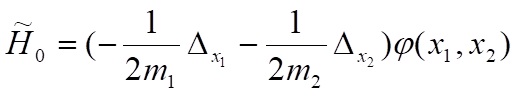MATHEMATICS
In the paper, a one-dimensional two-particle quantum system interacted by two identical point interactions is considered. The corresponding Schrödinger operator (energy operator) h" depending on " is constructed as a self-adjoint extension of the symmetric Laplace operator. The main results of the work are based on the study of the operator h". First, the essential spectrum is described. The existence of unique negative eigenvalue of the Schr¨odinger operator is proved. Further, this eigenvalue and the corresponding eigenfunction are found.
In the article, the uniqueness and solvability of one boundary value problem for a high-order equation with two lines of degeneracy with a fractional Riemann–Liouville derivative in a rectangular domain is studied by the Fourier method. Sufficient conditions for the well-posedness of the problem posed are obtained.
We consider the three-particle discrete Schrödinger operator H; (K); K 2 T3, associated with the three-particle Hamiltonian (two of them are fermions with mass 1 and one of them is arbitrary with mass m = 1= < 1), interacting via pair of repulsive contact potentials > 0 on a three-dimensional lattice Z3. It is proved that there are critical values of mass ratios = 1 and = 2 such that if 2 (0; 1), then the operator H; (0) has no eigenvalues. If 2 ( 1; 2), then the operator H; (0) has a unique eigenvalue; if > 2, then the operator H; (0) has three eigenvalues lying to the right of the essential spectrum for all sufficiently large values of the interaction energy.
PHYSICS
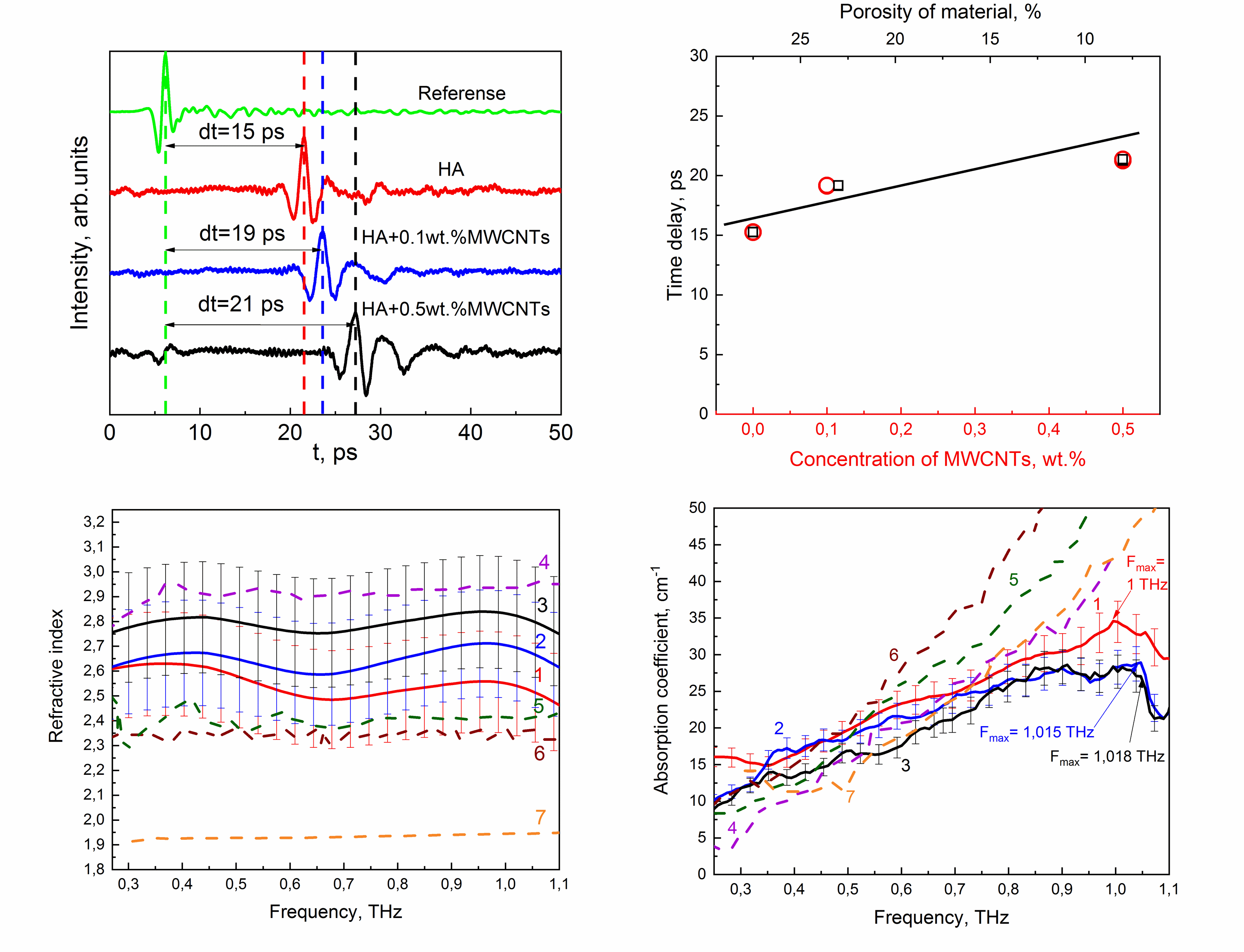
Optical properties of a ceramic biocomposite material based on hydroxyapatite (HA) with the additives up to 0.5 wt.% of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have been studied by terahertz timedomain spectroscopy in the frequency range 0.25 – 1.1 THz. It was found that the refractive index of the composite varies between 2.6 and 2.8 depending on the porosity of the material. The absorption coefficient decreases with increasing of MWCNTs concentration in the ceramic biocomposite. The values of the refractive index and the absorption coefficient of our ceramics close to those for cortical bone, dentine and enamel. The absorption curves show frequency peaks whose positions