MATHEMATICS
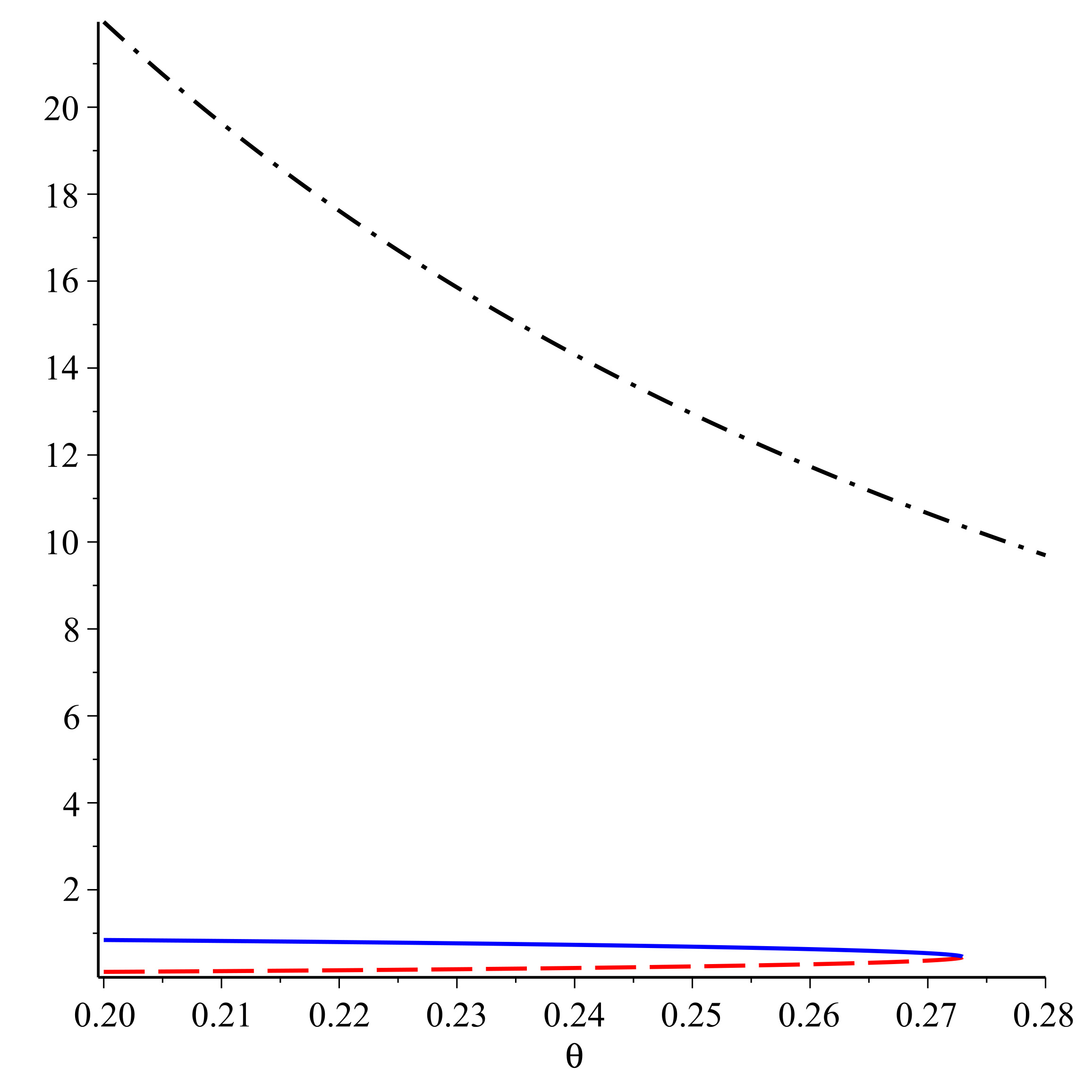
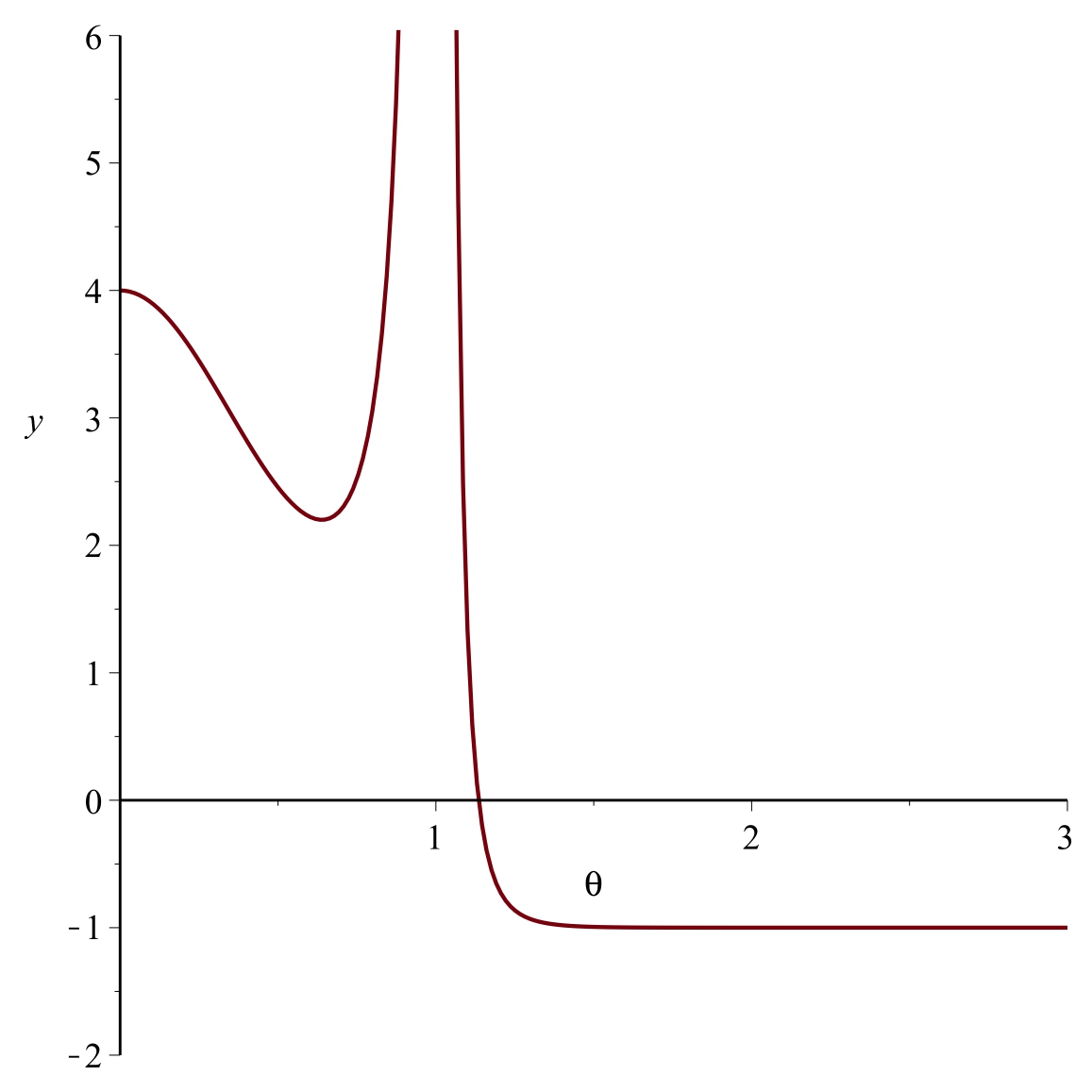
In this paper, we consider a three-state solid-on-solid (SOS) model with two competing interactions (nearest-neighbor, one-level next-nearest-neighbor) on the Cayley tree of order two. We show that at some values of the parameters the model exhibits a phase transition. We also prove that for the model under some conditions there is no two-periodic Gibbs measures.
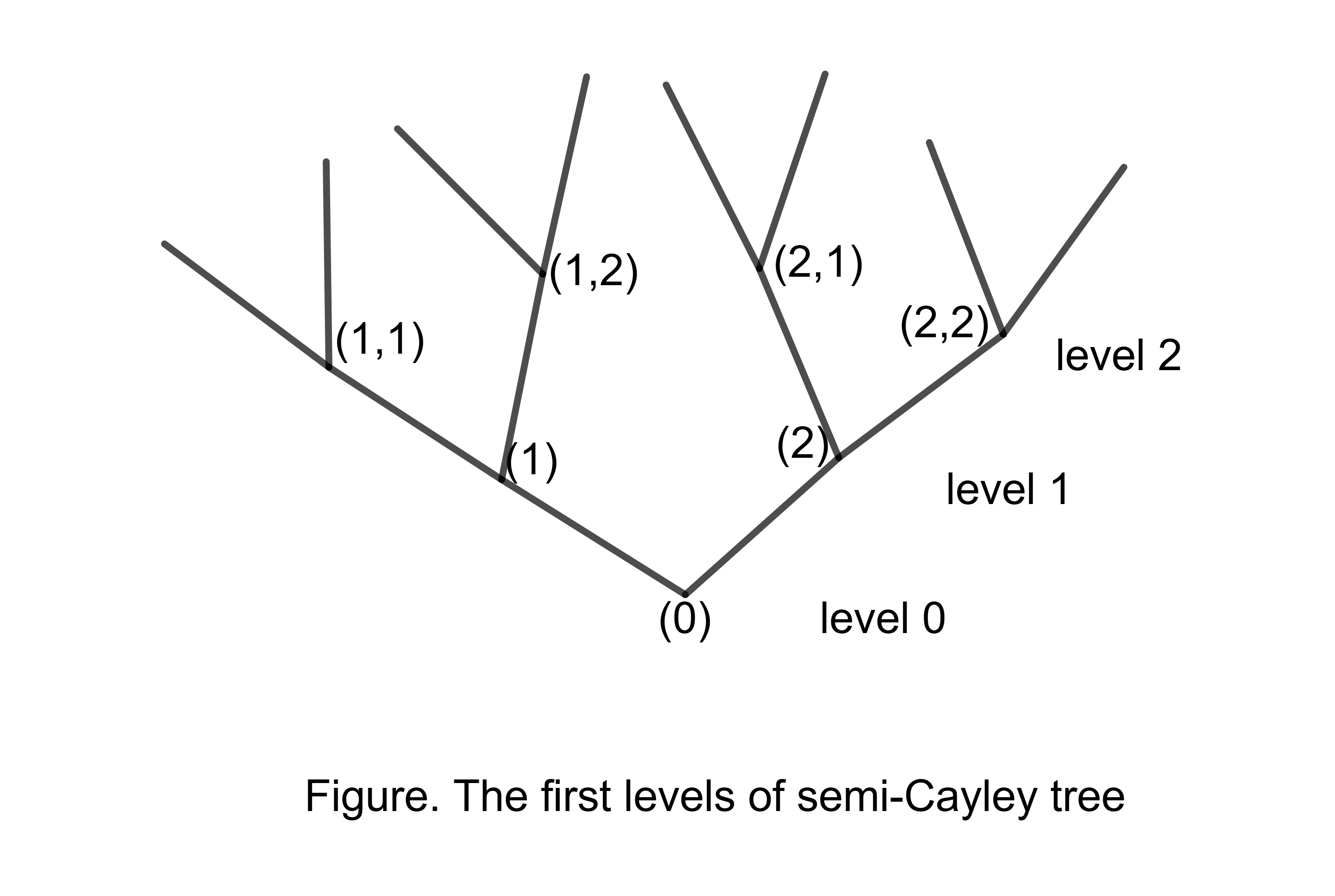
We examine a model of a DNA-Ising molecule on a Cayley tree of order k ≥ 2. For this model, we derive a system of functional equations, where each positive solution corresponds to a Gibbs measure. On the general order Cayley tree, we can solve the model exactly. Specifically, we can find the exact value of the critical temperature Tc for any k ≥ 2 so that, if T ≥ Tc, there is a unique translation-invariant Gibbs measure (TIGM), and if T < Tc, there are three TIGMs. We determine the model’s typical configurations and stationary distributions for high enough and low enough temperatures. The primary attention is focused on the systematic study of the structure of the set of the Gibbs measures. In this paper, we present a non-trivial adaptation of famous techniques, such as the Martinelli-Sinclair-Weitz criterion for determining the extremality of TIGMs and the Kesten-Stigum criterion for determining the non-extremality of TIGMs. One of the important contributions of this paper is the resolution of the extremality versus non-extremality regions for one of the TIGMs on a Cayley tree of the general order. For the other TIGMs, the extremality and non-extremality regions are determined on Cayley trees of orders up to 5.
