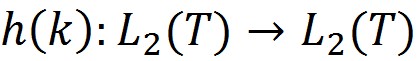The Hamiltonian h of the system of two quantum particles moving on a 3-dimensional lattice interacting via some attractive potential is considered. Conditions for the existence of eigenvalues of the two-particle Schrödinger operator hμ(k), k∈T3, μ∈R associated to the Hamiltonian h, are studied depending on the energy of the particle interaction μ∈R and total quasi-momentum k∈T3 (T3 - three-dimensional torus).
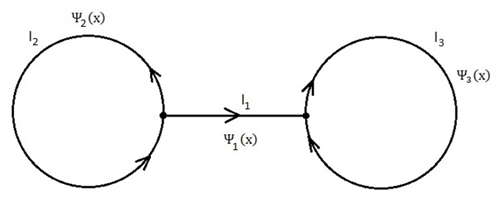
The spectral problems for two types of quantum graphs are considered. We deal with star-like graph and a graph consisting of two rings connected through a segment. The spectral gap, i.e. the difference between the second and the rst eigenvalues of the free Schro¨ dinger operator, is studied. The dependence of the gap on the geometric parameters of the graph is investigated. Particularly, it is shown that the maximal gap is observed for the symmetric quantum graph.
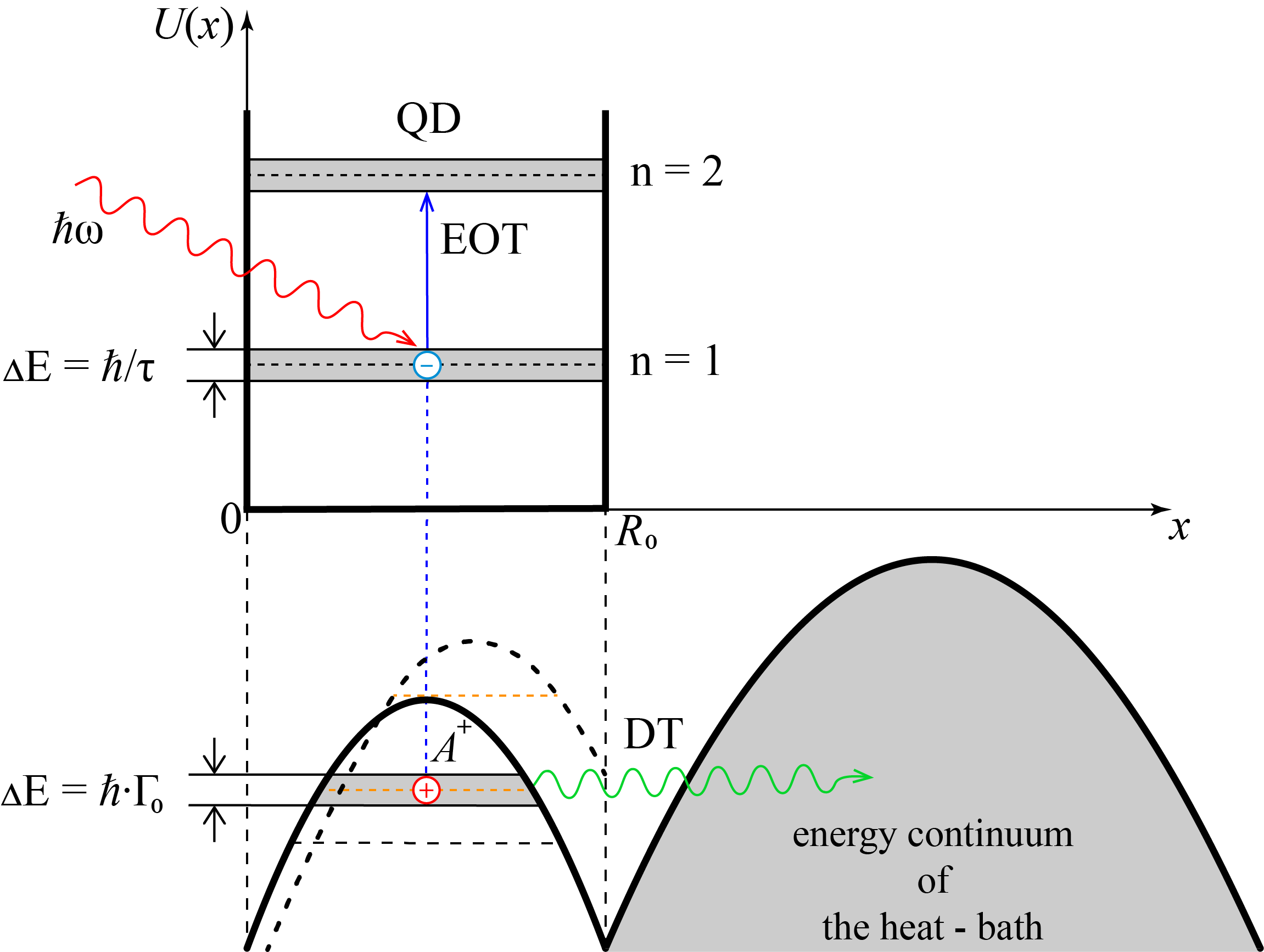
Effect of tunneling decay for the quasi-stationary A+-state, in an impurity complex A+ + e (a hole, localized on a neutral acceptor, interacting with an electron, localized in the ground state of a quantum dot) on the photodielectric effect, associated with the excitation of impurity complexes A+ + e in a quasi-zero-dimensional structure, has been studied in the zero-radius potential model in the one-instanton approximation. Calculation of the binding energy of a hole in an impurity complex A+ + e was performed in the zero radius potential model in the adiabatic approximation. It is shown that as the probability of