correspond to the macrocrystallite sizes. The size of macrocrystallites decreases with increasing concentration of MWCNTs, which leads to an increase in microhardness according to the Hall–Petch equation. The time delay of the terahertz signal through the sample increases for higher concentration of MWCNTs. This indicates that nanotubes embedded into the HA matrix fill the pores and decrease the area of the pore space, which increases the density of the ceramic composite and decreases its porosity.
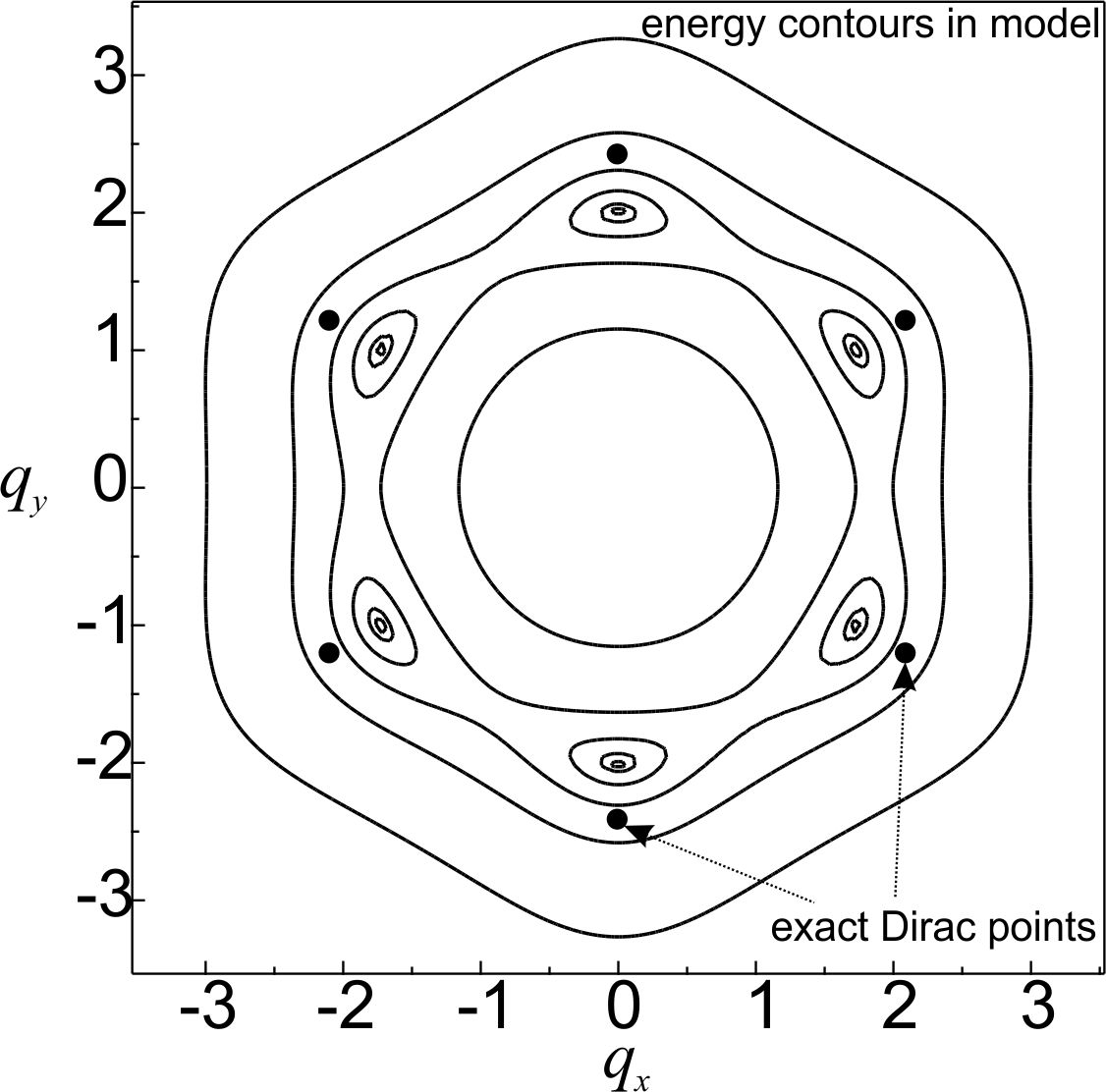
The continuous medium approximation to the description of a carbon material previously used to model the properties of spherical carbon shells of nanometer diameter. This approach is based on the transition from lattice operators to field operators. The present study verifies the given model evaluating the energy spectrum of electrons in a perfect flat carbon monolayer. An implementation of the Dirac cones within the continuous medium framework is demonstrated. Its are close to the positions of the vertices of the Brillouin zone for graphene. Increase of the Taylor series expansion order of field operators makes the result precise, and the approximate positions of the Dirac cones match the exact data for graphene.
