0:02, 0:03, 0:04 single crystals were grown using the Bridgman method. The thermal conductivity of single crystals was measured using the absolute method of longitudinal heat flow in the range of 50 – 300 K. With an increase in the concentration of yttrium fluoride in the solid solution, a transition is observed from the temperature dependence characteristic of single crystals to a monotonically increasing one with increasing temperature, which is characteristic of disordered media. This behavior is associated with the scattering of phonons on nanosized clusters of defects present in the solid solution. Within the framework of a two-component model, including a superposition of thermal resistance coefficients from ordered and disordered media, a system of equations was obtained that provides a quantitative description of the experiment.
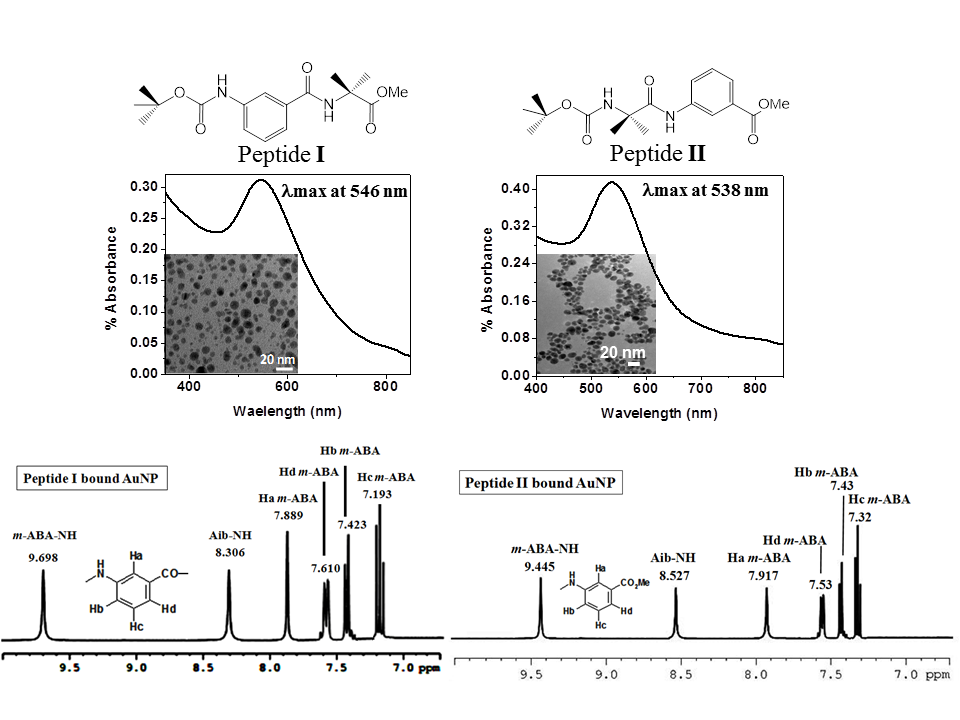
It has been observed that two isomeric protected dipeptides which show altered nano-morphologies under similar conditions but behave unaltered to form stable gold nano-particles (AuNPs) having similar shape and size; whereas both the peptides showed fluctuating bio-compatibility but after conjugation with AuNP they show stable bio-compatibility. These gold nano conjugates are very stable, even up to 2 months the AuNPs showed no change in size or shape. Using a straightforward and reproducible one-pot synthetic technique, we were able to produce stable biocompatible gold nanoparticles using two isomeric protected dipeptides.