dissipative tunneling increases, the binding energy of a hole in a complex A+ + e decreases, which is accompanied by an increase in the effective localization radius of the impurity complex and, accordingly, an increase in the magnitude of the photodielectric effect. The spectral dependence of the photodielectric effect has been calculated in the dipole approximation taking into account the dispersion of the quantum dot radius. A high sensitivity of the magnitude of the photodielectric effect to such parameters of dissipative tunneling as the frequency of the phonon mode, temperature, and coupling constant with the contact medium, has been revealed.
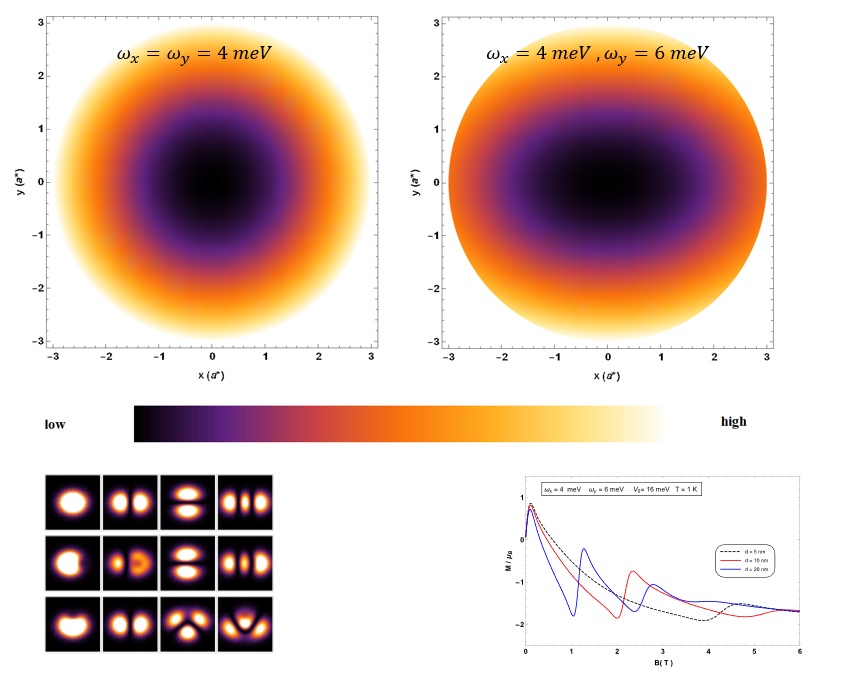
The Hamiltonian of a single electron trapped in a lateral quantum dot in the in uence of an acceptor Gaussian impurity has been solved using a variational wavefunction as a superposition of a product of eigenfunctions of the harmonic oscillator in x and y coordinates. The effects of Gaussian impurity parameters on the system’s spectra have been investigated as a function of the magnetic eld. Furthermore, the electron probability has been displayed to investigate the impurity position effect on the energy levels. As a second step, the calculated energy spectra were utilized to compute and visualize the system’s magnetic properties in the presence of the magnetic eld and impurity. The obtained energy spectra show level crossings in the presence of acceptor impurity, which causes oscillations in the magnetic susceptibility and magnetization curves, resulting in an exciting diamagnetic-paramagnetic phase transition.
