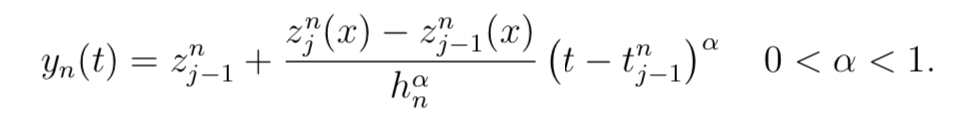MATHEMATICS
This paper aims to study the existence and uniqueness of a weak solution for the boundary value problem of a time fractional equation involving the Caputo fractional derivative with an integral operator. By utilizing the discretization method, we first derive some a priori estimates for the approximate solutions at the points (x, tj). We then evaluate the accuracy of the proposed method to demonstrate that the implemented sequence of α-Rothe functions converges in a certain sense, and its limit is the solution (in a weak sense) of our problem. It must be pointed out that the constructed L1 scheme is designed to approximate the Caputo fractional derivative mentioned in the problem.
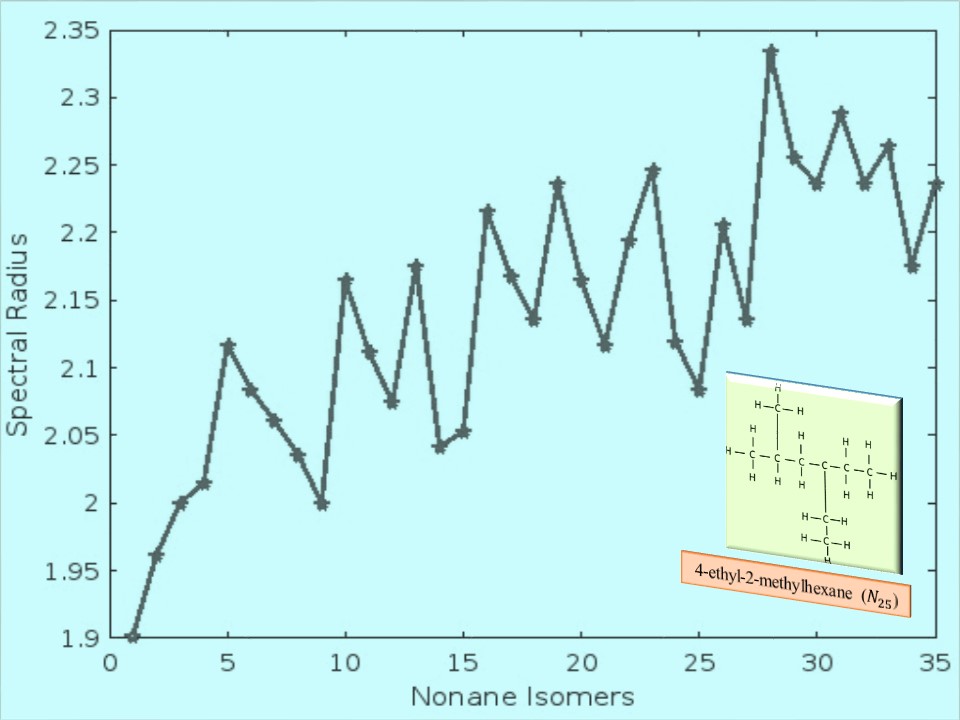
A group of substances known as alkanes is made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms bound together only by single covalent bond with the chemical formula CnH2n+2. Isomers are those molecules with identical chemical formula but different structural arrangement. Due to this, their corresponding molecular graphs differ in structure thereby leading to distinct spectral parameters. In this work, the spectral parameters of all isomers of nonane C9H20 have been computed and its relationship with its eigenvalue-based entropy is established. The spectral results are then correlated with the density value of the nonane isomers and it is found that the “spectral gap” is closely associated to that of density.