This paper investigates pinned gradient measures for SOS (Solid-On-Solid) models associated with HA-boundary laws of period two, a class that encompasses all 2-height periodic gradient Gibbs measures corresponding to a spatially homogeneous boundary law. While previous research has predominantly focused on a spatially homogeneous boundary law and corresponding GGMs on Cayley trees, this study extends the analysis by providing a comprehensive characterization of such measures. Specifically, it demonstrates the existence of pinned gradient measures on a set of G-admissible configurations and precisely quantifies their number under certain temperature conditions.
The study is focused on investigation of p-adic Gibbs measures for the q-state Potts model with an external field and determination of the conditions for the existence of a phase transition. In this work, we derive a functional equation that satisfies the compatibility condition for p-adic quasi-Gibbs measures on a Cayley tree of order k ≥ 2. Furthermore, we prove that if |q|p = 1 there exists a unique p-adic Gibbs measure for this model. Additionally, for the Potts model on a binary tree, we identify three p-adic quasi-Gibbs measures under specific circumstances: one bounded and two unbounded, which implies a phase transition.
PHYSICS
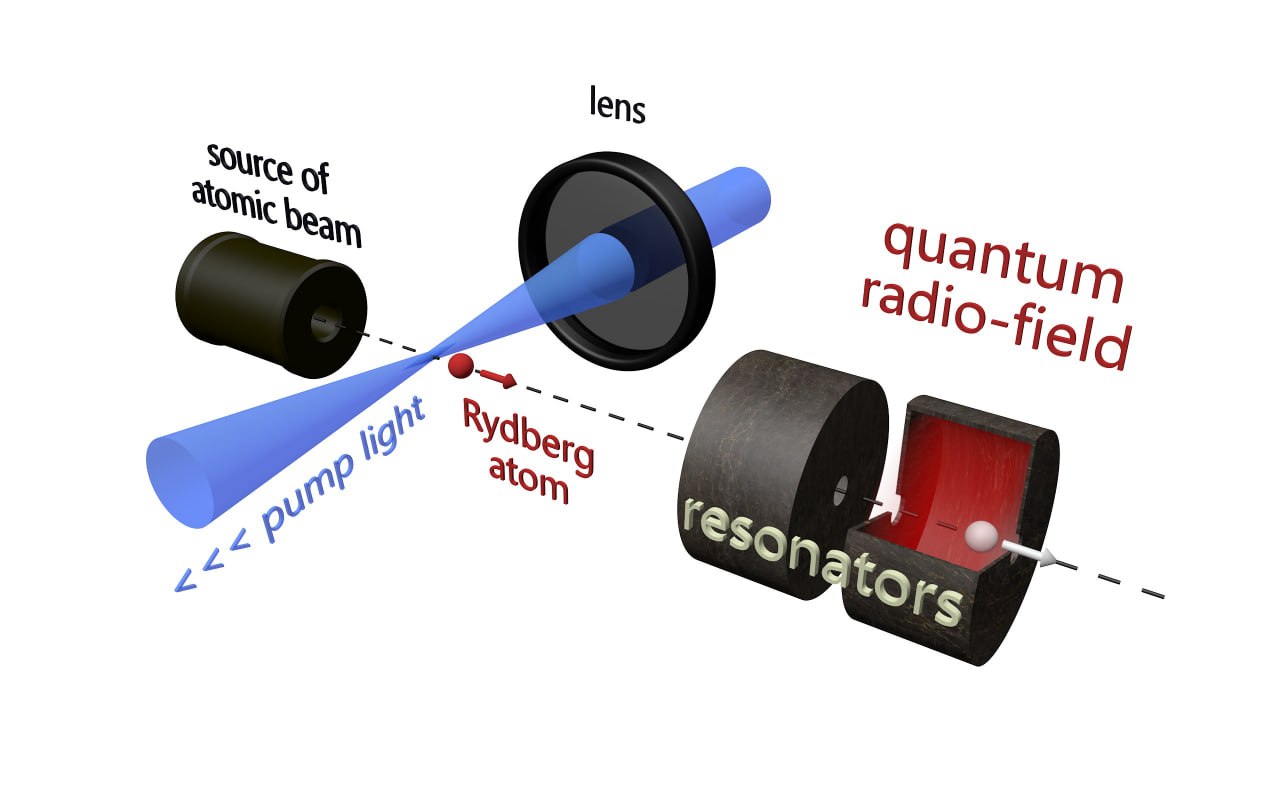
In this work, we investigate the effect of quantum coupling between radio fields in a single-atom maser with two spatially separated resonators. Each atom in a beam, depending on its state, can emit one photon into the first resonator and absorb another from the second, thereby entangling the quantum states of two independent modes. Resulting from entanglement, we obtain a coherence between states of two-mode field with the same total number of photons in the both modes. To study the arising coupling, an analytical solution of the stationary master equation is found under conditions of a trapped field state and the dependence of the von Neumann entanglement entropy on the quality factor of the resonators. Numerical analysis reveals that the best conditions for the appearance of quantum coupling are the low quality factor of the first resonator and the high quality factor of the second one.