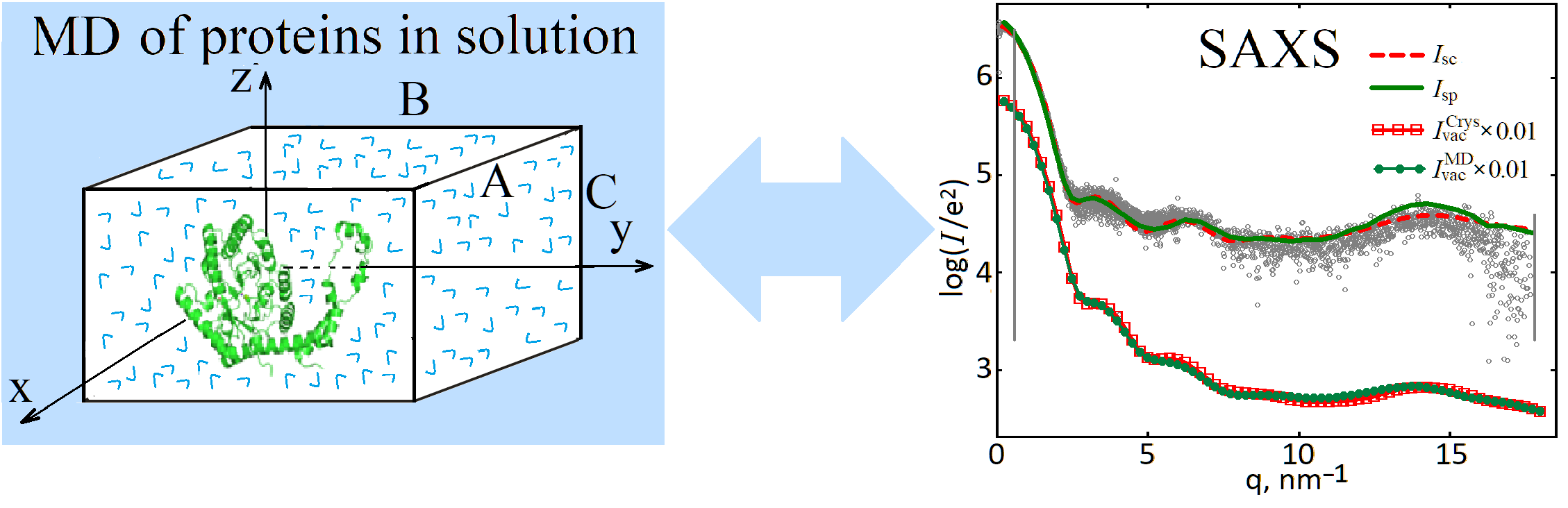
The SASPAR program for calculation of SAXS of proteins in solution uses trajectories of molecular dynamics (MD) and an explicit solvent model. The program allows one to take into account real interactions of solvent molecules both between each other and with the protein molecule. The previously developed SAS-CUBE program (the “cube method”) is also used, it assumes that the protein structures in crystal and in solution coincide, and the water surrounding the proteins is considered as a homogeneous continuum. Using these programs, SAXS curves were calculated for 18 proteins of different molecular weights and then compared with one another and with the corresponding experimental scattering curves. “Vacuum” SAXS curves (i.e., without taking into account the surrounding water) were also calculated for each protein for two approaches: a) based on the coordinates of protein atoms in crystal and b) based on the coordinates of protein atoms for each MD frame with further averaging of the intensities from all the frames. 1) It was shown that for the 14 single-domain proteins considered, the “vacuum” scattering curves calculated by two methods coincide well for almost each protein. Hence, the structure of the studied proteins in a solution is similar to their structure in a crystal and, therefore, the presence of the surrounding water molecules does not alter the protein structure itself signi cantly. The SASPAR- and SASCUBE-curves coincide well only in two cases (i.e., water is only slightly structured near the protein surface), but in the other cases these curves are markedly different, which indicates the structuredness of the water near the protein surface, although to a different extent. 