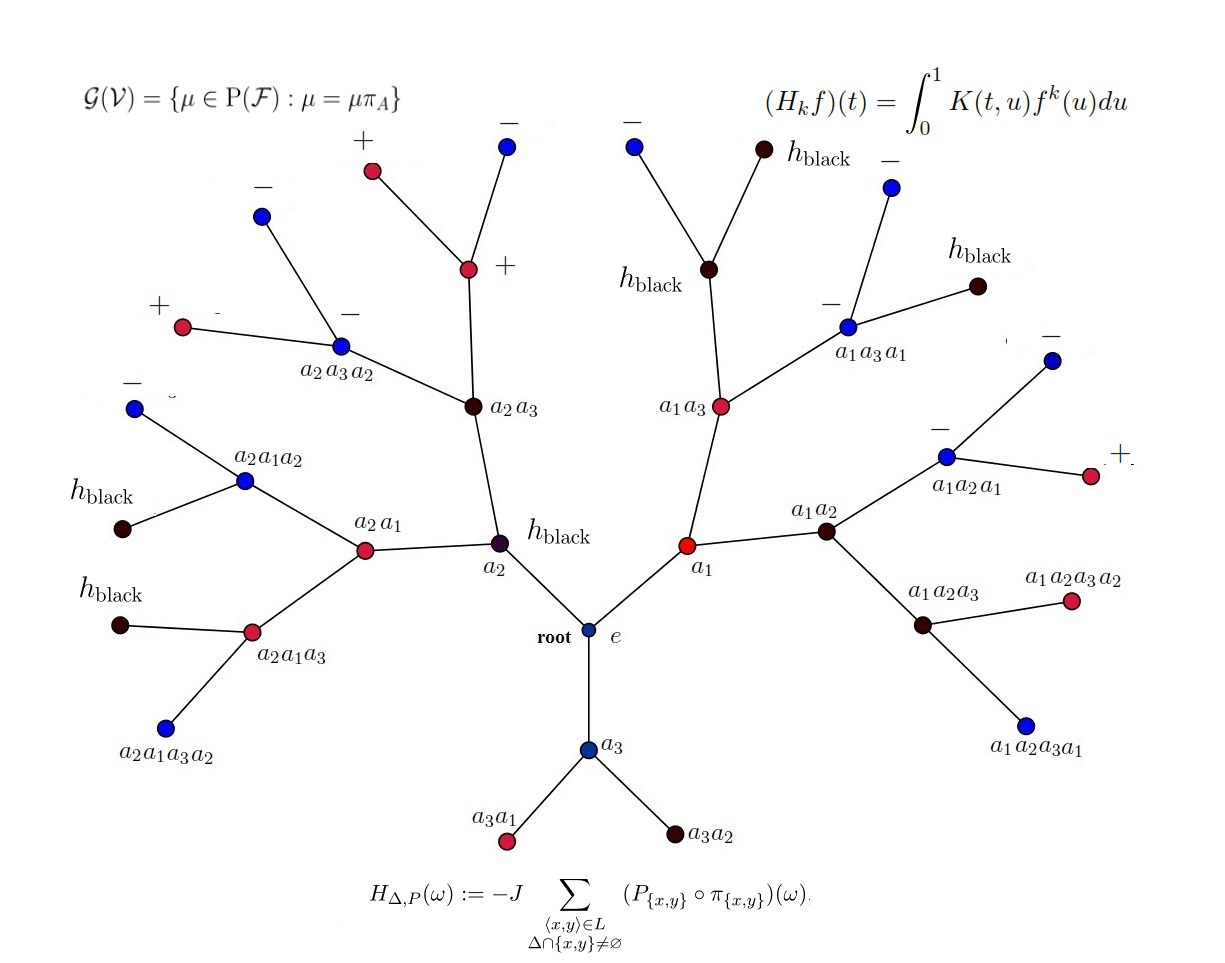
The paper deals with the problem of constructing kernels of Hammerstein-type equations whose positive solutions are not unique. This problem arises from the theory of Gibbs measures, and each positive solution of the equation corresponds to one translation-invariant Gibbs measure. Also, the problem of finding kernels for which the number of positive solutions to the equation is greater than one is equivalent to the problem of finding models which has phase transition. In these articles, the number of solutions corresponding to the constructed kernels does not exceed 3, and in turn, it only gives us a chance to check the existence of phase transitions. The constructed kernels in this paper are more general than the kernels in the abovementioned papers and except for checking phase transitions, it allows us to classify the set of Gibbs measures.
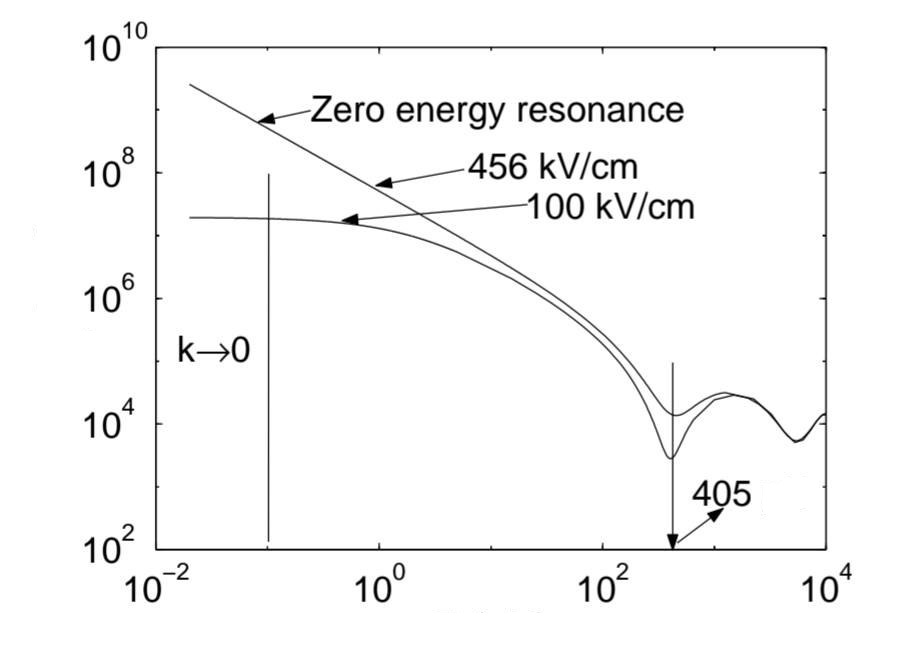
In this paper, the change of the spectrum of multiplier H0f (x, y) = k0(x, y)f (x, y) for perturbation with non-compact partially integral operators is studied. In addition, the existence of resonance is investigated in the model H = H0 — (γ1T1 + γ2T2).