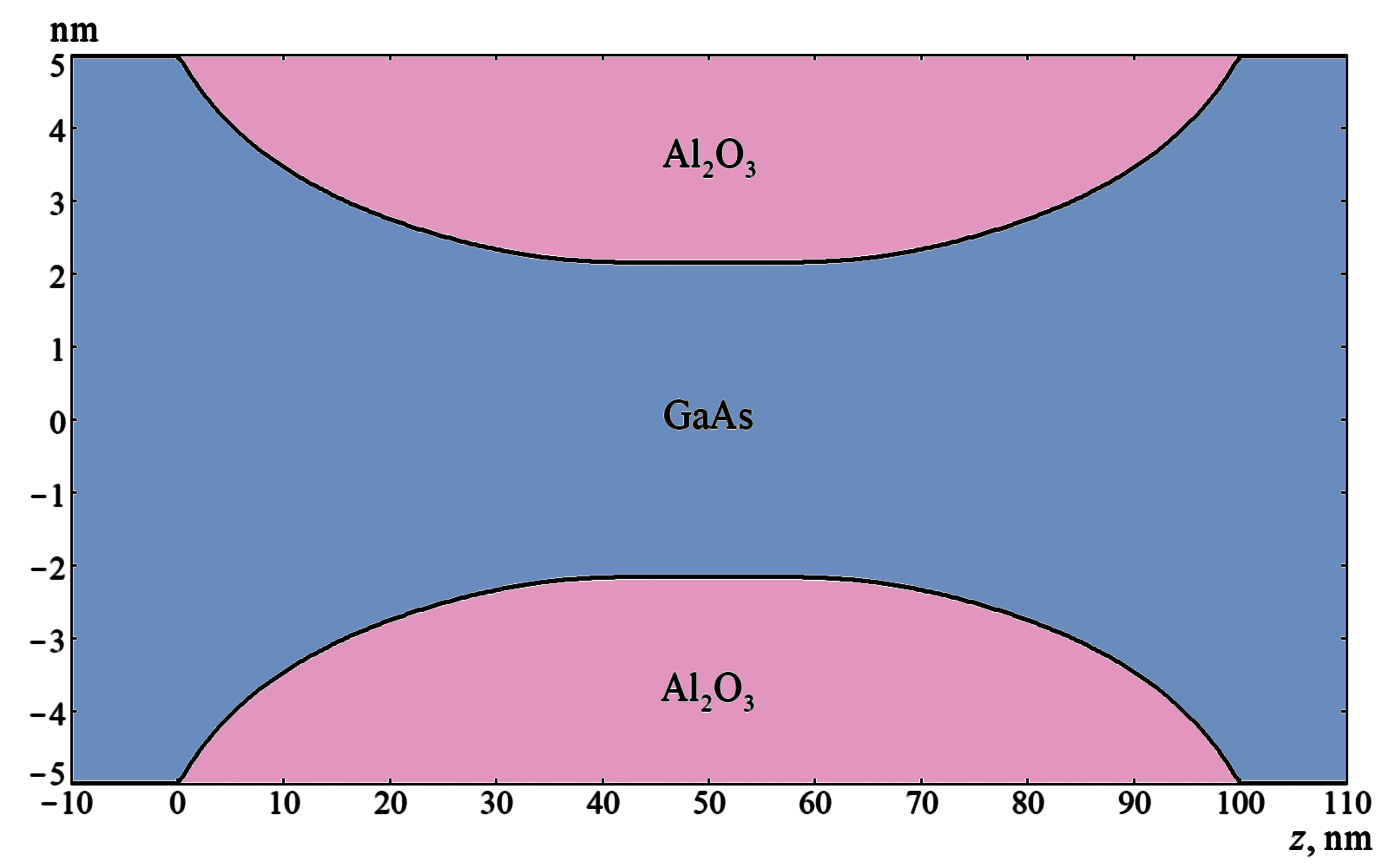
A new constructive solution of field-effect transistor (FET) with a Schottky barrier in a conducting channel has been identified. The FET is a quasi-ballistic quantum-barrier transistor based on a cylindrical undoped GaAs quantum wire in Al2O3 matrix surrounded by a cylindrical metallic gate. A technique for determining the optimal variation of the semiconductor quantum wire diameter along its axis has been developed. The optimal dependence of the nanowire diameter on the spatial coordinate along its axis has been determined providing the possibility of both the elimination of quantum barrier for electrons by the positive gate voltage and the minimization of transistor channel electrical resistance in contrast to a typical FET with a Schottky barrier in its conducting channel. The current-voltage characteristics of the transistor based on GaAs quantum wire with an optimal cross-section have been calculated within the framework of a developed combined physico-mathematical model describing the electron transport in the transistor channel. This model takes into account the nonparabolicity of the semiconductor band structure, the quantum-dimensional effects, and such secondary quantum effects as the collisional broadening and displacement of electron energy levels.