2) It was shown that for the 4 multi-domain proteins considered, their “vacuum” scattering curves, calculated with the two methods indicated above, differ noticeably, which is an evidence that their crystalline and “water” struc- tures are different. It was also shown that the most of the calculated curves coincide well with the experimental ones.
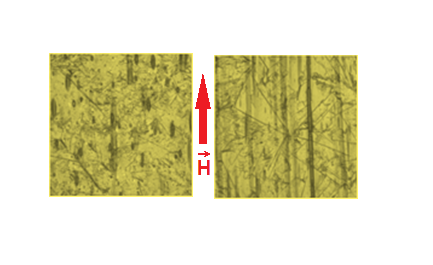
In this work, nanostructured composites in the form of polymer matrices with inclusions of magnetic particles were studied by the method of static scattering of laser radiation. The particles were embedded into polyvinyl alcohol and epoxy resin from magnetite -containing ferro uid. It is shown that in a magnetic eld they form a system of extended aggregates acting as light scatterers and established that optical technique based on this provides important information about the properties of such nanomaterial.
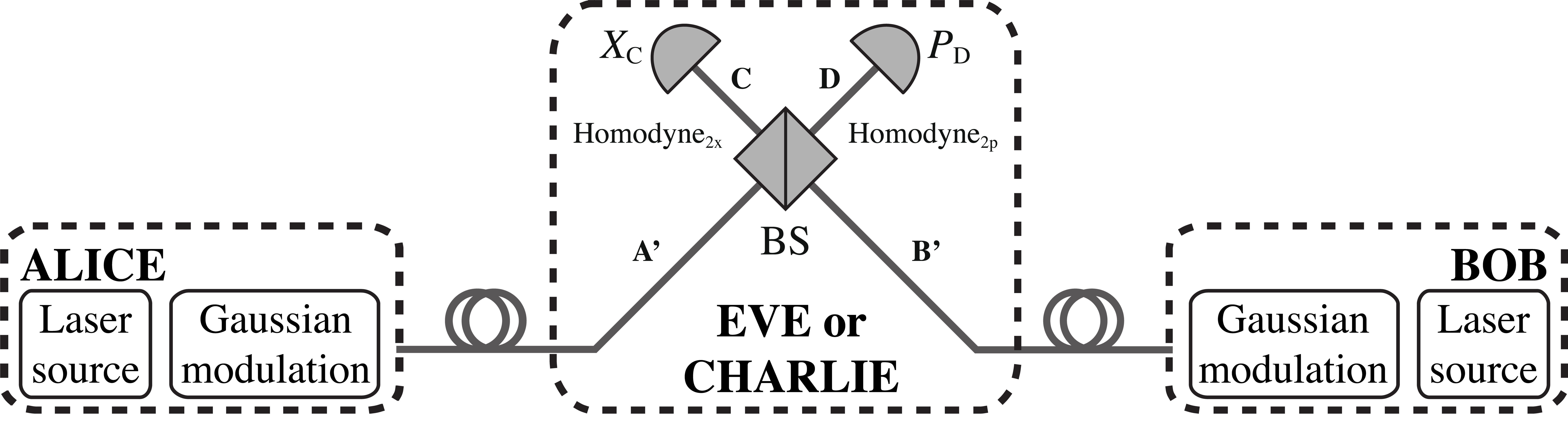
The objects of study of this paper are quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols and systems, in particular, continuous variable (CV) ones with untrusted devices (measurement devices or light sources). The present work is devoted to the consideration of such systems, namely, device-indepentent CV-QKD, and to the discussion of their performance.