In this article, the structures formed by the action of the magnetic field to magnetite nanoparticles, embedded into transparent matrices from ferrofluids, were analyzed. As the matrices polyvinyl alcohol and epoxy resin were used, however, the results obtained may be applicable to other media, for example, biological. The data of this work can be useful both for physical investigations of magnetic nanomaterials and for more practical studies, for instance, aimed at solving some environmental problems.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
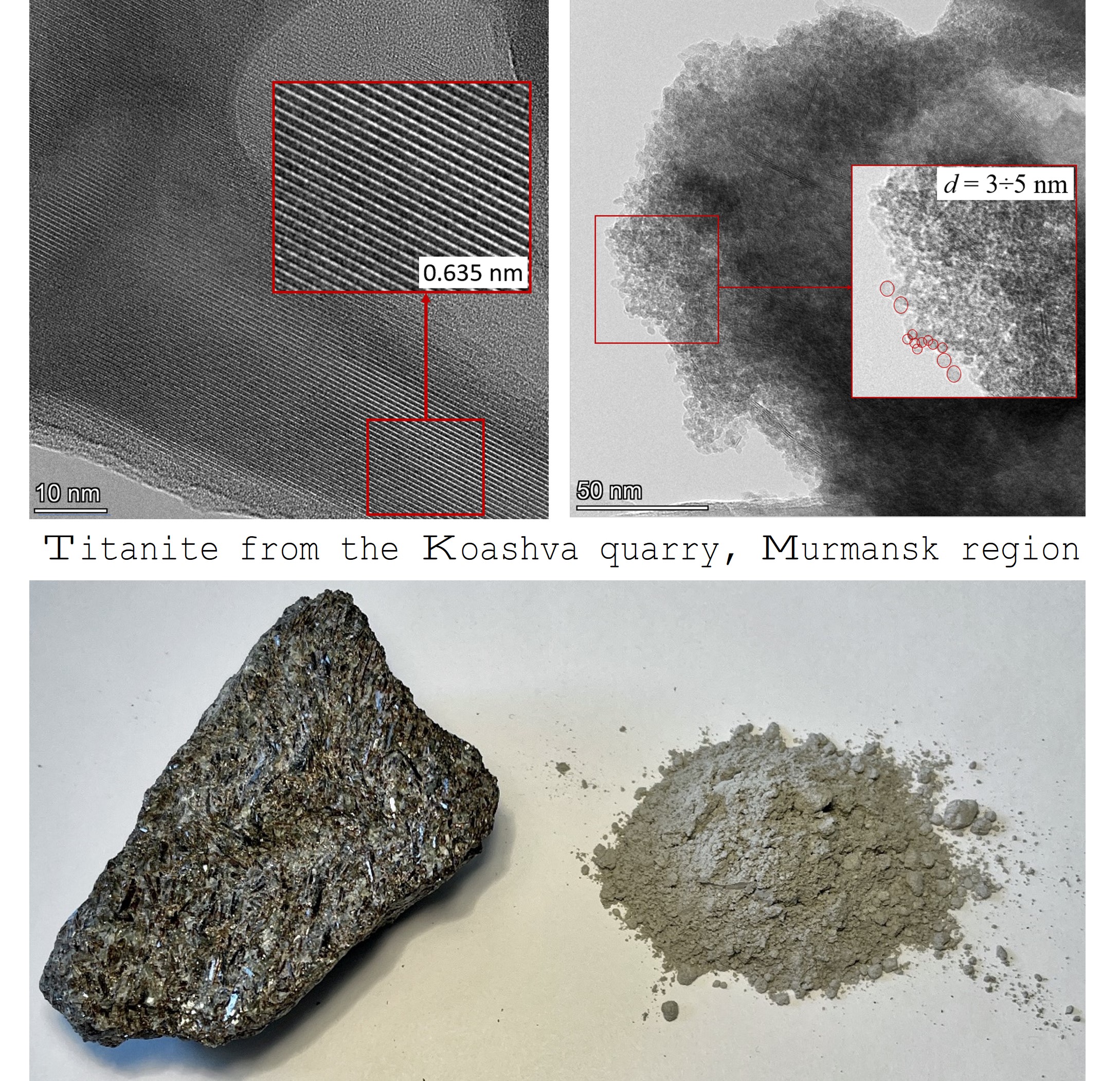
Nanoparticles in titanite CaTiSiO5 were found using transmission electron microscopy. Chemical and XPS analyzes of the nanoparticles were performed. The study showed the content of the elements Si, Ti and Ca to be about 19, 14 and 12 % in the ore, respectively, belonging to the titanite phase. Based on TEM images, it was established that titanite exhibits a disordered lamellar structure with a diameter of 3 to 5 nm and an interplanar distance of about 6.3 A° .