PHYSICS
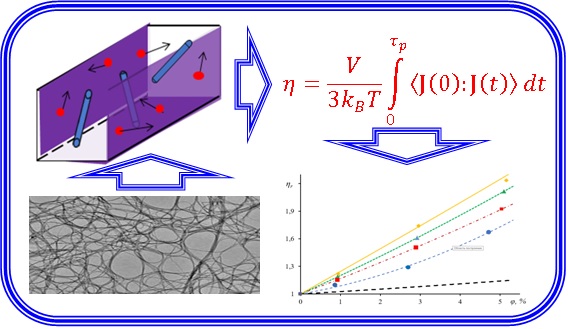
The purpose of this paper is molecular dynamics simulation of viscosity of benzene-based nanofluids with carbon nanotubes, and carbon or copper nanoparticles. The nanotubes diameter and lengths were 1.1 nm and 1.1, 3.5, 7.2, 14.6 nm, respectively. The size of spherical nanoparticle was 1.39, 2.5, and 3.2 nm. The viscosity is calculated using the fluctuation-dissipation theorem (the Green–Kubo formula). It was shown that the viscosity coefficient of all the studied nanofluids with carbon nanotubes increases with their concentration and length. This increase is significantly higher than predicted by the corresponding theories for coarse dispersed fluids. At given weight concentrations, the viscosity coefficient of nanofluids with carbon nanotubes is higher than that of nanofluids with spherical particles. The increase in viscosity of nanofluids compared to that of the base fluid is explained by the structuring of the base fluid molecules in the vicinity of nanoparticles or carbon nanotubes.
The features of generation and properties of surface Bessel Plasmon-polaritons (SBPPs) in optical anisotropic hyperbolic metamaterials formed by a periodic lattice of metal nanowires made of gold and silver embedded into pores of aluminum oxide is studied. We investigate the influence of the thickness of the porous material matrix on the generated plasmon-polaritons. Calculation of energy flows in the structure is made.
The structure of domain walls in cylindrical nanoand microwires with a non-uniform anisotropy distribution in the transverse-radial direction has been studied. This distribution can be controlled by mechanical stresses associated with specific wire manufacturing methods as well as with the glass coating in some types of microwires. Our calculations have shown that in the