The eigenvalues of the complete commuting set of self-adjoint operators determine the classi cation of states. We construct a classi cation for the image of the Jordan-Schwinger mapping of the su (2) algebra. We use the ladder operator approach to construct a canonical basis of irreducible representations and de ne the self-adjoint operators of the complete commuting set.
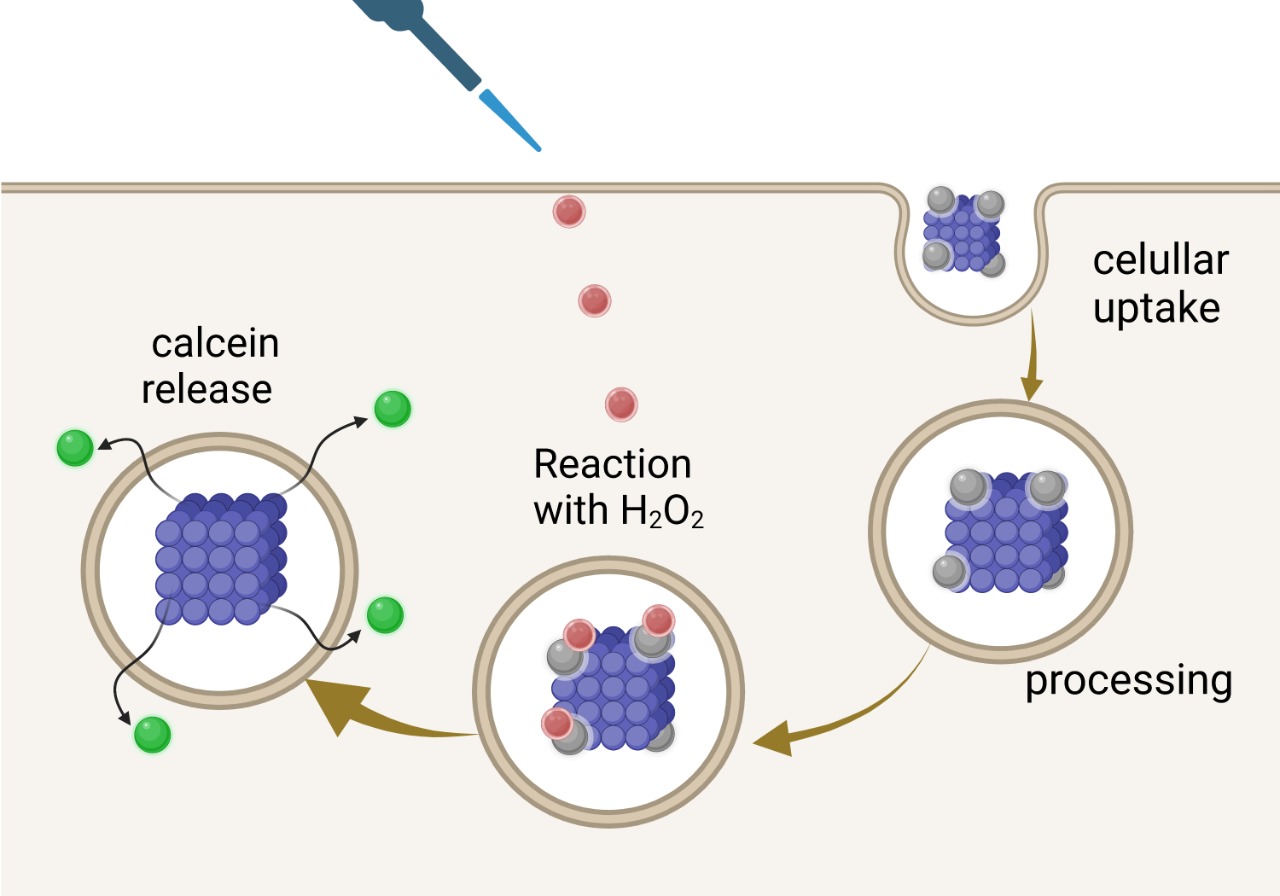
We studied cerium oxide-calcein nanoconjugate, which is capable of providing intracellular detection and simultaneous inactivation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The synthesized nanoconjugate is easily uptaken by human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and demonstrates antioxidant properties, protecting cells from H2O2-induced oxidative stress in vitro. Cerium oxide-calcein nanoconjugate neutralizes hydrogen peroxide, meanwhile releasing brightly fluorescent calcein from its