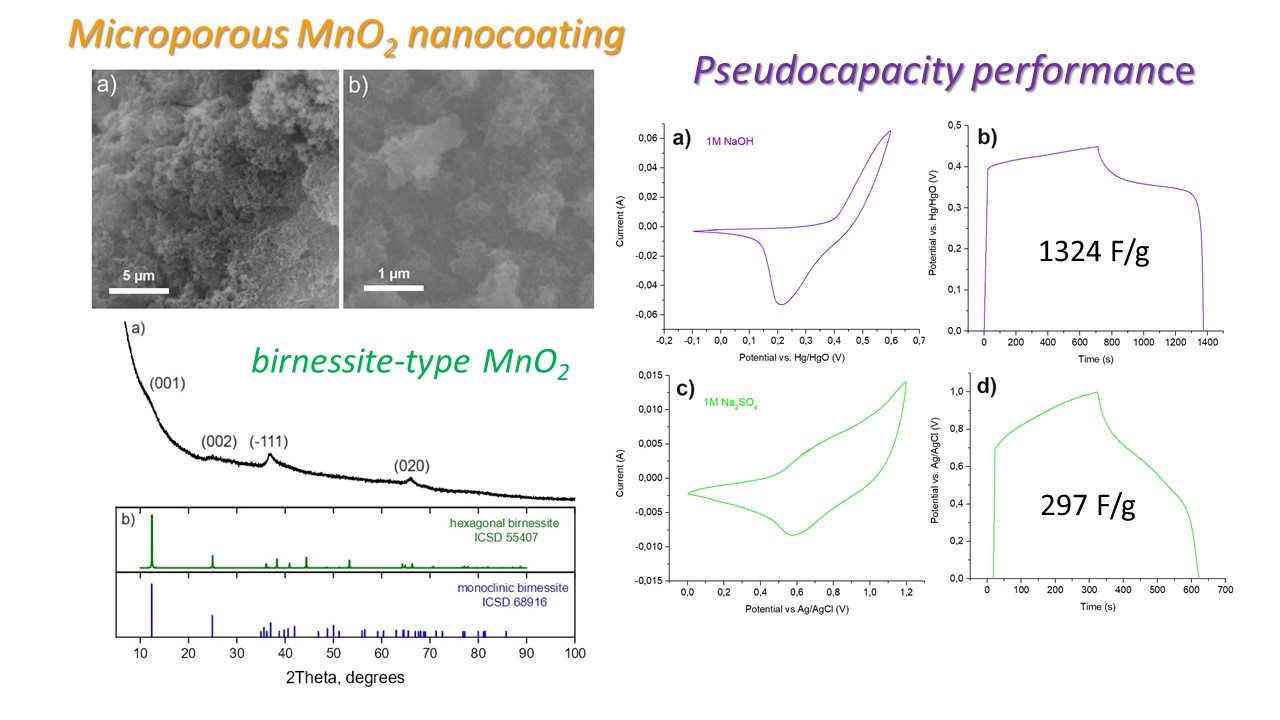
In present work the porous nanocoating of manganese oxide were obtained via successive ionic layer deposition from aqueous solutions of potassium permanganate and DMSO. The morphology, phase and chemical composition of the synthesized nanocoatings were characterized by XRD, SEM, EDX and Raman spectroscopy. The possibility of controlled changes in the morphology of the resulting compounds was demonstrated by changing the concentration of reagents and the number of processing cycles in order to obtain optimal electrochemical characteristics. Electrodes based on nickel foam and coated with films of porous manganese oxide showed high specific capacity (1324 and 297 F/g at a current density of 1 A/g in 1 M NaOH and 1 M Na2SO4, respectively), both in neutral and in aqueous alkaline electrolytes.