presence of axial anisotropy in the core of the wire and radial anisotropy near its surface, various configurations of domain walls can be stabilized. A diagram of magnetic states has been calculated depending on the radial anisotropy values. The stability of various types of domain walls and their possible transformation under the excitation of thermal fluctuations and external perturbations are discussed.
In this work, we study the dynamics of electromagnetic radiation in a thin polymer film containing carbon nanotubes. Maxwell’s equations are supplemented with a term that takes into account the presence of polymers in the medium. The dependence of the spatial-energy characteristics of the optical pulse on the polymer concentration is revealed.
CHEMISTRY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE
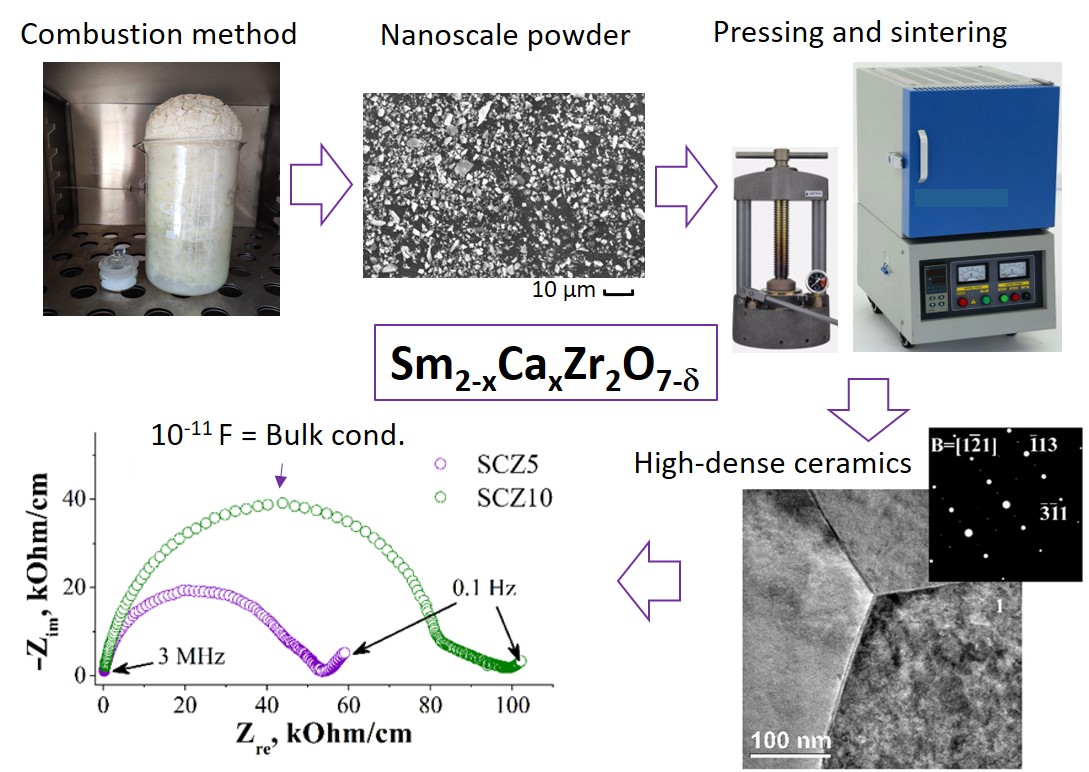
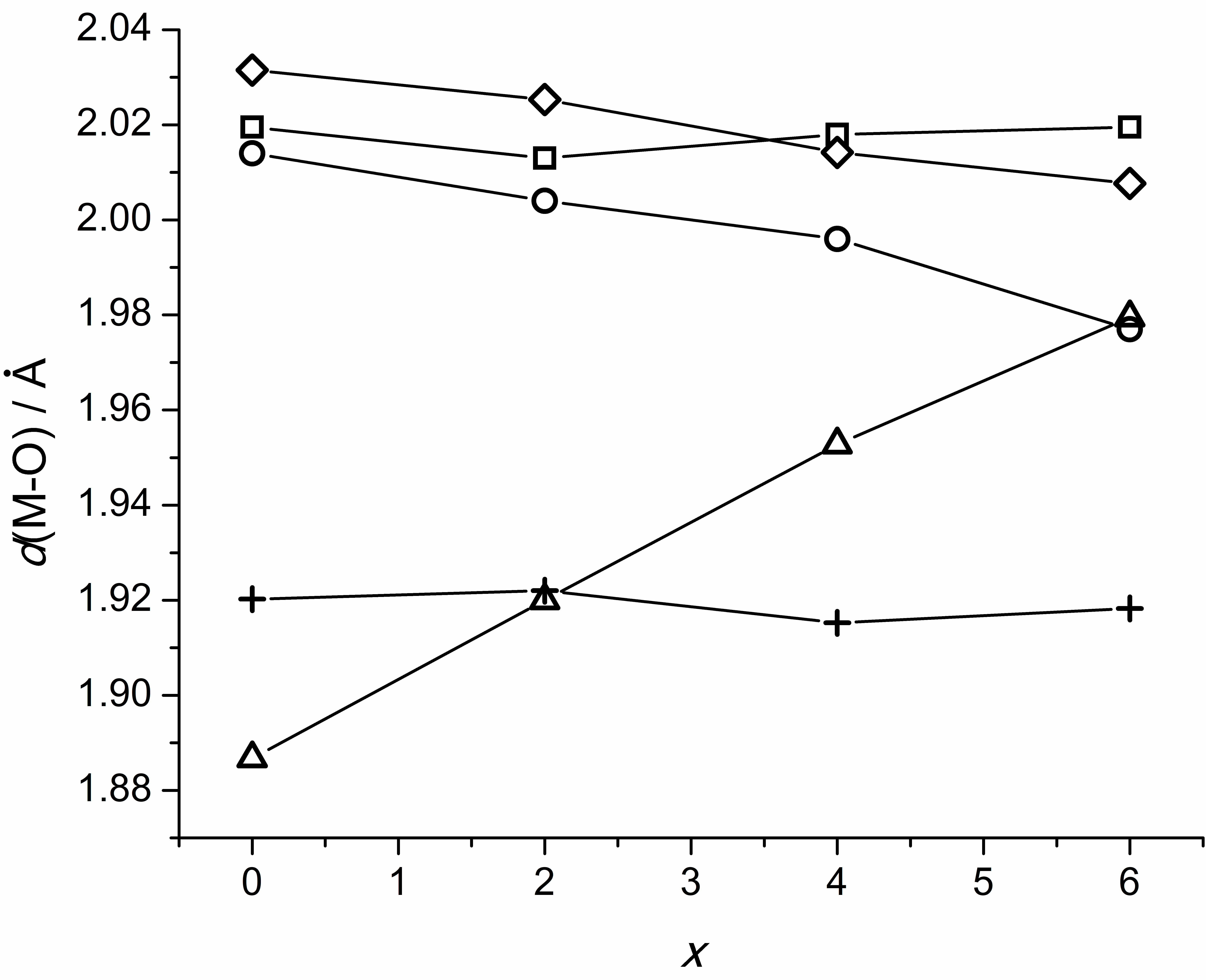
In this work, a doping strategy was used to achieve a good conductivity in samarium zirconate which crystallizes in the pyrochlore. The production of nanopowders made it possible to form high-density ceramics with an optimal microstructure. It is shown that intrinsic and impurity defects coexist in Sm2−xCaxZr2O7−δ, impairing ion transport at high doping levels. Despite this, Sm1.95Ca0.05Zr2O7−δ maintains low activation energy of the parent and has good ionic conductivity (10−3 S·cm−1 at 600 ◦C) which is one of the largest among oxide pyrochlores. It has been shown to have a good chemical stability. The material has a thermal expansion coefficient (TEC) of 12 ppm K−1 which is higher than YSZ and provides better compatibility with electrode materials. The above makes it possible to successfully use it as a highly stable oxygen electrolyte or an intermediate thin layer at the electrolyte-electrode interface in electrochemical devices.