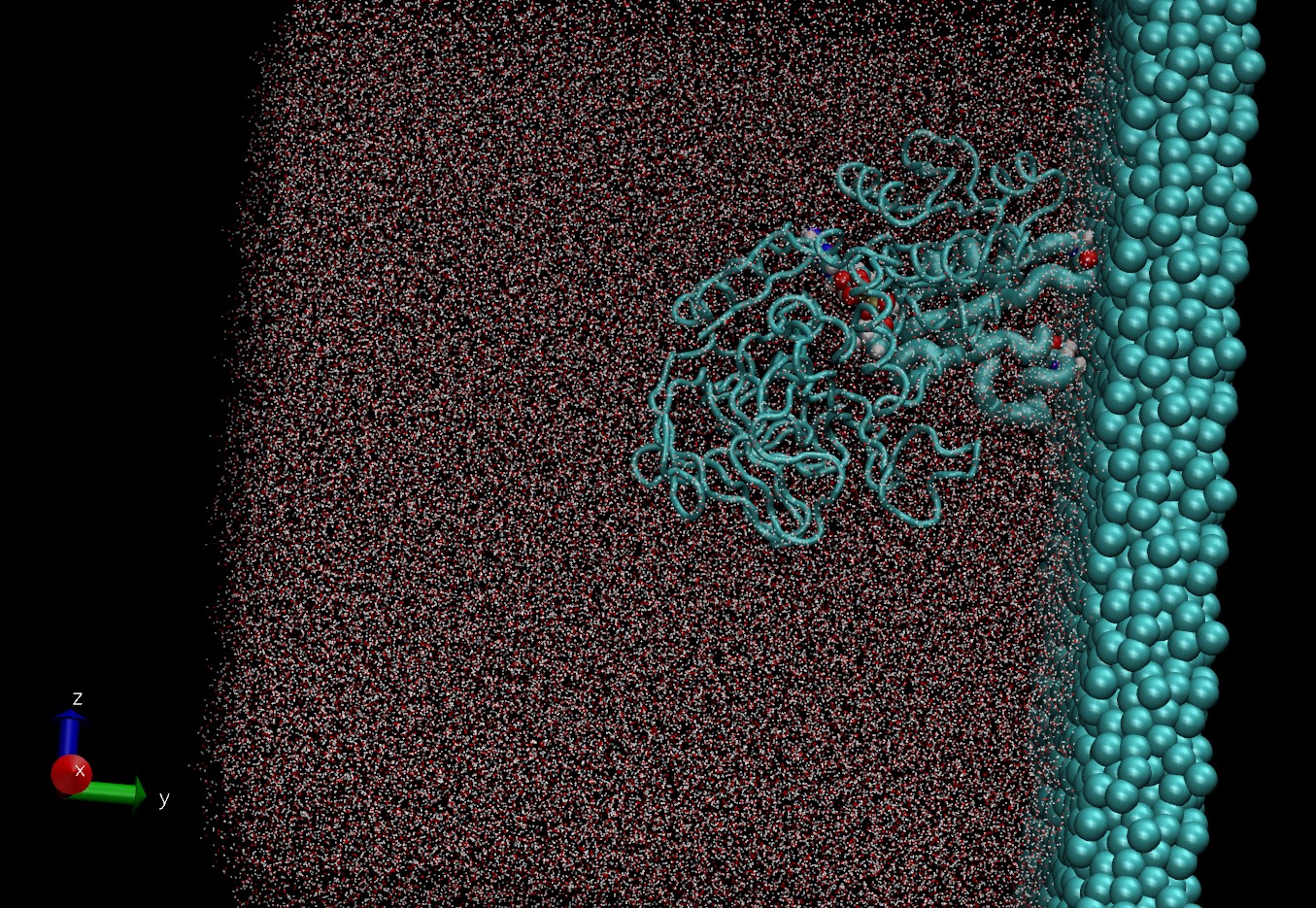
In this work, computer molecular dynamics (MD) studies of the orientation and structural conformations of the alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme (hereinafter ADH) in complex with nicotine adenine dinucleotide (hereinafter NAD) during sorption on the surface of electrode materials using graphite as an example were carried out.
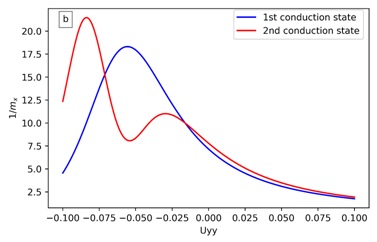
This paper presents a comprehensive investigation of the essential properties of topological insulator materials like electronic, thermal, and magnetic quantities. We considered crystalline topological insulators tin telluride (SnTe), deposited on a magnetic substrate material. The anisotropic mass Hamiltonian is considered to obtain eigenenergy spectra expression in the presence of exchange proximity and strain effects. We showed that the strain has an important effect in shifting the position of the valley or Dirac points in the reciprocal space; an important result that leads to significant role in using the topological material as an electronic component in the new hot research area called valley electronics. We displayed the dependences of the computed density of states, heat capacity, and the magnetic susceptibility of the crystalline topological material, SnTe, on the Hamiltonian physical parameters.