surface, which is easily detected by fluorimeter or fluorescent microscope. This nanoconjugate is biocompatible and non-toxic to MSCs in concentrations below 2 mM. Such a theranostic agent can be considered as a promising tool for tracking the redox status of human MSCs in vivo.
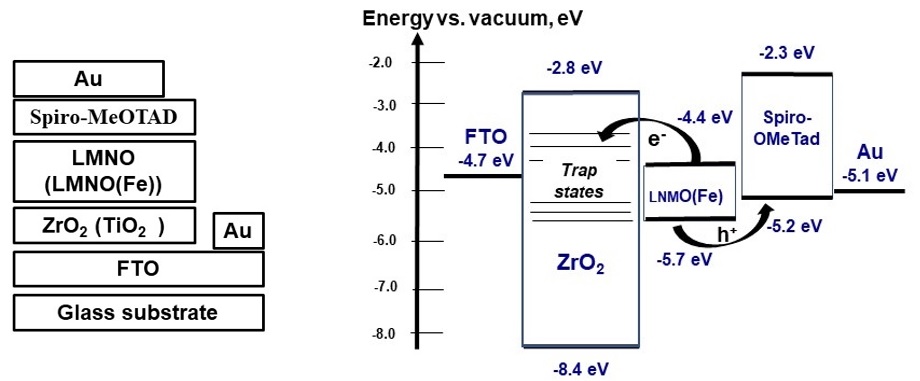
Nanopowders of La2Ni0.8Fe0.2MnO6 and La2NiMnO6 double perovskite oxides were synthesized by glycine-nitrate combustion method. The obtained materials were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and optical measurements. Thin nanostructured layers based on the prepared materials were used as light absorbing layers for fabrication of inorganic perovskite solar cells (PSCs). Electron transport layers for the PSCs were prepared using TiO2 and ZrO2 nanostructured layers. The best performance of 3.7 % under AM1.5G illumination was obtained for the PSC structure glass/FTO/ZrO2/La2Ni0.8Fe0.2MnO6/Spiro-MeOTAD/Au.