Single-phase barium hexaferrite powders with crystallite sizes in a single-domain region and with the general composition BaFe12−xMnxO19, where x = 0, 2, 4, 6, were synthesized applying a citric sol-gel auto-combustion technique with final annealing temperatures of 900 – 1200 ◦C. The crystal structures were refined, and the magnetic properties were studied. The observed variations in atomic positions with the Mnfor-Fe substitution revealed presence of Mn in three oxidation state +2, +3, and +4, with a preference of Mn2+ to the tetrahedral 4f1 site and Mn4+ to the octahedral 2a and 12k sites. With the Mn-doping, the samples’ magnetization decreased, while coercivity increased and reached 8.4 kOe for x = 6. The rise of the annealing temperature resulted in a slight growth of magnetization with a general tendency of the coercivity to decrease. A Curie temperature decreased with the Mn-doping remaining above room temperature for the maximal doping.
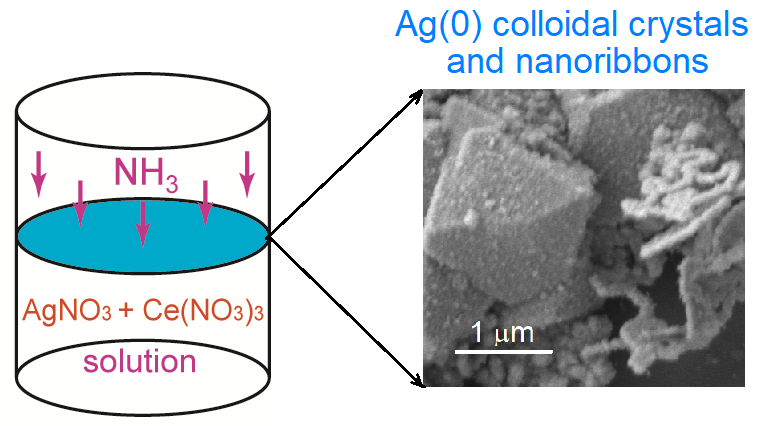
The proposed study shows for the first time that gaseous ammonia treatment of AgNO3 and Ce(NO3)3 salts mixture aqueous solution surface gives rise to formation of a composite layer consisting of Ag(0) faceted colloidal crystals and nanoribbons, as well as CeO2 nanocrystals. A study of such a composite carried out by FESEM, XRD, EDX, TEM, STEM and HRTEM methods has shown that the nanoribbons are about 50–150 nm wide and up to 2–3 µm long, and that there are 2–3 nm CeO2 nanocrystals on the surface thereof. Colloidal crystals of about several micrometers consist of separate, almost identical silver nanocrystals about 20 nm in size. The obtained results provided a basis for construction of schemes of chemical reactions taking place during the synthesis, and gave grounds for recommendations on practical application of the obtained compounds.