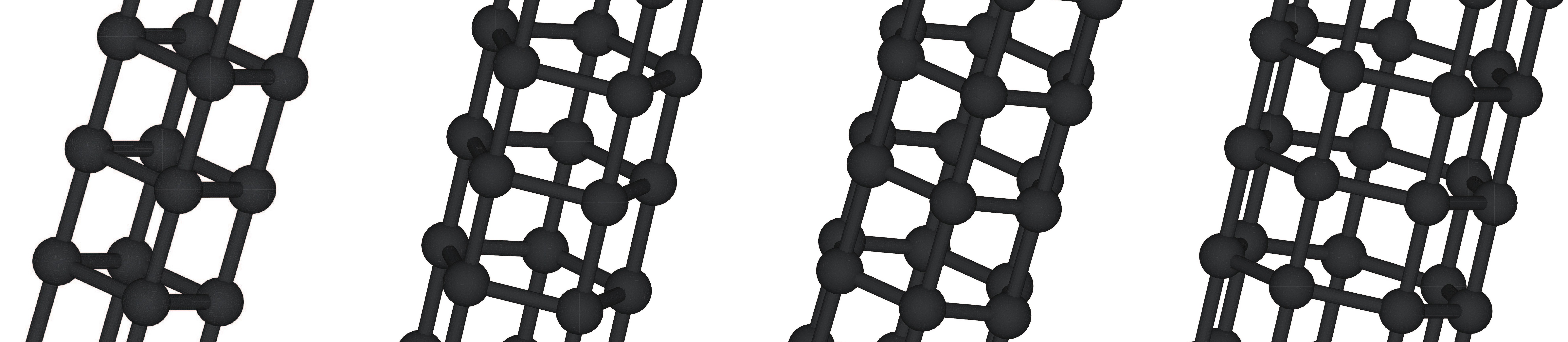
Carbon polyprismanes are 1D nanostructures that should be classified as diamond-like phases because they (polyprismanes) also consist of the 4-coordinated carbon atoms. A carbon polyprismane contains polygonal atomic rings arranged in layers along the common symmetry axis, at uniform distances from each other. According to previous density functional theory based studies, carbon polyprismanes can exhibit metallic conductivity, which is very unusual for diamond-like phases. In this paper, we present the sp3 tightbinding model based calculations of the band structures for carbon polyprismanes of different diameters and compare the obtained results with their analogs for a 2D square carbon lattice, which can be considered as the limiting case of a carbon polyprismane of infinite diameter. Our results confirm that the sp3 tight-binding model describes the electronic properties of carbon polyprismanes well, since we obtain their band structures over a wide range of parameter values for the proposed model. We believe that such electronic transport characteristics are an intrinsic topological feature of polyprismanes and should also occur in non-carbon polyprismanes.
This review examines the development of modern semiconductor technologies using various carbon nanomaterials, as an element base, to replace classical semiconductors (silicon, germanium, etc.). Examples of specific electronic devices demonstrate the gradual displacement of classical semiconductors by carbon compounds, which are much more promising, with the potential to create all-carbon electronics.
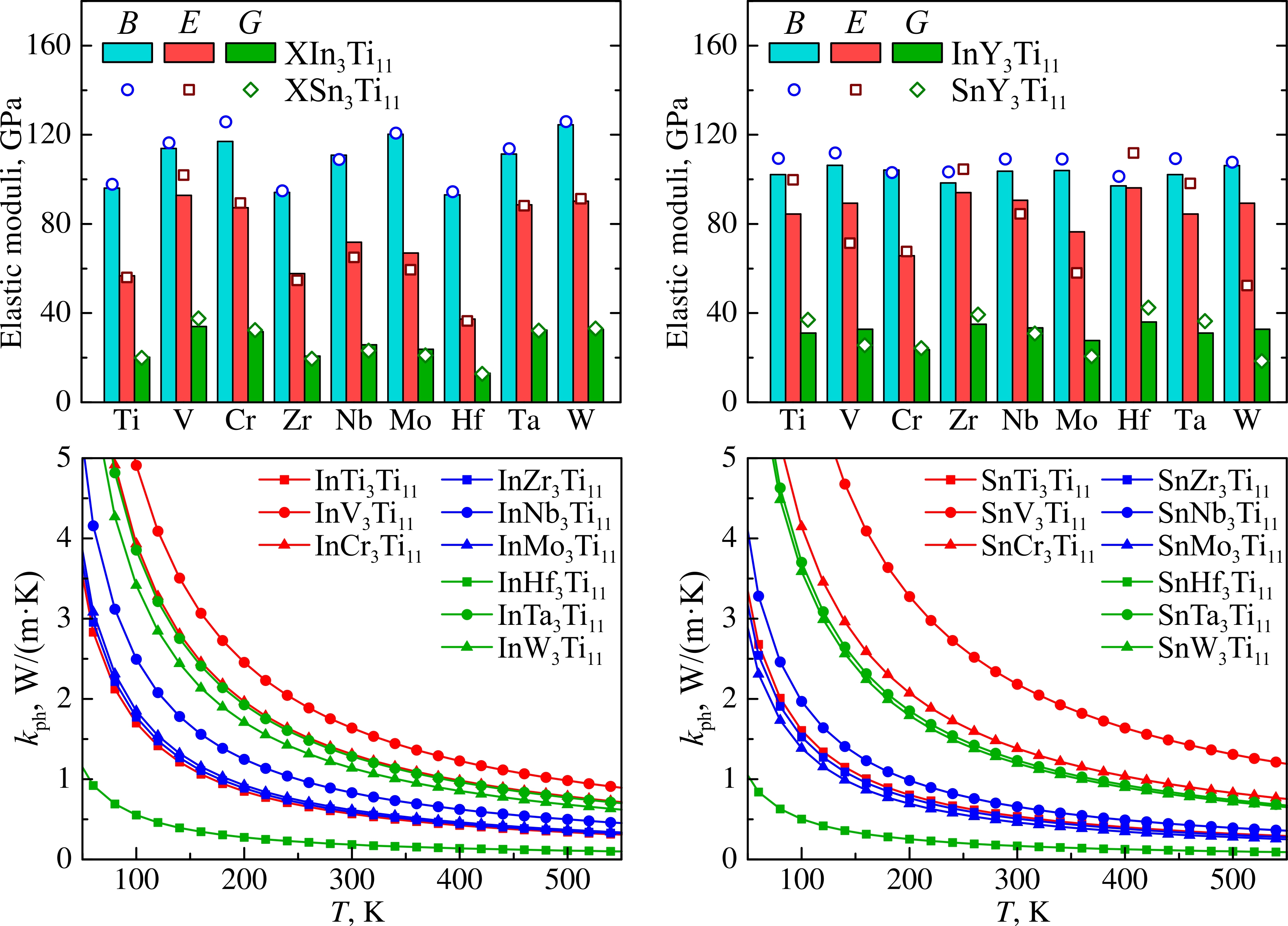
The elastic moduli and some thermal properties of four series of ternary β-Ti based alloys of the XY3Ti11 composition, where X and Y are elements of IVB–VIB, IIIA and IVA groups, have been studied using the projector augmented wave method within the density functional theory. It has been shown that the calculated Young’s moduli in these series of alloys are lower than those in