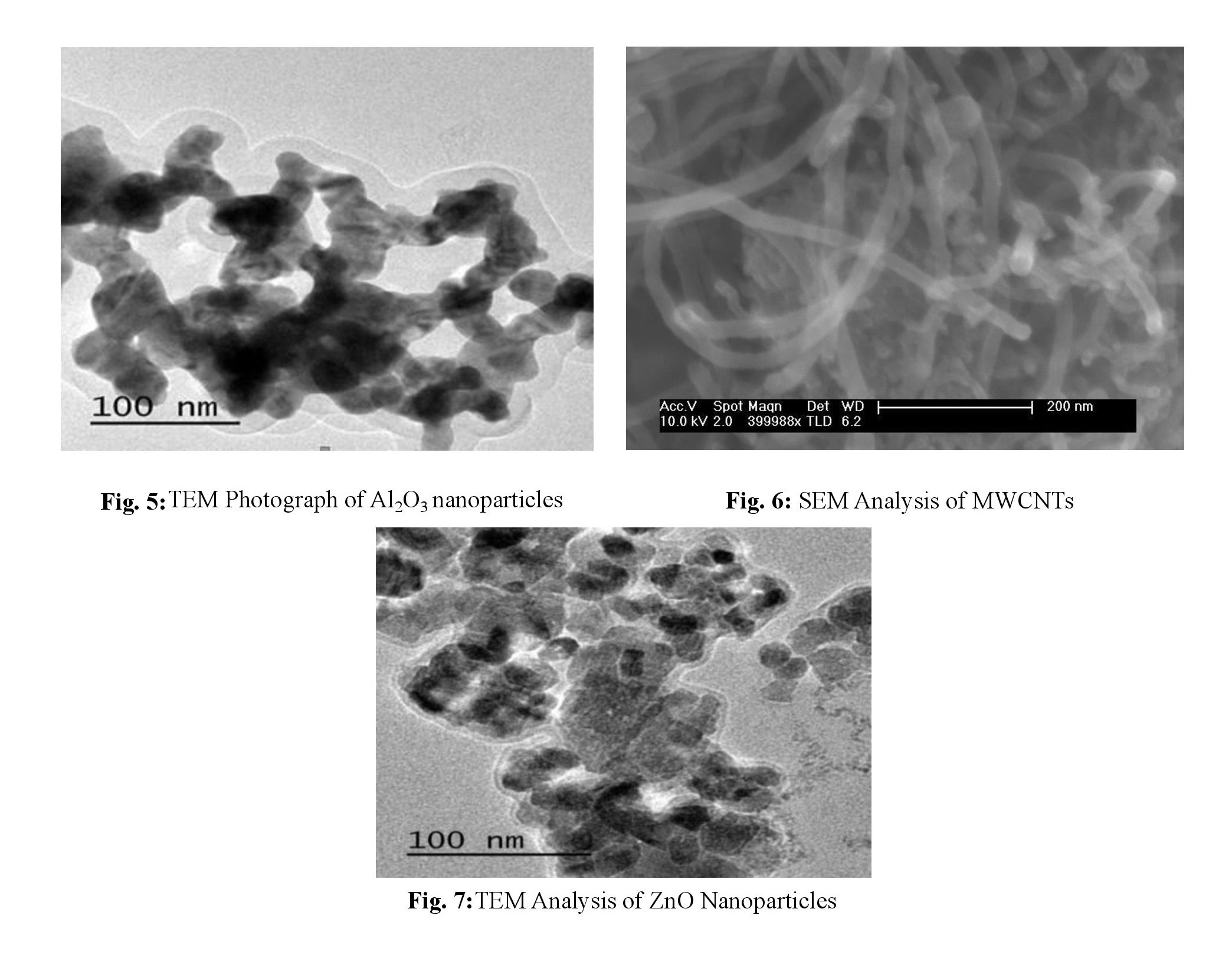
This research paper aims to present experimental findings on important thermophysical properties such as thermal conductivity, viscosity, and density of selected nanofluids. Ethylene glycol is considered as the base fluid, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, zinc oxide, aluminum oxide nanoparticles are used in the present study. The nanopartices are chosen due to their remarkable thermal and physical properties. The results indicate that the thermal conductivity of the ethylene glycol increases in a linear manner when Al2O3, MWCNT, and ZnO nanoparticles are dispersed in the base fluid. Particle concentration varied from 0.1 to 0.3 vol %. The highest increment noted is 39 % at the highest concentrations. The viscosity of the nanoparticles containing ethylene glycol improves with temperature, and Al2O3 and MWCNT have the highest improvement. Thus, the density analysis shows that the nanofluids with 0.1 and 0.2 vol % nanoparticles dispersed in ethylene glycol and having 0.2 vol % have less fluctuation compared to nanofluids with 0.3 vol %, which may affect various characteristics of the coolant considerably. This shows how nanofluids can help in managing the thermal conditions of automobiles and electronic gadgets.