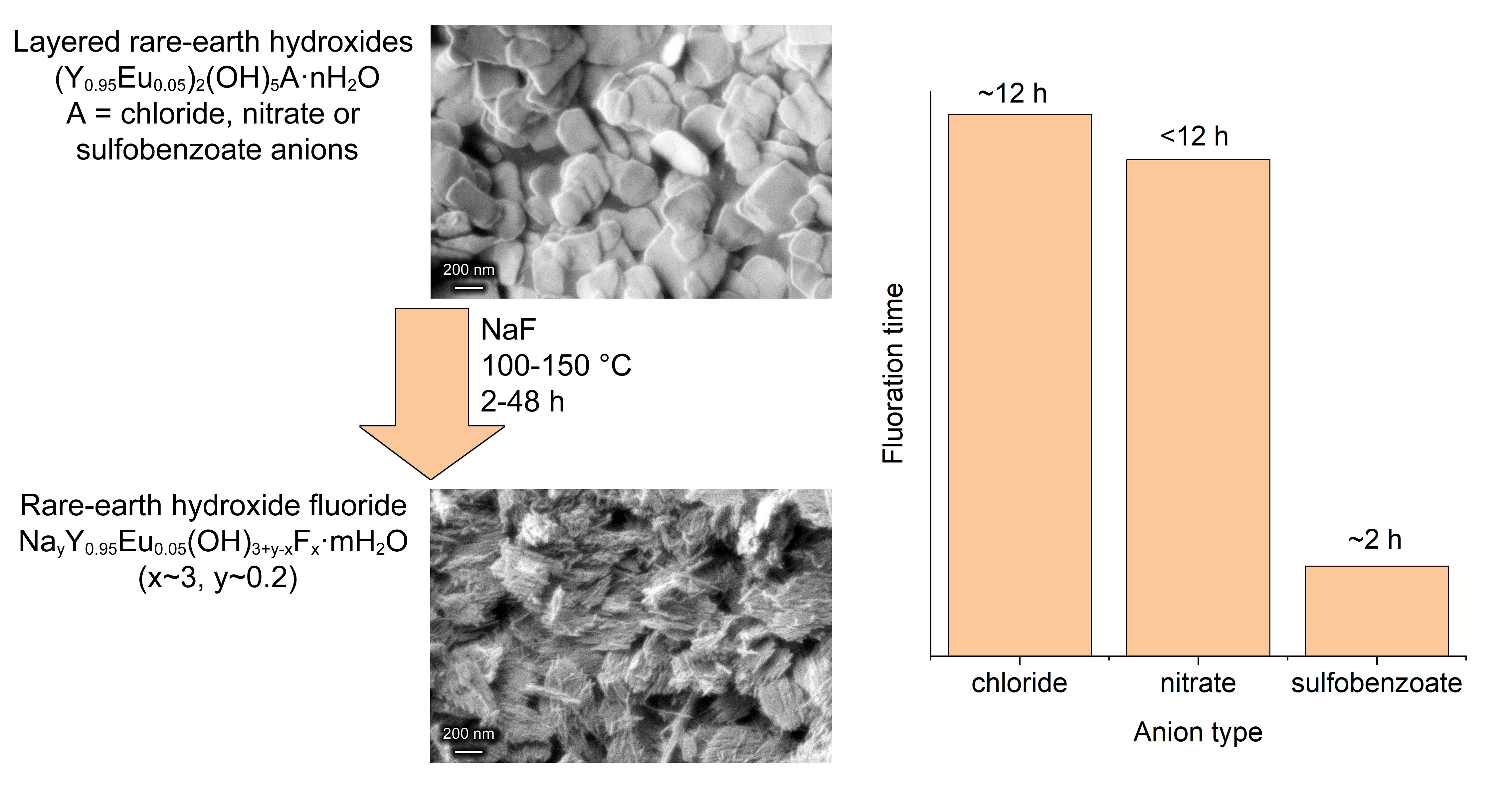
The fluorination processes of layered rare-earth hydroxides (LRHs) intercalated with various anions, including organic ones, have been compared for the first time. The fluorination process was investigated for chloride-, nitrateand 4-sulfobenzoate-intercalated Eu-doped layered yttrium hydroxides by interaction with aqueous solutions of sodium fluoride at 100–150 ○C for 2–48 hours. The final product of fluorination in all cases is the hexagonal yttrium hydroxide fluoride (YHF) phase of NayY0.95Eu0.05(OH)3+y−xFx · mH2O (x ∼ 3, y ∼ 0.2) composition. The formation rate of the YHF increases with the interlayer spacing of the Eu-doped layered yttrium hydroxide.
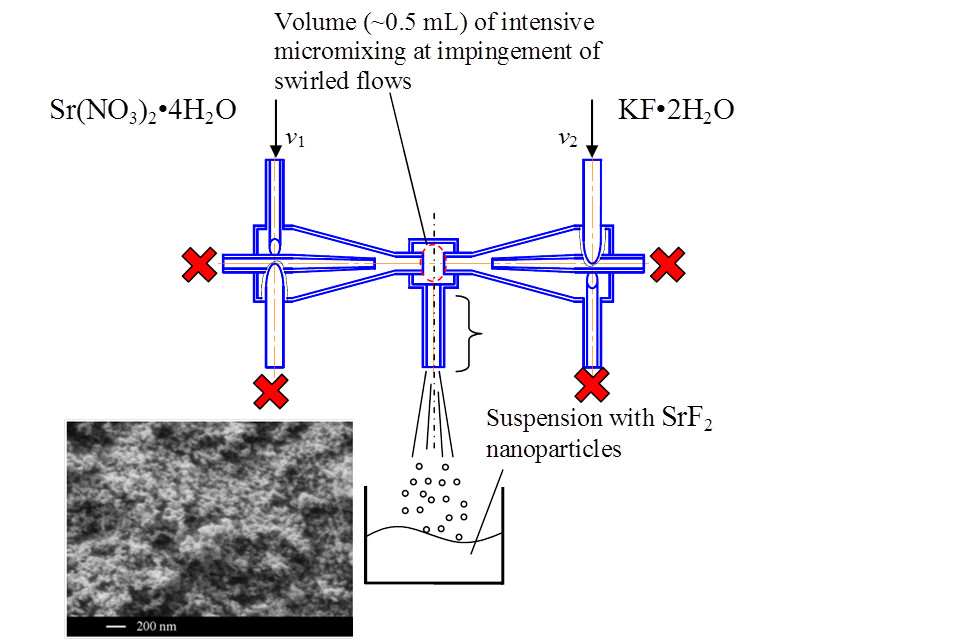
The technique of micromixing was used for synthesis of SrF2 nanopowders in a microreactor with intensely swirling flows. The chemical reaction between aqueous solutions of strontium nitrate (C(Sr(NO3)2) = 0.15 – 0.45 M) and potassium fluoride (C(KF) = 0.3 – 0.9 M) was realized in a microreactor with intensely swirling flows with reagent consumption 1.5 – 3.5 L/min. Colloidal solutions were obtained, during the settling of which SrF2 powders were isolated without crystallographic faceting. An increase in the rate of reagent flow has negligible effect on the size of coherent scattering regions D, while an increase in the concentration of solutions leads to an increase in D from ∼ 20 to ∼ 30 nm.