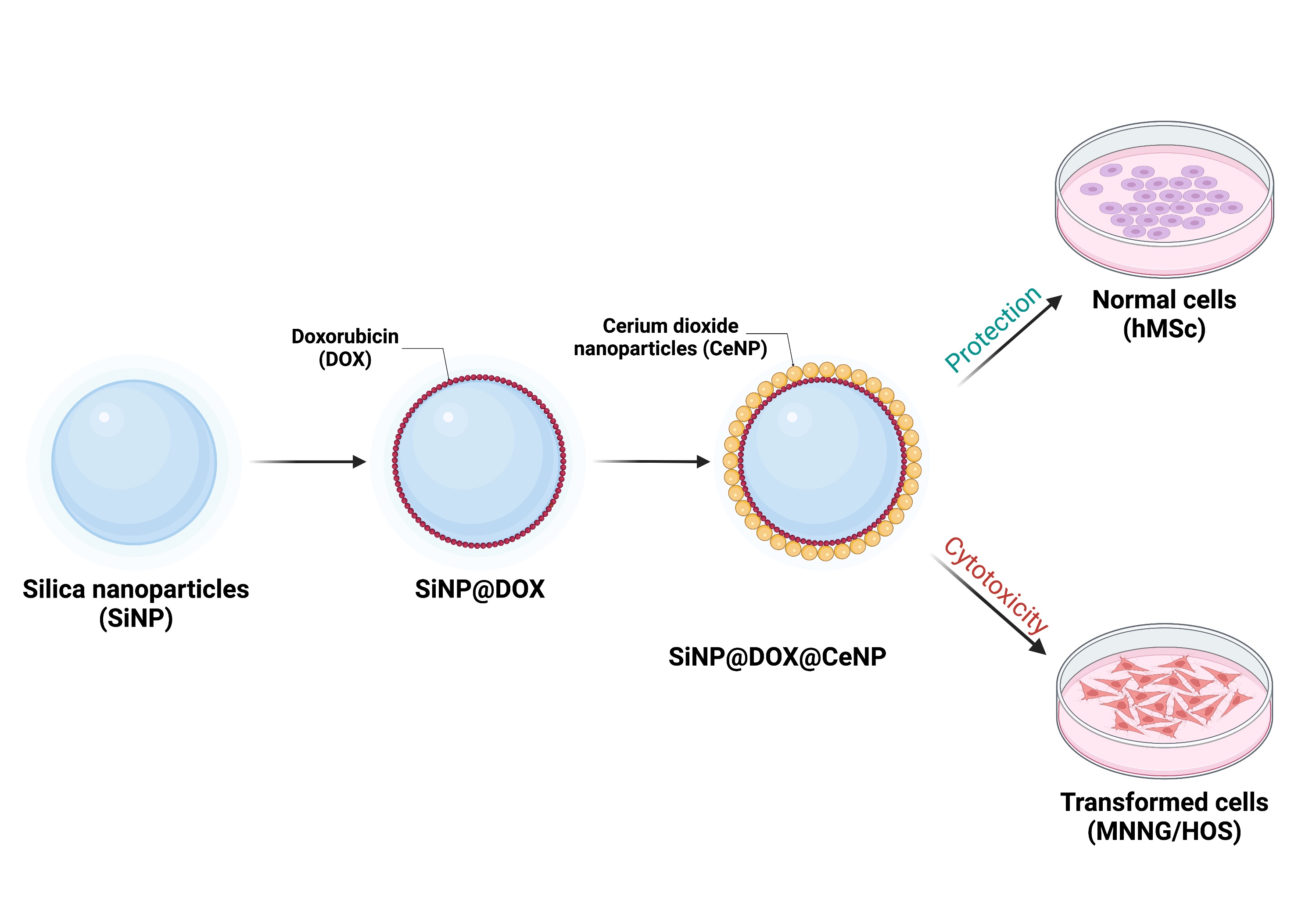
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeNPs) are among the most promising materials with pH-sensitive redox-activity for biomedical nanotechnologies. CeNPs are known to reduce the toxicity of the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin (DOX) for normal cells. Here we have proposed and analyzed a new hybrid cerium/silica containing SiNPs@DOX@CeNPs nanocomposite. We showed that the average size of the nanocomposite is 190 nm and it has a spherical shape. The SiNPs@DOX@CeNPs nanocomposite provides effective synergistic anticancer activity of CeNPs with doxorubicin (DOX), as well as selective toxicity against human osteosarcoma (MNNG/HOS) cells in vitro. The SiNPs@DOX@CeNPs nanocomposite may be a good candidate to increase the effectiveness of cancer doxorubicin chemotherapy.
The mutual influence of the process of electric charge generation in nitrate organic precursors and a constant external magnetic field on the magnetic properties formation was considered for lanthanum strontium manganite La0:7Sr0:3MnO3y powders obtained via combustion reactions. The investigated properties of the obtained samples include hysteresis, magnetocaloric and magnetoresistive effects. The correlation between formation process of extended ensembles of nanoparticles and the functional properties of complex oxide materials was also discussed. The manifestation of a strong magneto-gas-selective effect has been observed during the combustion of precursors in a constant magnetic field, which affects the charge generation process.