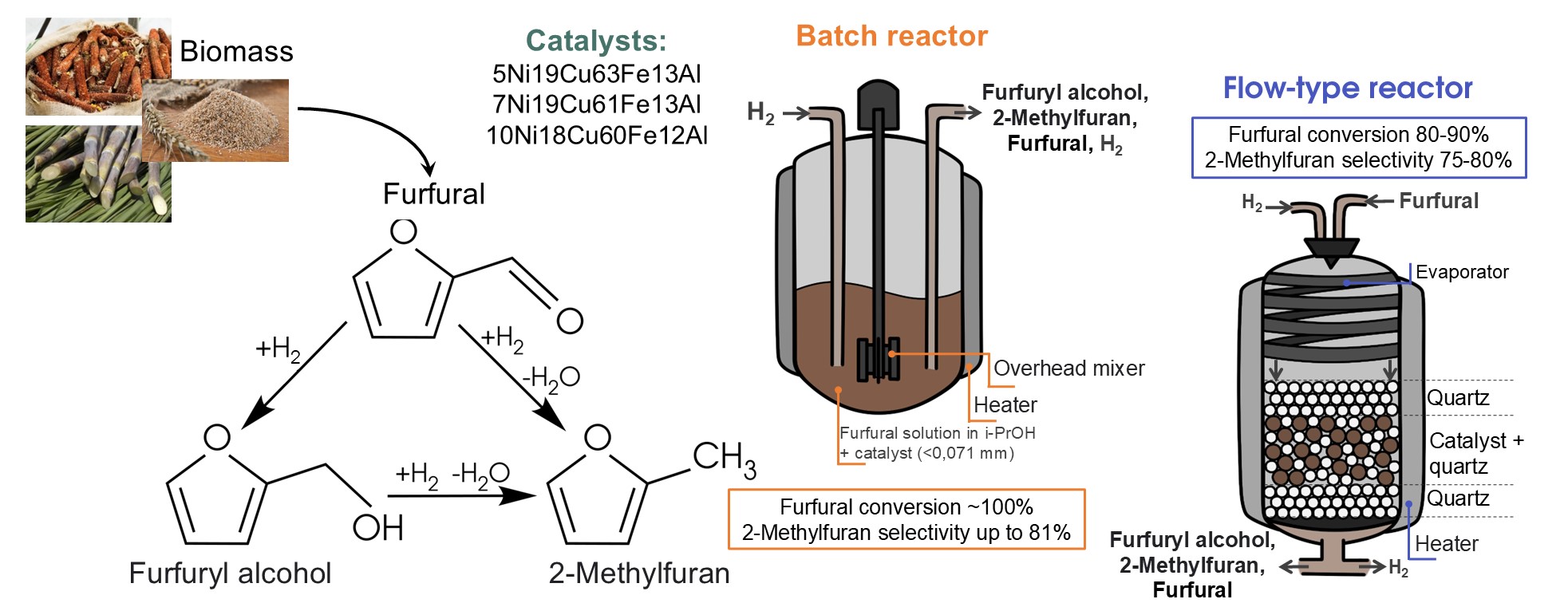
In this work, nickel-copper-containing alloy catalysts with different contents of nickel oxide were prepared and used in the furfural hydroconversion to 2-methylfuran and furfuryl alcohol. The most active catalyst (7Ni19Cu61Fe13Al) was chosen. We selected the reaction conditions, providing a high yield of 2- methylfuran (81 wt. %) at 100 % furfural conversion in a batch reactor: T = 200 C, P(H2) = 5:0 MPa, reaction time 4 h. The selected catalyst was studied by a complex of physicochemical methods; we determined the phase and surface composition, the morphology of the active component, and the possible cause of catalyst deactivation during the reaction due to the irreversible sorption of reactants and reaction products, as well as their polymeric structures on the catalyst surface. We have demonstrated the possibility of obtaining 2- methylfuran for the 7Ni19Cu61Fe13Al catalyst with a selectivity of 70 % at 87 % conversion of furfural in a flow-type reactor without solvent at LHSV = 6 h-1, T = 200 C, P(H2) = 5:0 MPa.