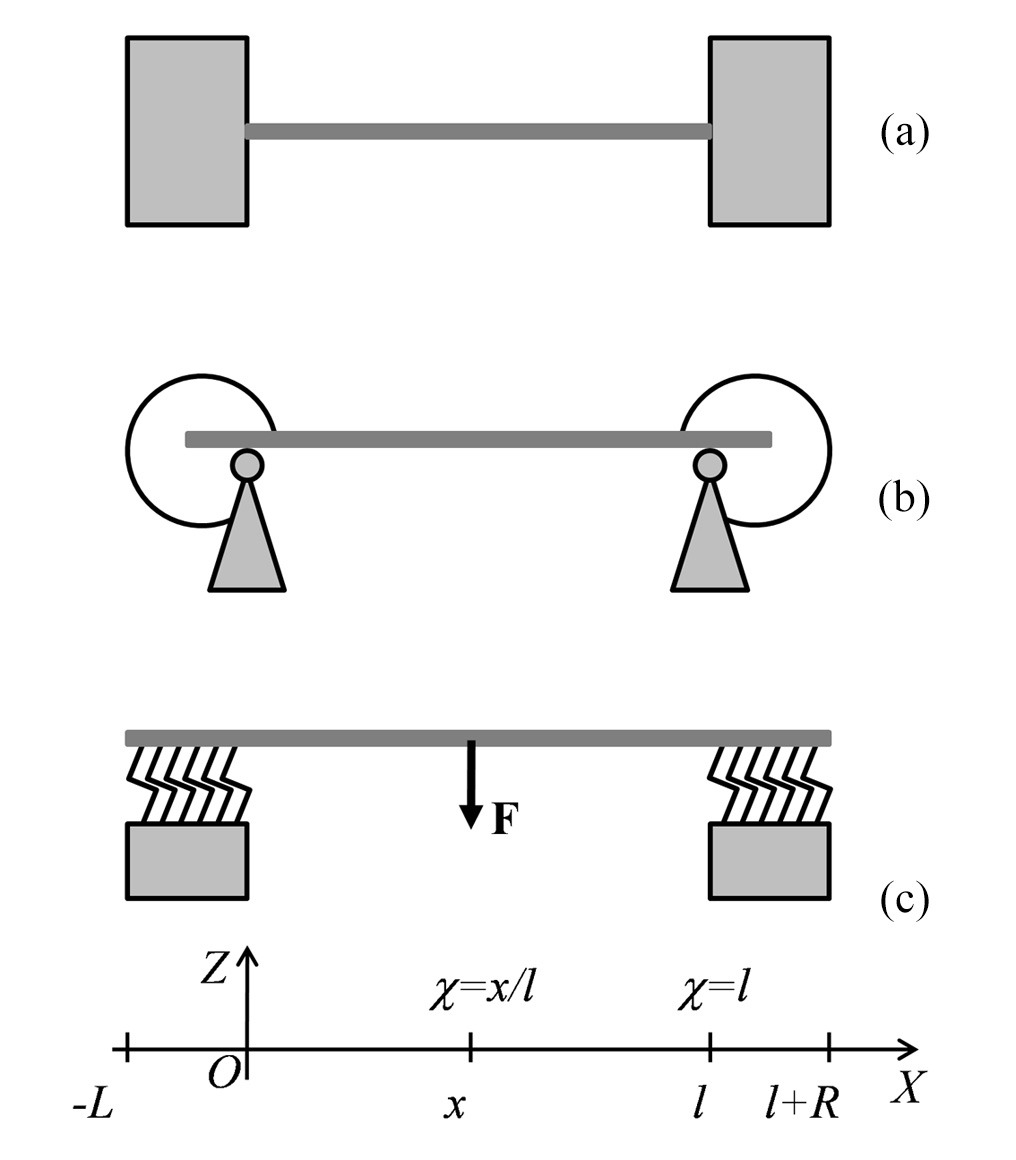
The technique of AFM bending test of a suspended nanoobject has been improved. An analytical method has been created for calculating Young’s and shear moduli of object’s material based on data of such tests. In Timoshenko approximation, we consider problems of bending a beam one or both ends of which lie on elastic Winkler foundations. The obtained solutions are used to eliminate uncertainties in the calculation of elastic moduli that arise when the conditions of fixing an object (console or bridge) on the edges of a recess in the substrate are unknown.