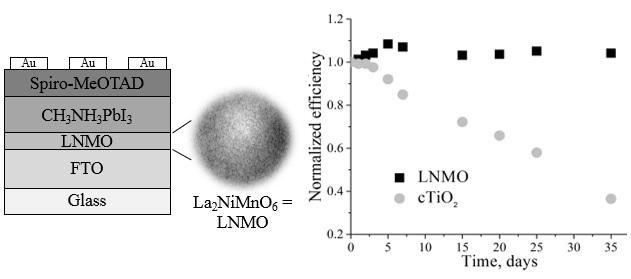
Thin films of La2NiMnO6 (LNMO) double perovskite oxide were first used as buffer layers in planar perovskite solar cells (PSCs) with the architecture of glass/FTO/LNMO/CH3NH3PbI3/Spiro-MeOTAD/Au. All PSCs were fabricated under ambient conditions and their photovoltaic parameters were measured under standard illumination (AM1.5G, 1000 W/m2). Power conversion efficiency (PCE) values (10 – 11 %) for the PSCs developed were comparable with those obtained for conventional PSCs with compact TiO2 (cTiO2) layer, but the stability of PSCs with LNMO buffer layer was significantly higher than for cTiO2-based PSCs.
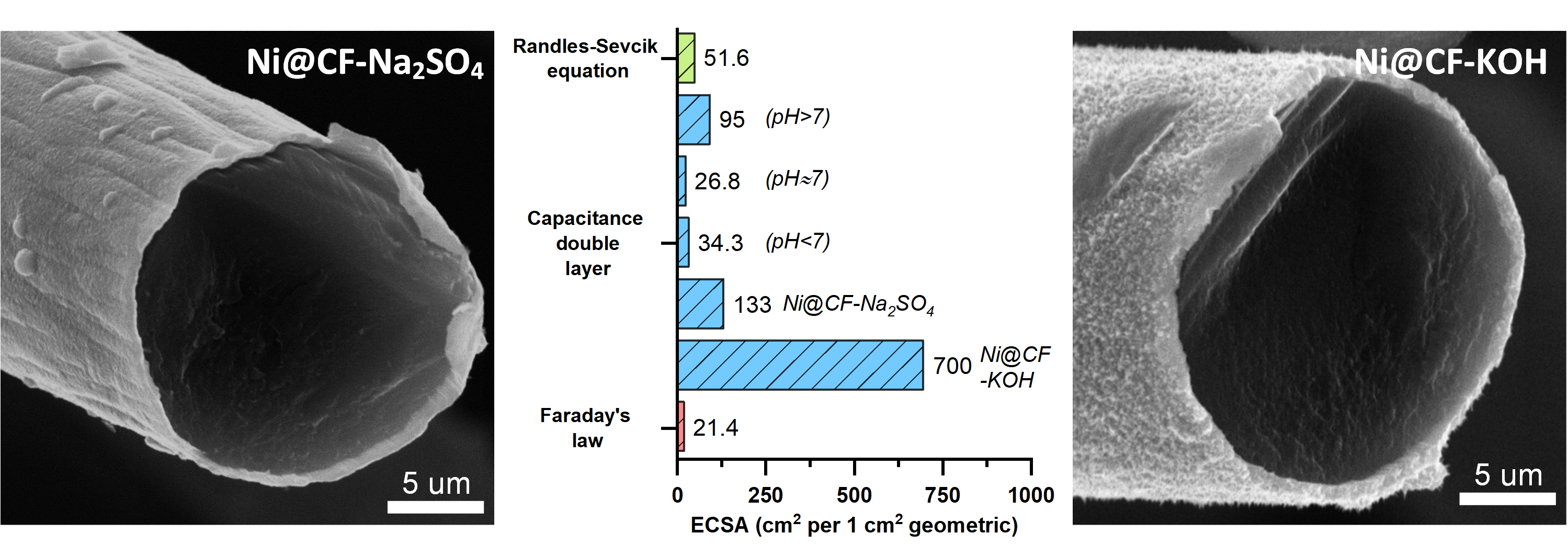
This study is devoted to the evaluation of electrochemical active surface area (ECSA) for carbon felt used in various fields of electrochemical technology. For the evaluation, we used techniques based on Faraday’s law, the Randles–Sevcik equation and the calculation of the electric double layer capacitance in the electrolyte with different pH value. The measurement results are consistent with each other and for neutral, acidic and alkaline medium, the ECSA value are 20 – 30, 30 – 40 and 50 – 90 cm2 per 1 cm2 of geometric surface, respectively. Based on the results, the synthesis of nanostructured nickel coatings on carbon felt with prior electrochemical activation was performed. The pre-treatment in 1M KOH vs 1 M Na2SO4 reduces the crystallite size from 26 to 15 nm and increases the ECSA from 133 to 700 cm2 per 1 cm2 of geometric surface. These changes cause an improvement in other electrocatalytic features for hydrogen evolution reaction.