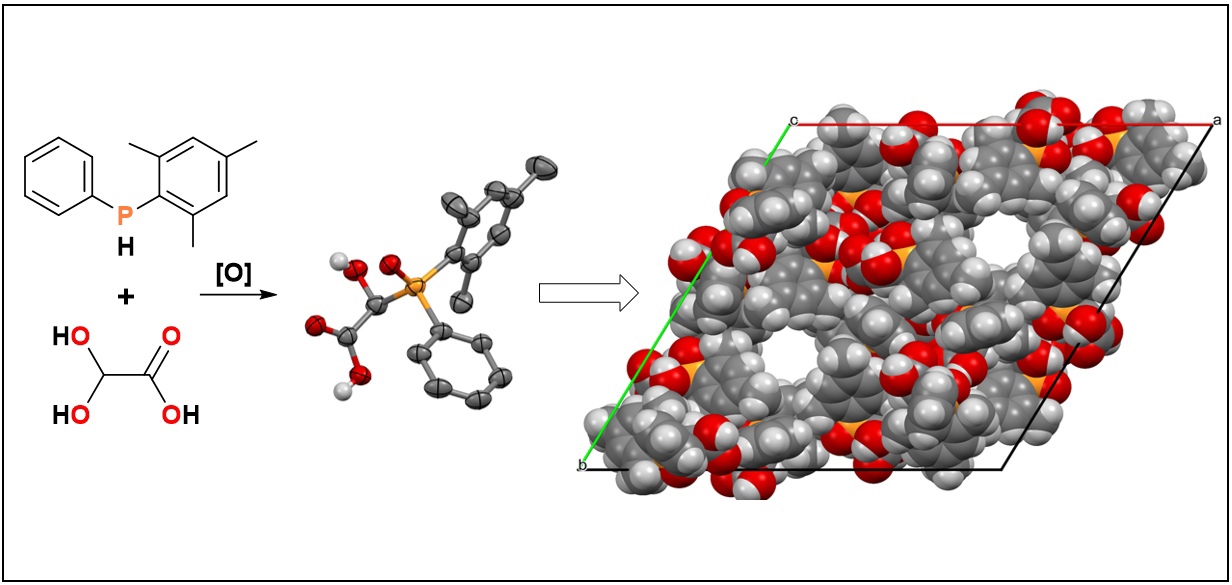
The reaction of glyoxylic acid monohydrate with mesityl(phenyl)phosphine in air led to the formation of mesityl(phenyl)phosphine oxide glycolate. The synthesized mesityl(phenyl)phosphine oxide glycolate has been characterized by various analytical methods including X-ray crystal structure analysis. The analysis of intermolecular interactions in the crystal revealed interesting modes of the noncovalent bonding between pairs of molecules. These intermolecular interactions cause the formation of one-dimensional cylindrical channels with diameter of 1 nm (10 A° ) and provide the crystal with the properties of precise nano-sized crystalline porous material which can be served as the component for precise nanofiltration membranes improving the properties of amorphous polymers which suffer from disordered pore structures and reduced selectivity towards separating molecules.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)