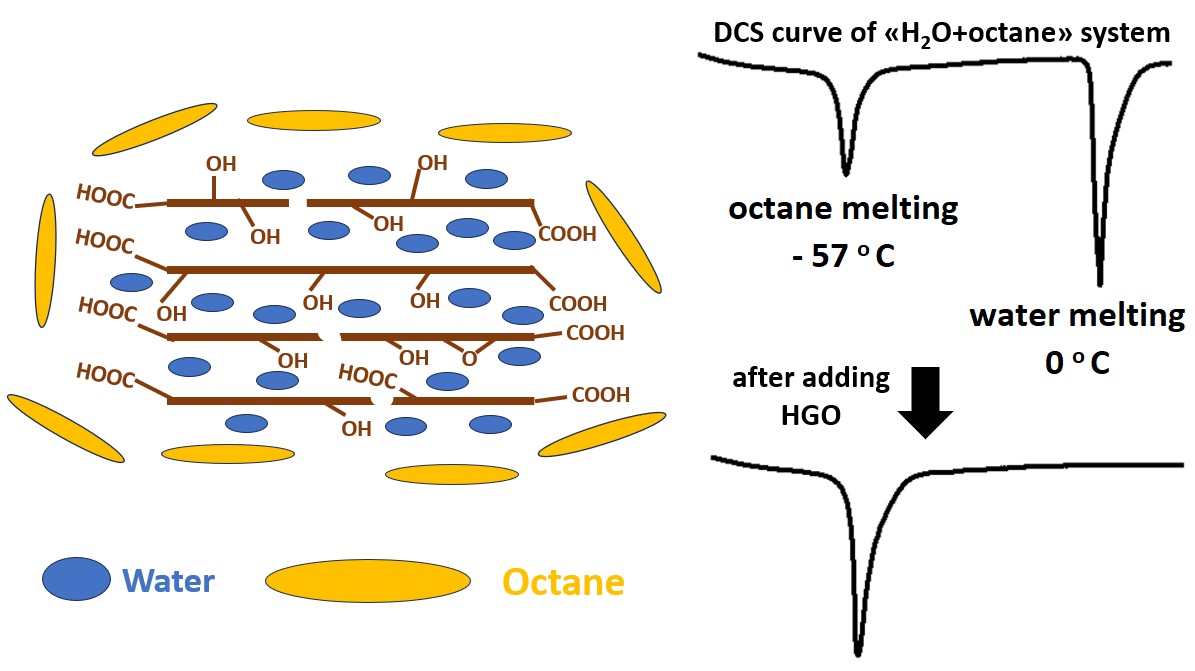
The sorption properties of Hummers (HGO) and Brodie (BGO) graphite oxides with respect to various liquids were studied by the DSC method. In the case of HGO, the reduced material (RHGO) was obtained by hydrothermal synthesis. The effective reduction of the material was confirmed by XRD. The difference in the sorption of water and acetonitrile by HGO and RHGO was experimentally observed. The DSC experimental procedure was developed to estimate the selective sorption of the component from the immisible liquid mixtures. The procedure has been tested on the sorption of the water-octane mixture by HGO. It was shown that water can be sorbed by HGO from the mixture in an amount equal to equilibrium sorption of pure water by HGO at 273 K. The results obtained will serve as the basis for further studies of the sorption properties of GO.
Solar cells that contain perovskite have been a significant object for consideration within the field of solar energy, consistently enhancing their efficiency year by year. In our study, we devised a novel architectural configuration for a tin-based perovskite solar cell, incorporating FTO/ZnO/CH3NH3SnI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Au. Our investigation into the working of this solar cell involved the utilization of the SCAPS-1D, a versatile tool tailored for the analysis of solar cell behavior. Through this simulation software, we explored different electrontransporting layer (ETL) materials and made adjustments to multiple parameters, including ETL and absorber layer thickness. The outcomes of our research produced promising results, showcasing significant enhancements in different solar cell parameters. These favorable findings underscore the growing allure and potential of perovskite solar cells within the realm of renewable energy. The reported CH3NH3SnI3-based PSCs provide a viable path to the implementation of environmentally benign, low-cost, and high-efficiency PSCs.
ISSN 2305-7971 (Online)