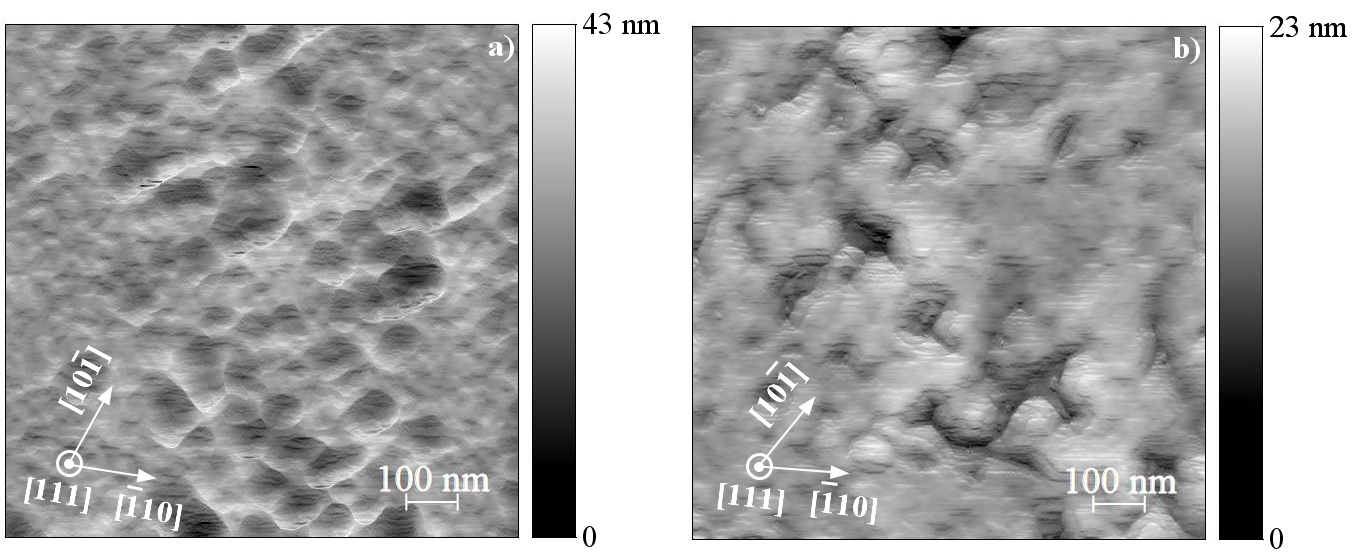
GaInAsP and GaInAsSbBi solid solutions were grown on GaP (111) substrates by pulsed laser deposition using a laser fluence of 2.3 J/cm2. Energy Dispersive X-ray microanalysis, atomic force microscopy, and Raman spectroscopy were used for analysis of the elemental composition and study of the surface morphology and chemical bonds of the obtained solid solutions. It was found that at constant growth temperature and the fluence of 2.3 J/cm2, the elemental composition of the film has a significant effect on the growth kinetics. Surface-active elements (Sb and Bi) in the composition of the solid solution lead to a change in the surface diffusion of In and Ga, which is accompanied by a decrease in roughness. It was established that the films growth in the Volmer–Weber mode. The grown films are nanotextured with a predominant orientation in the direction of growth (111).
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)