commercially pure α-Ti titanium or in the Ti-6Al-4V alloy. With an increase in the concentration of s,p-elements and the number of electrons in the d-band of the X-metal, the Young’s modulus tends to decrease. The variation of Debye temperature, acoustic Gruneisen parameter and thermal conductivity in titanium alloy series is discussed. It is shown that¨ high thermal conductivity correlates with high Debye temperature, which in turn increases with increase of the values of the Young’s modulus.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIALS SCIENCE
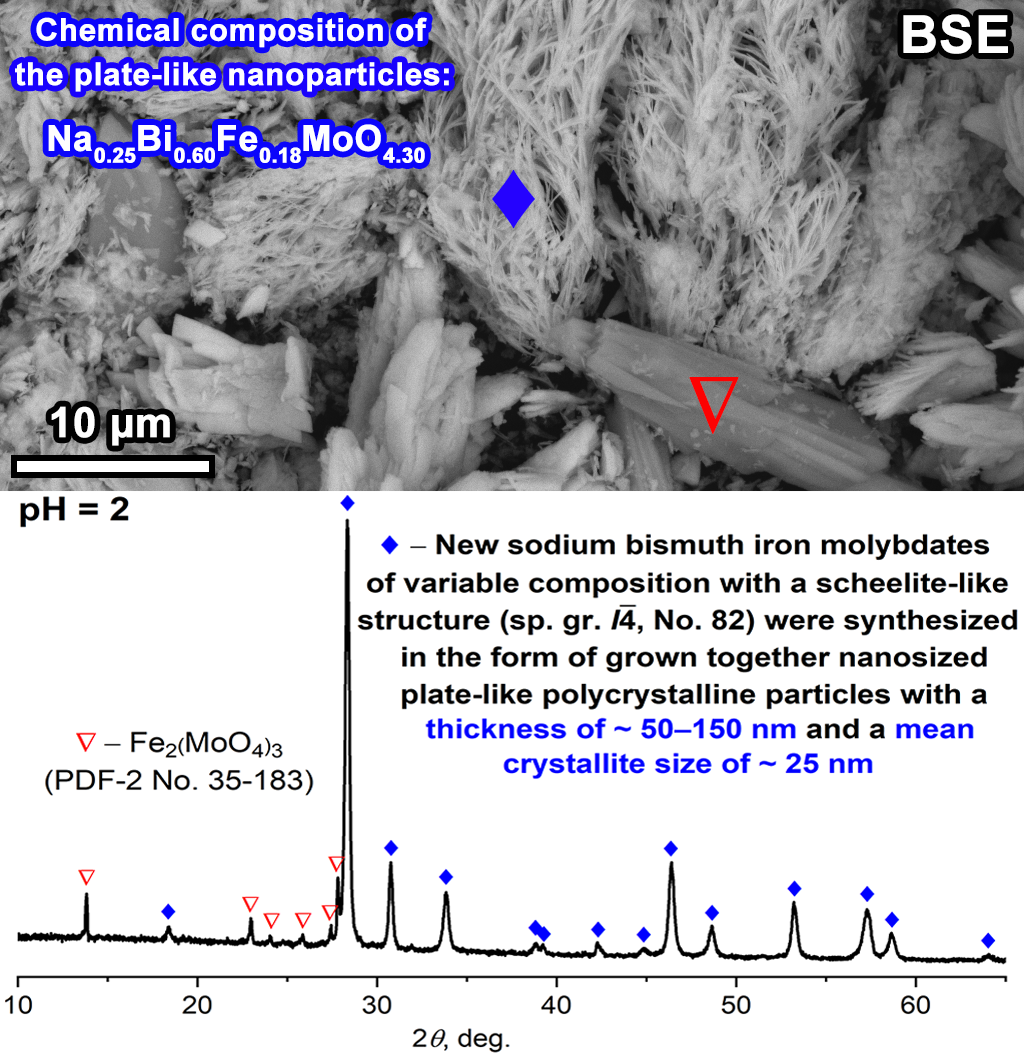
The effect of the hydrothermal fluid pH on the chemical and phase composition, as well as the size parameters and morphology of crystallites and particles of hydrothermal synthesis products formed in the Na2O–Bi2O3–Fe2O3–MoO3 system at T = 170 ◦C and P < 7 MPa has been studied. It has been established that in the acidic pH region, the bulk chemical composition of the hydrothermal synthesis products is depleted relative to the nominal composition specified for the synthesis in iron oxide, while in the alkaline pH region, it is depleted in molybdenum oxide and, to a lesser extent, in bismuth oxide, while the best correspondence between the nominal and bulk composition observed at pH = 2. It is shown that in the pH range from 2 to 6 new compounds of variable composition (Na0.19−0.47Bi0.42−0.85Fe0.14−0.31MoOy) with a scheelite-like structure (sp. gr. I¯4, No. 82) are formed, which have not been previously described in the scientific literature. These compounds with the smallest mean crystallite size (∼25 nm) were obtained at pH = 2, and it was shown that under these conditions polycrystalline plate-like particles (thickness (h) ∼50–150 nm) are formed, often having a curved shape, which grow together to form agglomerates with a “flower-like” morphology. It was found that fluorite-type solid solutions (Bi3.65−4.30Fe0.37−0.45MoOz) are formed in alkaline media (isostructured to the oxide δ-Bi2O3 (sp. gr. Fm¯3m, No. 225)).