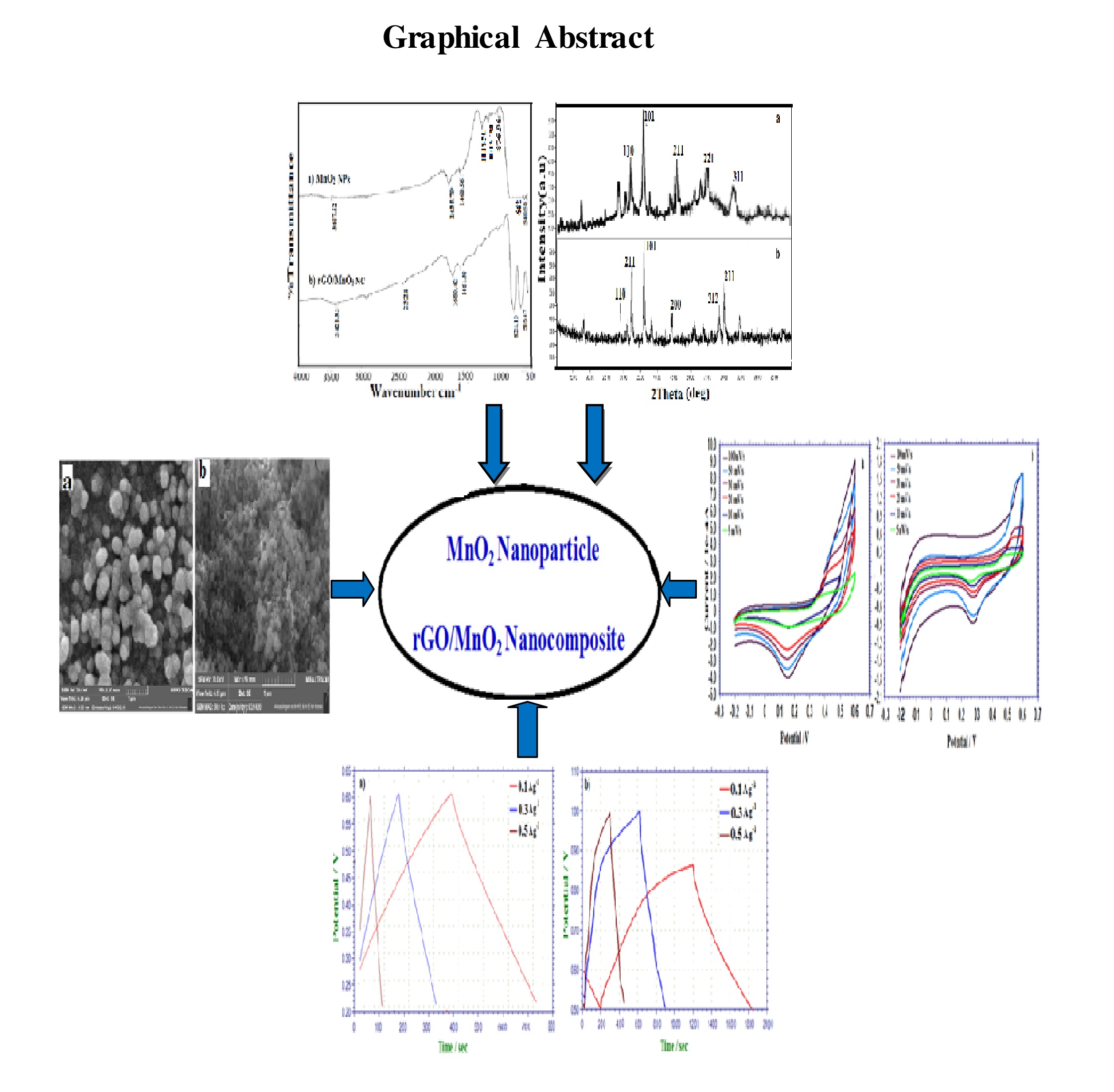
In this study, we improved the capacitance of carbon based reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and metal oxide based MnO2 by preparing nanocomposites of rGO/MnO2 nanocomposite using chemical synthesis method. The prepared nanoparticles and nanocomposites are characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, XRD, PL spectroscopy and FESEM with EDAX spectroscopy. FTIR studies disclose the characteristic chemical bonding between the respective materials. The FESEM images demonstrate that the surface structure of rGO and MnO2 can be easily tuned by forming the composite of rGO/MnO2 materials leading to excellent process ability of the system. The super capacitive behaviors of nanocomposites are evaluated using cyclic voltammetry and galvanostatic charge-discharge techniques. The specific capacitance of rGO/MnO2 composite is high compared to that of MnO2 nanoparticle. In addition, impedance measurements of the MnO2 nanoparticles and rGO/MnO2 electrodes are executed proposing that the rGO/MnO2 composite electrodes are promising materials for super capacitor (186.6 Fg-1).