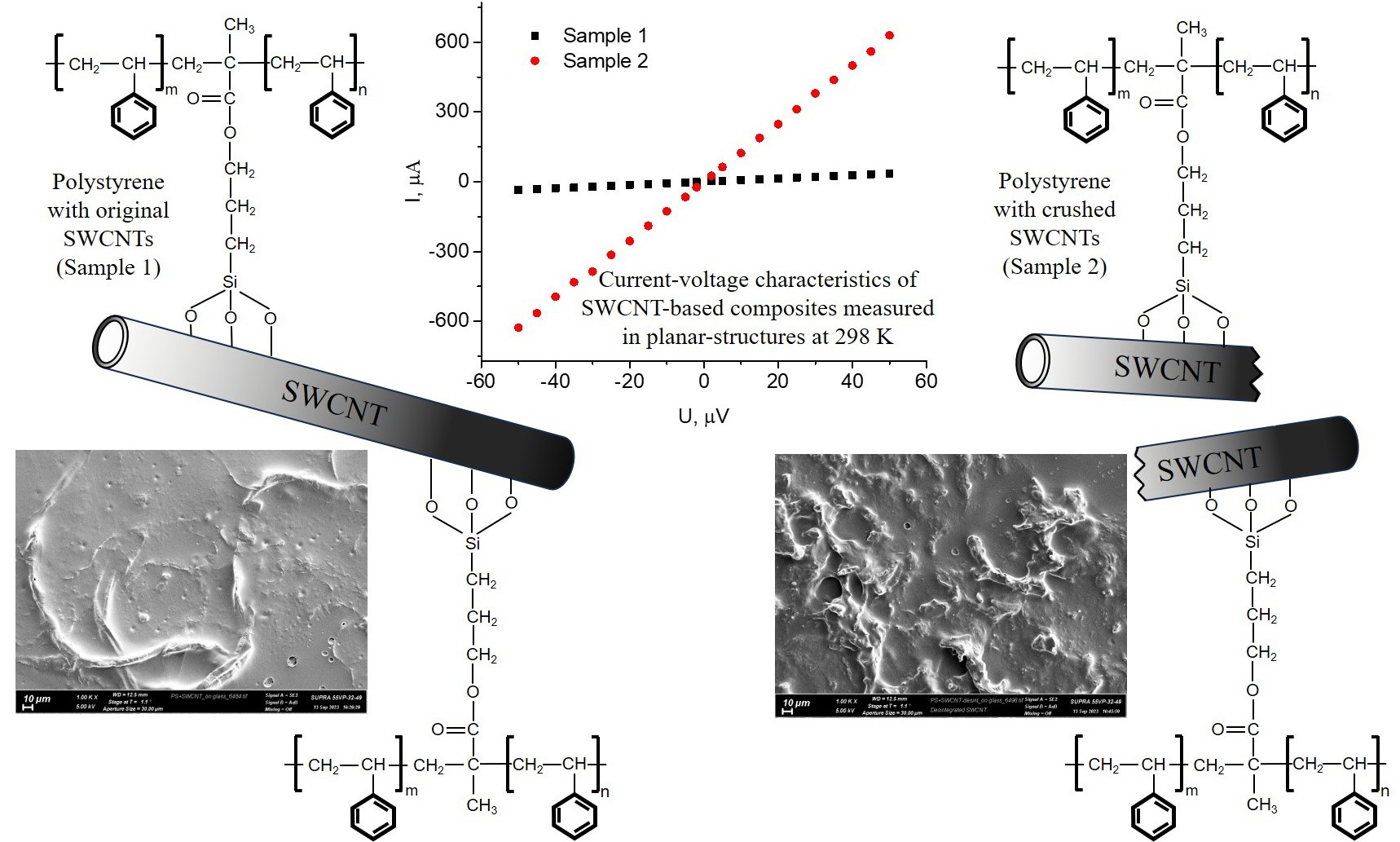
Composite films were synthesized by radical copolymerization of styrene with methacrylate groups on the surface of modified single-walled carbon nanotubes. Mechanical grinding and reforming of films on the electrode led to a decrease in the electrical resistance values by two magnitude orders. This effect was observed when measuring the current-voltage characteristics in both sandwich and planar structures. This decrease in the electrical resistance of the composite films is likely due to the disintegration and reorientation of carbon nanotubes, as well as the creation of mechanical stresses in them as a result of covalent bonding to the polymer matrix, which could affect the electronic structure of carbon inclusions.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)