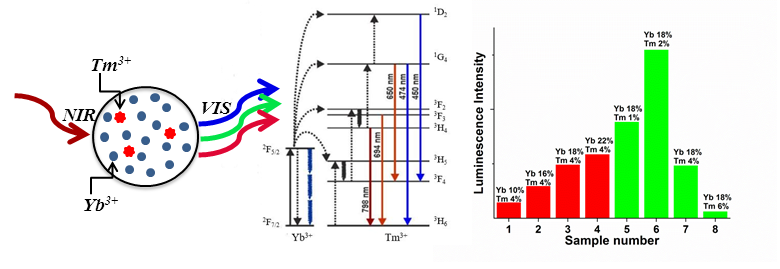
In this study, the impact of sensitizer and activator ions concentration on the intensity of up-conversion luminescence of nanoluminophores β-NaYF4:Yb3+/Tm3+ in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was investigated. Analysis of all luminescence spectral bands allows one to establish that the ratio of concentrations of ytterbium and thulium ions strongly effects on the luminescent properties of nanoluminophores. Increase of sensitizer concentration at constant activator concentration leads to an increase of the luminescence integral intensity. Optimal concentration of activators at fixed sensitizer concentration was determined: 2 mol.% for thulium and 18 mol.% for ytterbium. The sensitivity of each luminescence spectrum band to changes in the concentration of activators and sensitizers was explained by cross-relaxation processes in activator ions.
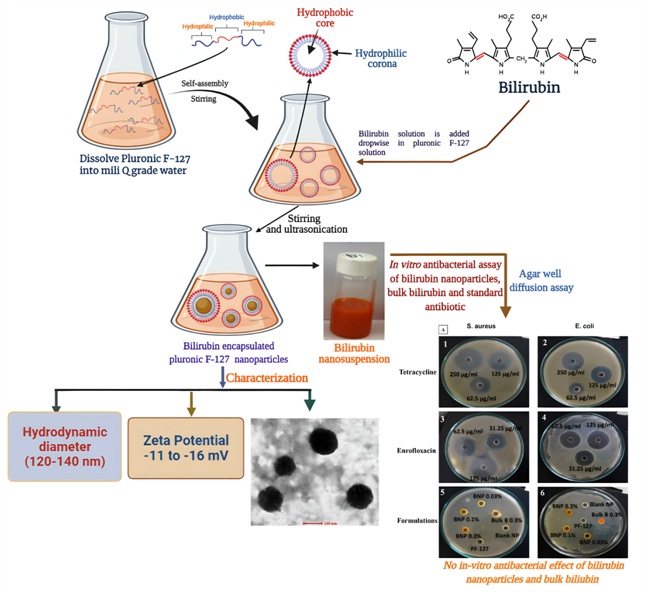
Antimicrobial resistance is a major emerging clinical and public health issue across the globe. Nanotechnology is an emerging eld and developing area of scienti c interest in the world. Earlier reports showed in vivo antibacterial activity of bilirubin. Therefore, in present study, bilirubin nanoparticles (BNP) were synthesized of ∼100 - 150 nm, spherical shape and negative charge. Antibacterial activity of BNPs at different concentrations (0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 %) was evaluated by agar well diffusion method against the gram-positive i.e. S. aureus and gram-negative i.e. E. coli bacteria. Tetracycline and enro oxacin used as positive control. Tetracycline and Enro oxacin at different concentrations exhibited zones of inhibition against both S. aureus and E. coli . However, BNPs as well as bulk bilirubin showed no in vitro antibacterial effect on S. aureus and E. coli , however, testing by broth method and at higher concentration as well as against other microorganisms can be explored in future.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)